A
delivery strategy identifies how the application is delivered to the
user. The primary method of delivery is to install it on the user's
computer. When the user wants to run the program, it is launched from
the Start menu.
However, there are
several other methods of delivery available. These additional methods
use different types of virtualization techniques. Virtualization
techniques include the following:
1. Windows XP Mode
After adding Windows XP Mode,
you can install applications in the Windows XP Mode VPC. Applications
will appear and can be launched from the Windows 7 Start menu without
starting the Windows XP Mode VPC. From the user's perspective, it looks
just as if it's running in Windows 7.
If an application is not
compatible with Windows 7, this will often be your first choice as an
alternative. It doesn't require any additional servers on the network.
However, Windows XP Mode does work best if the hardware supports
virtualization. You can install the update from KB 977206 (http://support.microsoft.com/kb/977206) as a workaround.
2. Virtual PC
If the PC hardware
doesn't support virtualization and you don't want to use the workaround,
you can still use Microsoft Virtual PC (VPC) on the system. With VPC,
you can install another operating system (such as Windows XP) in the
Virtual PC and then install the application within the VPC.
|
Microsoft Virtual PC is
available as a free download. It is the precursor to Windows Virtual PC.
Windows XP Mode must use Windows Virtual PC.
|
|
The drawback is that the
user must launch VPC and then launch the application within the VPC
image. Although this will work, the extra steps can sometimes confuse
the end user. VPC also requires more RAM and processing power.
3. Remote Desktop Services
Remote Desktop Services (RDS)
can be used to deliver applications to users. The application is hosted
on a server configured as an RDS Session Host server. Users can then
connect to the server and run applications remotely.
|
Remote Desktop Services was previously known as Terminal Services. It was renamed in Windows Server 2008 R2.
|
|
Figure 1
shows how RDS can be used in a network. In the figure, three clients
are using RDS. The clients can be running Windows 7, Windows XP, or just
about any operating system. They need only network connectivity to the
RDS Session Host server.
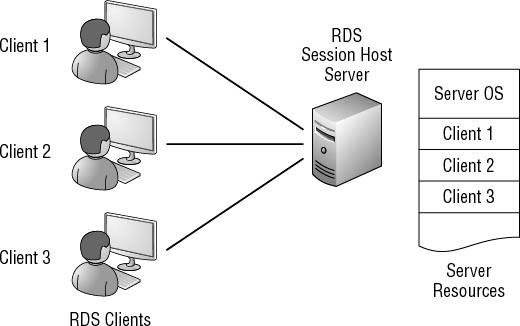
The server can host full desktops or individual applications.
Full desktops
The client could be running Windows XP and then connect to the server
to launch a Windows 7 desktop. The Windows 7 desktop will operate within
a window on the client's system.
Applications
A single application can be run on the server. RemoteApp applications
can be hosted on an RDS Session Host server. Clients can then start the
application from their Start menu, from a desktop icon, or from a web
page depending on how the RemoteApp application is configured. The
application runs in a window on the user's desktop and has the look and
feel of a locally run program.
4. Application Virtualization
Applications can also be
streamed to a user's desktop on demand similar to how audio and video
can be streamed to the client. Microsoft's Application Virtualization
server (App-V server) can be used to stream applications to SoftGrid
clients. App-V was previously known as Microsoft SoftGrid.
Figure 2
shows how an App-V server works in a network. The client has the
Microsoft Application Virtualization for Desktops tool, which is also
known as the SoftGrid client. The client requests the application.
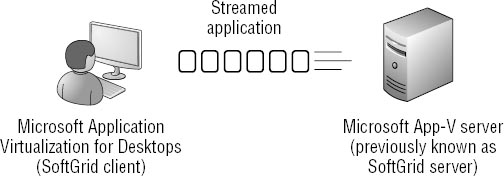
The App-V server then
sends the application in streamed chunks. Depending on the activity of
the user, different chunks of the application will be sent. The SoftGrid
client formats the streamed application and presents it to the user.
Although
applications can be very large, most users don't access all of the
features. For example, Word has many different capabilities related to
formatting, translating, and more. These capabilities will be streamed
to users who need them but not sent to users who don't.