Whenever you have a hardware
problem that's causing a device to misbehave or just not work at all,
finding an updated driver will usually be your best bet. But even before
you do that, you might want to try Windows built-in Troubleshooting
tools to see if they can resolve the problem.
|
Windows 7 integrates
troubleshooting components into a single applet in the Control Panel,
replacing the Help and Support troubleshooting tools in previous
versions.
|
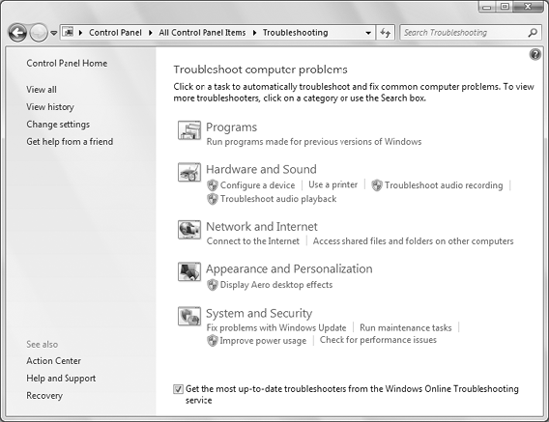
To get help on programs, hardware, and drivers, open the Troubleshooting applet from the Control Panel (Figure 1).
Each of the items in this Control Panel applet provides a
troubleshooting wizard that can automatically search for, detect, and
potentially fix problems. The applet offers the following groups:
Programs:
Launch the Program Compatibility Wizard, which enables you to apply
settings to programs to make them run as if they were running in an
earlier version of Windows. For example, you can potentially run a
Windows 98 program under Windows 7 by configuring its compatibility
settings for Windows 98. This group also includes items for
troubleshooting printers, Media Player, and Internet Explorer.
Hardware and Sound:
Use the Hardware and Sound item to scan for hardware changes and
troubleshoot problems with general devices, printers, network adapters,
and audio devices.
Network and Internet:
Troubleshoot problems connecting to the Internet or accessing shared
files and folders on a local area network. Also troubleshoot Homegroup,
incoming network connections, and DirectAccess.
Appearance and Personalization: Troubleshoot problems with the Windows Aero desktop visual effects (such as transparent windows).
System and Security:
Troubleshoot problems with Windows Update, modify power settings, check
for computer performance issues, and run maintenance tasks including
cleaning up unused files and shortcuts. Also check search and indexing
problems, and adjust performance settings.
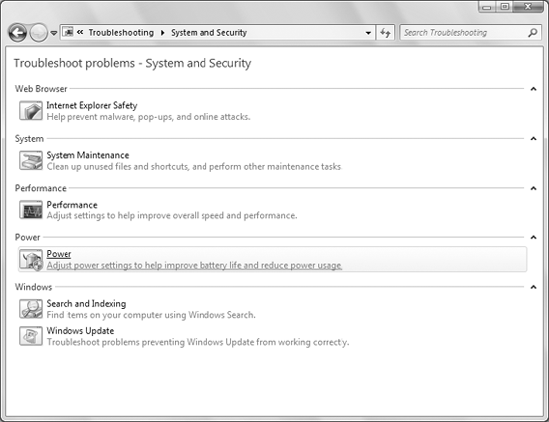
The Troubleshooting
applet lists only some of the items for each category. Click the group
name (such as Hardware and Sound or Network and Internet) to see all of
the troubleshooting tools for that category. Figure 2, for example, shows the System and Security category.
|
Make sure to leave
enabled the option at the bottom of the Troubleshooting window, Get the
Most Up-to-Date Troubleshooters from the Windows Online Troubleshooting
Service, to allow Windows to update the troubleshooters as new or
modified ones become available.
|
|
A second alternative is
to troubleshoot from the hardware device's Properties dialog box in
Device Manager. To open Device Manager, tap  , type dev,
and click Device Manager. Or click the Start button, right-click
Computer, and choose Properties. Then click the Device Manager link on
the left side of the screen. In Device Manager:
, type dev,
and click Device Manager. Or click the Start button, right-click
Computer, and choose Properties. Then click the Device Manager link on
the left side of the screen. In Device Manager:
Right-click the name of the device that's causing problems and choose Properties.
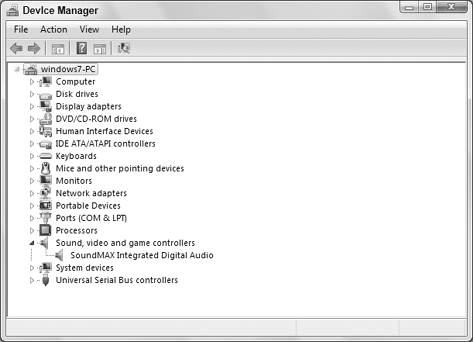
If the device shows an error in the Device Manager (Figure 3),
use that information to begin troubleshooting. For example, if Device
Manager indicates that there is no driver installed, try installing or
reinstalling the device's driver.
If
needed, use the options on the Driver tab to reinstall the drivers for
the device. You can also disable the device from this tab and eliminate
potential conflicts with other devices.
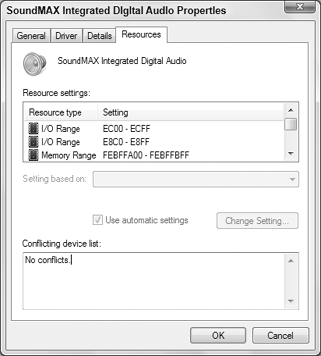
On the Resources tab (Figure 4),
check for a conflict message under Conflicting Device List and resolve
problems by reassigning resources to the conflicting devices, or by
disabling one of them. Note that not all hardware devices will have a
Resources tab.
|
If you've made a hardware change but Windows hasn't noticed the change, open Device Manager and choose Action =>
Scan for Hardware Changes to have Windows rescan the system. For
example, if you have an external modem that was turned off when you
turned on the computer, rescanning should cause Windows to redetect the
modem after you have turned it on.
|
|