If you suspect you’re having network trouble—such as
computers on the network not being able to see each other or file
transfers or other network activity behaving erratically—but you aren’t
sure, one easy way to find out is to run the Network Diagnostics
utility. This is a Help and Support Center connectivity troubleshooting
tool that can help you isolate network problems.
To get started, use any one of the following techniques:
In the
Network Connections window, click the task pane’s Network Troubleshooter
link, and then click the Diagnose Network Configuration and Run
Automated Networking Tests link.
Select
Start, Help and Support, click Fixing a Problem, click Networking
Problems, and then click the Diagnose Network Configuration and Run
Automated Networking Tests link.
In
the System Information utility (Start, All Programs, Accessories,
System Tools, System Information), select Tools, Net Diagnostics.
In a Command Prompt window, enter the following command:
Network Diagnostics operates by performing three different actions:
| Ping | Pings
various objects to check for basic connectivity. For example, Network
Diagnostics pings the loopback address (127.0.0.1), your IP address, the
default gateway, the DHCP and DNS servers, and more. |
| Connect | Attempts to connect to certain servers, such as your Internet mail and news servers. |
| Show | Displays
information about various objects, including your network adapters,
network clients, DHCP servers, IP addresses, modems, and more. |
Setting Scanning Options
To specify which of
these actions are performed on which objects, click the Set Scanning
Options link in the Network Diagnostics window. You see the Network
Diagnostics window shown in Figure 1. You have two ways to proceed:
In the Actions section, activate the check box beside each action that you want Network Diagnostics to perform.
In
the Categories section, activate the check box beside each object that
you want the actions performed on. (Note, however, that not all actions
are performed on all objects. For example, the Connect action is
performed only on the mail and news server and the Internet Explorer
proxy server, if one exists on your network.)
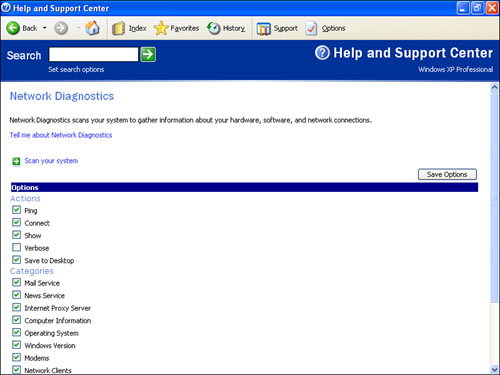
When you’re done, click Save Options.
Running Network Diagnostics
To start the Network
Diagnostics scan, click the Scan Your System link. Network Diagnostics
displays the progress of the scan, as shown in Figure 2.
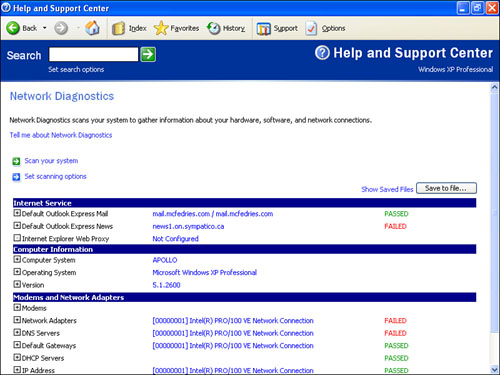
When the scan has finished, you’ll see the results in a window similar to the one shown in Figure 3.
Open the branches to see more detailed objects and the actions that
Network Diagnostics performed on them. Look for FAILED in red type to
see where possible problems occurred.
Running Network Diagnostics from the Command Line
You can also run network diagnostics during a Command Prompt session using the NETSH (Net Shell) utility.
For the ping action, you use the following command:
Here, object
is a parameter that specifies the object you want to ping. You can
either specify an IP address or hostname, or you can use the built-in
object names listed in Table 1.
Table 1. The object Parameter’s Built-in Names for the ping Action
| Name | Pings |
|---|
| adapter | The network adapter |
| dhcp | The DHCP server |
| dns | The DNS server |
| gateway | The default gateway |
| ieproxy | The Internet Explorer proxy server |
| ip | The computer’s IP address |
| loopback | The loopback address (127.0.0.1) |
| mail | The default mail server defined by Outlook Express |
| news | The default news server defined by Outlook Express |
| wins | The WINS server |
For example, the following command pings the default gateway:
For the connect action, you use the following command:
netsh diag connect object
Here, object
is a parameter that specifies the object you want to connect with. You
can either specify an IP address or hostname, or you can use the
built-in object names listed in Table 2.
Table 2. The object Parameter’s Built-in Names for the connect Action
| Name | Connects With |
|---|
| ieproxy | The Internet Explorer proxy server |
| mail | The default mail server defined by Outlook Express |
| news | The default news server defined by Outlook Express |
For example, the following command attempts to connect to the mail server:
For the show action, you use the following command:
Again, object
is a parameter that specifies the object you want to display
information about. You can use the built-in object names listed in Table 3.
Table 3. The object Parameter’s Built-in Names for the show Action
| Name | Shows Information For |
|---|
| adapter | The network adapter |
| all | All the objects in this list |
| client | The installed network clients |
| computer | The computer |
| dhcp | The DHCP server |
| dns | The DNS server |
| gateway | The default gateway |
| ieproxy | The Internet Explorer proxy server |
| ip | The computer’s IP address |
| mail | The default mail server defined by Outlook Express |
| modem | All installed modems |
| news | The default news server defined by Outlook Express |
| os | The operating system |
| test | All the objects in this list; also performs all the actions in the Ping and Connect categories |
| version | The Windows and WMI (Windows Management Instrumentation) versions |
| wins | The WINS server |
For example, the following command shows information for the network adapter: