Troubleshooting Dial-Up
Remote Access Connections
Use the following
checklist to troubleshoot dial-up remote access connections:
Verify that
the Remote Access Server option is enabled on the server properties
General tab in the Routing And Remote Access console.
If you have configured a static
address pool, verify that the pool is large enough to accommodate the
number of simultaneous client connections needed.
If you have configured the
remote access server to assign addresses through a DHCP server, verify
that the address scope defined at the DHCP server is large enough to
accommodate blocks of 10 addresses requested by the remote access
server.
Verify
that enough modem devices are configured in the Ports node to
accommodate the number of simultaneous client connections needed.
Verify
that the dial-up client, the remote access server, and the remote
access policy are configured to use at least one common authentication
protocol.
Verify
that the dial-up client, the remote access server, and the remote
access policy are configured to use at least one common encryption
strength.
Verify
that the dial-up remote access connection has the appropriate
permissions through dial-in properties of the user account and remote
access policies.
Verify
that the remote access server (or RADIUS server) computer is a member
of the RAS And IAS Servers security group in the local domain.
Verify that the settings of
the remote access policy profile are not in conflict with properties of
the remote access server.
Verify that, if MS-CHAP v1 is being used as the authentication
protocol, the user password does not exceed 14 characters.
Configuring Access
Beyond the Remote Access Server
To configure a
computer running Windows Server 2003 as a remote access server, you can
simply run the Routing And Remote Access Server Setup Wizard and specify
a Remote Access (Dial-Up Or VPN) configuration. However, even when
properly configured, such a remote access server does not allow dial-up
connections to see or use network resources beyond the remote access
server.
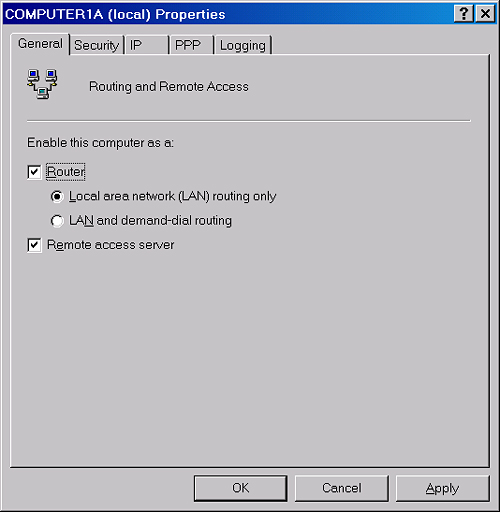
To allow clients
access to resources beyond the remote access server, you need to enable
the remote access server as a router. To achieve this goal, select the
Router check box on the General tab in the remote access server
properties in the Routing And Remote Access console. This tab, and the
required configuration, is shown in Figure 14.
Access beyond the server depends on the
proper configuration of other aspects of the remote access server as
well. First, you need to make sure the remote access server assigns
clients (through a DHCP server or static address pool) with an IP
address configuration that places them on the same logical subnet as the
computers immediately beyond the remote access server. If instead you
assign remote access clients with an IP configuration that places them
on a logical subnet distinct from the subnet beyond the answering modem,
you must configure a routing protocol on the remote access server; or
you can configure static routes on your network routers to identify the
location of the remote access subnet.
Note
When you
deploy a routing protocol on the remote access server, you also need to
configure neighboring routers to accept updates from that server. |
Second, on the
IP tab of the server properties dialog box in the Routing And Remote
Access console, you need to verify that the Enable IP Routing check box
is selected. (It is enabled by default.)
Third, for the use of
network functions (such as a computer browsing through My Network
Places) that require broadcast NetBIOS name resolution, and for
conditions in which the remote access clients are not found on a
distinct subnet, you must verify that the Enable Broadcast Name
Resolution check box is selected. This check box is also found on the IP
tab and is also selected by default. If this setting is not enabled, a
WINS server must be configured on the network to provide NetBIOS name
resolution, and the client must be configured with the address of the
WINS server.
Troubleshooting
Access Beyond the Remote Access Server
Use the following
checklist to troubleshoot access to resources beyond the remote access
server:
Verify that
the Router option is selected on the General tab of the server
properties dialog box.
Verify that the LAN And Demand-Dial Routing option is
selected on the General tab of the server properties dialog box.
Verify that the Enable IP
Routing option is selected on the IP tab of the server properties dialog
box.
If your
remote access clients are assigned an address range that places them on
a subnet that is logically separate from the one immediately beyond the
answering router, verify that the routers on your network have been
configured with the location of the remote access subnet.
Verify that the Enable Broadcast Name
Resolution option is selected on the IP tab of the server properties
dialog box. This step is necessary only if your remote network uses
NetBIOS name resolution, does not use WINS, and your remote access
clients are located on the same logical subnet as the NetBIOS services
to which they will connect.
Managing Remote
Access Clients
Using the Routing And
Remote Access console, you can view currently connected remote access
clients in the details pane by selecting the Remote Access Clients node
in the console tree. You can then manage these clients by viewing their
status, disconnecting them, or sending a message to one or all of them.
The following procedures describe how to perform each of these four
functions.
To view connected
remote access clients, complete the following steps:
1. | Open the Routing And Remote Access console.
|
2. | In the
console tree, click the Remote Access Clients node.
|
3. | In the
details pane, right-click a user name, and then click Status.
|
To disconnect a
remote access client, complete the following steps:
1. | Open Routing And Remote Access.
|
2. | In the
console tree, click the Remote Access Clients node.
|
3. | In the
details pane, right-click a user name, and then click Disconnect.
|
To send a message to a
single remote access client, complete the following steps:
1. | Open Routing And Remote Access.
|
2. | In the
console tree, click the Remote Access Clients node.
|
3. | In the
details pane, right-click a user name, and then click Send message.
|
4. | In Send
Message, type your message, and then click OK.
|
To send a message to
all remote access clients, complete the following steps:
1. | Open Routing And Remote Access.
|
2. | In the
console tree, right-click the Remote Access Clients node.
|
3. | Click Send
To All.
|
4. | In the
Send Message dialog box, type your message, and then click OK.
|
Managing Clients
Through Remote Access Policies
Besides being able to manage currently connected
clients, you can also manage remote access clients in general by
defining rules through remote access policies. For example, you can
manage clients by restricting idle time, connection time, or access to
specific parts of your internal network. You can configure these
restrictions through a policy profile and apply them to any client type.