E-mail, short for electronic mail, is a fast and
convenient way to communicate with others by transmitting and sending
text messages with file attachments (documents, pictures, sound, and
movies) over a network, including the Internet. You can send a single
message to groups of people and forward messages that you receive to
other people. Because e-mail messages are created and sent
electronically, they can be easily stored and retrieved. Organizations
that are fully computerized and have many users make extensive use of
e-mail because it is fast, flexible, and reliable.
To use e-mail, you need
the following:
A network and/or Internet connection
An e-mail program or web-based service
An e-mail address that
consists of a username, the at symbol (@), and the name of your Internet
service provider (ISP) or web-based e-mail provider.
Windows
Mail is an e-mail and newsgroup
client software package that replaced Outlook Express, which came with
Windows XP. It enables you to exchange email with others, and it enables
you to organize, manage, and protect your e-mail.
Using Windows Mail
To use e-mail in Windows
Mail, you must set up an e-mail account. You need the following
information from your network administrator or ISP:
To add an account,
you run the Add User Account Wizard, which can be started by doing the
following:
1. | Open Windows Mail.
|
2. | On the
Tools menu, click Accounts.
|
3. | Click Add.
|
4. | Select
E-mail Account and click Next.
|
You then follow the
instructions through the wizard. If you do not know the names of your
services, your address, or your password, contact your ISP or network
administrator.
If you do not receive
e-mail, check the following:
Make sure your
computer is properly connected to the Internet by opening a web page on
the Internet.
If
this is your first time trying to receive e-mail from this e-mail
account on this computer, verify that the account/server information is
set up properly. If you don’t know your account information, check with
your system administrator or your ISP. Account information can be
accessed by opening the Tools menu and selecting Accounts.
Click Send/Receive to retrieve
your e-mail again.
After you have added an
account, Windows Mail checks for new e-mail messages when you first
start it. E-mail you receive is stored in your Inbox.
By default, it then
checks every 30 minutes after that. To change how often it checks for
new e-mail, open the Tools menu and select Options. Then, change the
Check for New Messages Every x Minute
option.
The Inbox is one of
several folders that hold e-mail. To see a list of e-mail you’ve
received, click the Inbox in the Folders list. Your e-mail messages
display in the Message list. The list shows who sent the mail, the
subject, and when it was received. To read a message, click it in the
Message list. The contents of the message display below the Message list
in the Preview pane. To read the message in a separate window,
double-click it in the Message list. To reply to a message, click the
Reply button.
To create a new e-mail
message in Windows Mail, click the Create Mail button. A new message
window opens. In the To box, enter the e-mail address of at least one
recipient. If you are sending the message to multiple recipients, enter a
semicolon (;) between e-mail address. You can also specify recipients
in the CC box, short for carbon copy. CC is typically used when you want
to send informational e-mails to a person and you don’t expect action
from them. In the Subject box, type a title for your message.
To attach a file to
the message, click the Attach File to Message button on the toolbar
(located just below the menu bar). Locate the file, select it, and then
click Open. The file displays in the Attach box in the message header.
To send the message, click
the Send button. If you are connected to a network, the e-mail will be
received by the recipients.
Configuring Windows Mail
To configure the
settings for Windows Mail, open the Tools menu and select Options. An
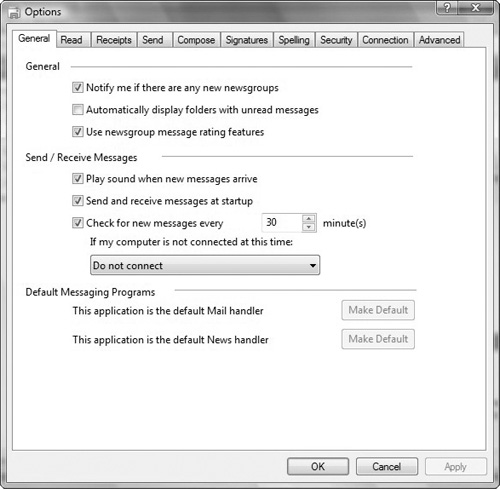
Options dialog box displays with multiple tabs, as shown in Figure 1. The options include the following:
General
settings for configuring newsgroup behavior, send and receive timings
and behavior, and default messaging programs
Read settings for configuring
how messages appear, how newsgroups messages are downloaded, and how
fonts are used in Windows Mail
Receipts settings for configuring how read receipts
behave
Send
settings for configuring the format to send e-mail and news messages,
and general settings for actions to take when mail is sent
Compose settings for
configuring fonts and stationery used in e-mail and news messages, and
settings for using business cards
Signatures
settings for configuring a personalized signature to add to your
outgoing e-mail
Spelling
settings for configuring your spelling checker preferences
Security settings for
configuring secure e-mail by using certificates, for using virus
protection for your e-mail, and whether to allow image downloads
Connection settings
for configuring how the connection to the mail server behaves
Advanced settings
for configuring maintenance and troubleshooting
Dealing with Junk E-Mail
With the popularity of
e-mail and because of its low cost, users have to deal with junk e-mail.
Junk
e-mail is unsolicited e-mail
that usually contains advertisements, flyers, and catalogs that may or
may not contain fraudulent schemes and pornography. In addition, viruses
are often spread through junk e-mail.
Windows
Mail includes a Junk E-Mail Filter that analyzes the content of
messages sent to you and moves suspicious messages to a special Junk
E-Mail folder, where you can view or delete them at any time. And if a
junk e-mail message slips past the filter into your Inbox, you can
specify that any future messages from the sender be automatically moved
to the Junk E-Mail folder.
Windows Mail automatically
screens junk e-mail. However, you can customize how junk e-mail is
filtered by opening the Tools menu, selecting Junk E-mail options, and
selecting one of the following protection levels:
No Automatic
Filtering. Use this option if you want to
stop blocking junk e-mail messages altogether. Windows Mail will
continue to block messages from domain names and e-mail addresses on
your Blocked Senders list.
Low. Use this
option if you don’t receive many junk e-mail messages and want to block
only the most obvious junk e-mail messages. This is the default setting.
High. Use this option if you receive a large number of junk e-mail
messages and want to block as many as possible.
Safe
List Only. Use this option if you want to
receive only messages from people or domain names on your Safe Senders
list. E-mail messages from people or domain names not on your Safe
Senders list will be treated as junk e-mail messages, so you should
choose this option only if you are certain that every person or domain
name that you want to receive messages from is on your Safe Senders
list.
Of course, you can
take the following steps to reduce your junk e-mail:
Use
caution in giving out your e-mail address. Avoid publishing your real
e-mail address in websites, newsgroups, or in other public areas of the
Internet.
Before
you give your e-mail address to a website, check the site’s privacy
statement to be sure it does not permit the disclosure of your e-mail
address to other companies.
Never reply to a junk e-mail message. The sender will know
that your e-mail address is valid and might sell it to other companies.
You are then likely to receive even more junk e-mail.
If you are getting
junk mail from a specific e-mail address, you can add that address to
the Blocked Senders list. If you have e-mail that is getting flagged as junk e-mail, you can
prevent the blocking of the messages from a specific e-mail address by
adding them to the Safe Senders list. If an address is on both the Safe
Senders list and the Blocked Senders list, the Safe Senders list has a
higher priority than the Blocked Senders list; therefore, the message
will be received rather than blocked. To add addresses to the Blocked
Sender’s list, follow these steps:
1. | Open Windows Mail.
|
2. | Click a
message from the sender that you want to add to the Blocked Senders
list.
|
3. | Click the
Message menu, point to Junk E-mail, and then do one of the following:
- To block all future messages from that specific sender,
click Add Sender to Blocked Senders List.
- To block all messages from any sender whose domain name
(the portion of the e-mail address after the @) is the same as the
sender’s, click Add Sender’s Domain (@example.com) to Blocked Senders
List.
|
To move a message from
the Junk E-mail folder to your Inbox, follow these steps:
1. | Open Windows Mail.
|
2. | Click the
Junk E-mail folder.
|
3. | Click the
message that you want to move to your Inbox.
|
4. | Click the
Message menu, point to Junk E-mail, and then click Mark as Not Junk. The
message is moved to your Inbox.
|
Note
Although marking a
message as not junk will move that message to your Inbox, future
messages from that sender might still end up in the Junk E-mail folder.
To prevent this from happening, add the sender to the Safe Senders list.
Securing Windows Mail
To keep Windows Mail
secure, follow these guidelines:
Use an up-to-date antivirus program.
Make sure that virus
protection is enabled for Windows Mail security options, including
warning when an application tries to send mail and not to open
attachments that could be potentially have a virus. You should also
consider blocking images within HTML e-mail.
Use caution when opening e-mail
attachments.
Be
careful when clicking links in messages.
Always use a secure password. Passwords that
use a combination of uppercase, lowercase, and alphanumeric characters
are harder to guess than passwords that can be found in a dictionary.
If more than one user uses a
computer, create a different profile for each user with its own e-mail
account.
Phishing Options
Phishing Filter is
a Windows Mail feature that helps detect phishing websites. The
Phishing Filter uses the following methods to help protect you from
phishing scams:
It compares the addresses of websites you visit
against a list of legitimate sites reported to Microsoft. This list is
stored on your computer.
It helps analyze the sites you visit to see whether they have
the characteristics common to a phishing website.
With your consent, Phishing
Filter sends some website addresses to Microsoft to be further checked
against a frequently updated list of reported phishing websites.
If you visit a
website that has been reported as a phishing website, Internet Explorer
will display a warning web page and a notification on the address bar.
You can then choose to continue or close the page. If the website
contains characteristics common to phishing sites, Internet Explorer
will notify you in the address bar that it may possibly be a phishing
website.