Quotas can be enabled and configured at the volume
level and applied to user and group objects. This is the same quota
management included with Windows 2000 Server, Windows Server 2003,
Windows Server 2003 R2, Windows Server 2008, and Window Server 2008 R2.
Quotas enabled at the volume will be calculated based on all files saved
to the volume by a particular user who is not part of the server
administrators group. Volume quotas can only be enabled on NTFS volumes
and cannot be applied to any lower level, such as a subfolder. The key
to a successful implementation of quotas on a volume is setting the
correct file permissions for the entire volume and folders and to limit
the data transferred to a volume for an end user by a third party, such
as a desktop or server administrator.
The quota management features available in the File Server
Resource Manager are different from the features included with NTFS
volume quotas; Table 1 details the differences.
Table 1. Quota Differences Between FSRM and NTFS
| Quota Capabilities | FSRM Quotas | NTFS Quotas |
|---|
| Quota tracking | By folder or by volume | Per user on a specific volume only |
| Calculation of storage usage | By actual disk space used | By the logical file size on the volume |
| Notification method | By email, custom reports, and event log entries | By event log only |
Note
Prior
to the release of FSRM, organizations used to depend on NTFS volume
quotas or third-party products to provide their quota storage management
capabilities; however, FSRM has effectively replaced the use of NTFS
volume quotas. The coverage of NTFS volume quotas in this section is
merely to describe the process and use of NTFS volume quotas; however,
most organizations should consider using FSRM quotas and should avoid
using NTFS volume quotas or both types because they are not
complementary to each other.
To enable quotas for an NTFS volume, perform the following steps:
1. | Log on to the Windows Server 2008 R2 system with an account with administrator privileges.
|
2. | Click Start, click All Programs, click Administrative Tools, and select Server Manager.
|
3. | In the tree pane, double-click the Storage node, and select Disk Management.
|
4. | In the tasks pane, scroll down to locate the desired volume, right-click the volume, and select Properties.
|
5. | Select the Quota tab and check the Enable Quota Management check box.
|
6. | Enter
the appropriate quota limit and warning thresholds and decide whether
users will be denied write access when the limit is reached, as shown in
Figure 1.
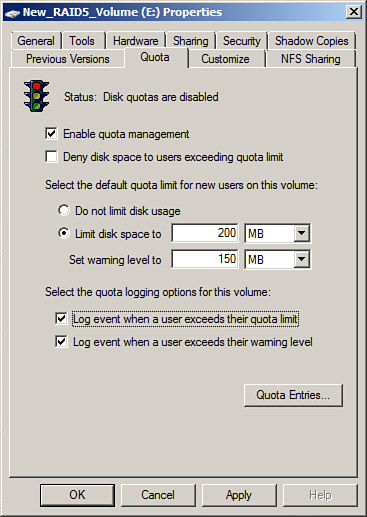
|
7. | Click OK to complete the quota configuration for the NTFS volume.
|
8. | A
window opens, prompting you to confirm the enabling of quotas; click OK
to enable the quota and scan the volume to update quota statistics.
|
9. | After
you configure quotas, open the properties of the volume, select the
Quota tab, and click the Quota Entries button to review the existing
quotas based on data already stored on the volume.
|