Control properties enable you to change the behavior
and appearance of a control. You can change most control properties at
design time or at runtime; this allows you to easily build flexibility
in to reports. For example, certain controls are visible only when
specific conditions are true. This section begins by discussing the
Format properties of a control. It then continues by covering the Data
and Other properties of a control.
The Format Properties of a Control
The Format properties of a control allow you to
customize the appearance of the control. Using the Format properties,
you can modify control attributes such as the back color, font, special
effect, and text alignment of the control. You can modify many of the
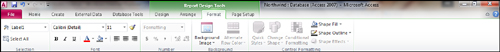
Format properties of selected objects by using the Format tab of the
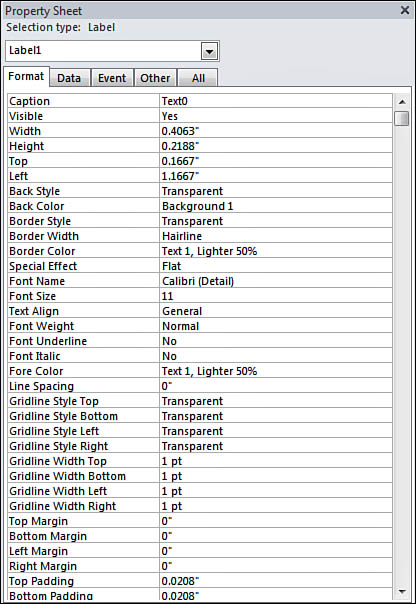
Ribbon (see Figure 1). If you prefer, you can set the Format properties in the Properties window (see Figure 2). The remainder of this section discusses the Format properties available to you.
Format— The Format
property determines how Access displays the data in a control. This
property is automatically inherited from the underlying field. If you
want the control’s format on the report to differ from the underlying
field’s format, you must set the Format property of the
control. It’s important to note that the format options available vary
based on the field type of the underlying field. In other words, the
formatting options vary if the underlying field is a Text field versus
a Number field.
Caption— The Caption
property specifies the text displayed for labels and command buttons. A
caption is a string that contains up to 2,048 characters.
Decimal Places— The Decimal Places property defines the number of decimal places displayed for numeric values.
Visible— The Visible
property determines whether a control is visible. You can use this
property to toggle the visibility of a control in response to different
situations.
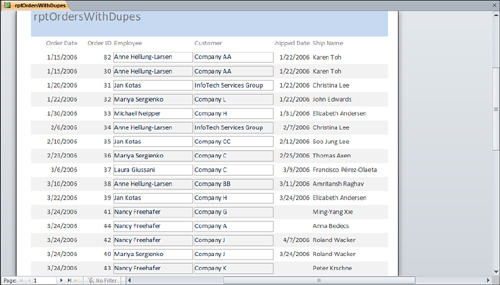
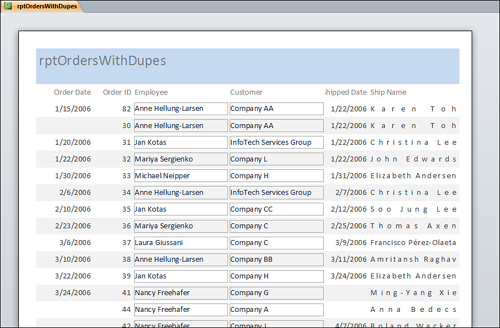
Hide Duplicates— The Hide Duplicates
property hides duplicate data values in a report’s Detail section.
Duplicate data values occur when one or more consecutive records in a
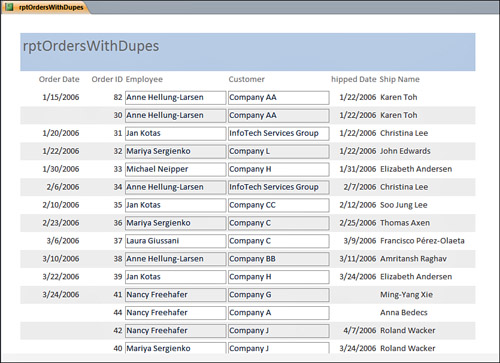
report contain the same value in one or more fields. Figure 3 shows a report with the Hide Duplicates property set to its default value, False. Notice the duplicate Order Date values. Figure 4 shows the same report with the Hide Duplicates property of the Order Date control set to True. Notice that the duplicate order date values no longer appear.
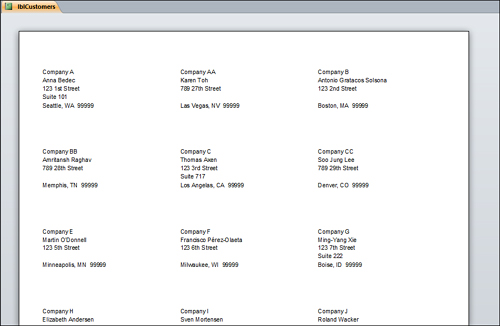
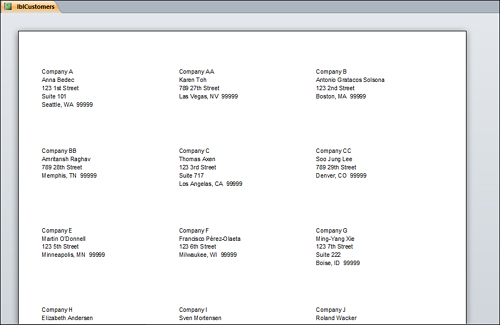
Can Grow and Can Shrink— When the Can Grow property is set to Yes in a control, the control can expand vertically to accommodate all the data in it. The Can Shrink
property eliminates blank lines when no data exists in a field for a
particular record. For example, if you have a second address line on a
mailing label, but there’s no data in the Address2 field, you don’t
want a blank line to appear on the mailing label (see Figure 5). You must therefore set the Can Shrink property for the Address2 control to Yes (see results in Figure 6).
Likewise, if you have a memo that sometimes has only one line of data
but at other times has multiple lines of data, you might want to set
the Can Grow property to Yes so that the control grows as necessary.
[View full size image]
Back Style and Back Color— You can set the Back Style
property to Normal or Transparent. When this property is set to
Transparent, the color of the report shows through to the control. When
it is set to Normal, the control’s Back Color property determines the object’s color.
Special Effect— The Special Effect property adds 3D effects to a control.
Border Style, Border Color, and Border Width— These properties set the physical attributes of a control’s border.
Fore Color— The Fore Color property sets the color of the text within a control.
Font Color, Font Name, Font Size, Font Weight, Font Italic, and Font Underline— These properties affect the appearance of the text within a control.
Text Align— The Text Align
property sets the alignment of the text within a control. You can set
this property to Left, Center, Right, or Distribute. When it is set to
Distribute, text is justified. (See the Ship Name column in Figure 7.)
Line Spacing— The Line Spacing property is used to control the spacing between lines of text within a control. The Line Spacing property is designated in inches.