3. Configure Client Connectivity
There have been many changes
in Exchange 2010 that redefined how clients, such as Microsoft Outlook,
connect to Exchange. One of the bigger changes is MAPI on the Middle
Tier (MoMT). MoMT moves the mailbox access point away from Mailbox
servers and to the Client Access servers instead. So when Outlook
clients connect to their mailbox, the connection is made to the Client
Access server and the Client Access server brokers the interaction with
the Mailbox server that contains the user's data. This is not the case
with public folders, however. When a client connects to a public folder,
the connection is made directly to the Mailbox server and is not
brokered through the Client Access server.
The primary users of public
folders are going to be the users in Outlook who use them to share data.
When Outlook clients connect to public folders, they use a well-defined
method for determining what Public Folder server to use and for
ensuring that performance doesn't suffer by using a Public Folder server
on the other side of the world. This section will help you understand
what to do in order to optimize this experience for users in your
organization.
3.1. Modify How Clients Choose a Public Folder Server
A user's mailbox database has
a default public folder store associated with it. When a client
accesses a public folder, it has to know which server has a copy of the
public folder that it wants. So the client contacts the default public
folder database that is associated with its mailbox database to get a
referral for the server that it should get the public folder from.
If the default public folder
database has a copy of the public folder that the client wants, the
client uses that server. Otherwise, a list of referrals is generated by
the server and given to the client. This referral process includes logic
that ensures that the client accesses the Public Folder server that is
closest to it. To determine which servers outside of the site are
closest, the default Public Folder server queries Active Directory for
site cost information. The servers that cost the least are placed near
the top of the referral list.
Instead of depending on the
site cost that is defined in AD for referrals, you can specify your own
arbitrary referral costs for public folders.
3.1.1. Modify the Custom Referral List Using the Exchange Management Console
To configure custom referral costs in the EMC, use the following steps:
Open the EMC and browse to the Organization Configuration => Mailbox node.
In
the Work area, click the Database Management tab and select the public
folder database for which you want to define a list of custom referral
costs.
Choose Properties from the public folder's Action menu in the Actions pane.
In the properties dialog box for the folder, select the Public Folder Referral tab.
Choose the Use Custom List option. To add servers with custom referral costs, click the Add button.
The
Server Referral Cost dialog box will open. Click the Browse button to
choose a Public Folder server that you want to assign a custom cost to.
Type
the cost that you want to use in the Cost field. This number must be
between 1 and 100. Remember that a lower cost means that it is cheaper
to contact that server, so that server is more likely to be used for
referrals. Click OK to add the server to the list.
Continue
adding additional servers to the custom cost list. If you exclude a
server from the list, the cost is considered infinite, so it's
effectively removed from getting a referral.
Click OK to make the changes and close the properties dialog box.
3.1.2. Modify the Custom Referral List Using the Exchange Management Shell
You can also modify this
custom referral list using the Set-PublicFolderDatabase EMS cmdlet. When
running the command, specify the public folder database that you are
setting the custom referral list on. You will also need to use the CustomReferralServerList
parameter, which details the list of servers and their custom referral
costs. When indicating the server and its cost, you will use the format ServerName:Cost. For example, if you use CONTOSO-PF01:100,
the referral cost of 100 would be used for referrals from that public
folder database to the server CONTOSO-PF01. To add entries to the custom
cost list, separate each entry with a comma. You will also need to set
the UseCustomReferralServerList parameter to $True,
to indicate that you are using a custom referral list. The following
command demonstrates how to set the custom referral list using the EMS:
Set-PublicFolderDatabase "PFDB (CONTOSO-PF01) "
-CustomReferralServerList CONTOSO-PF01:50,CONTOSO-PF02:100
-UseCustomReferralServerList $True
3.2. Change the Default Public Folder Database
As described in the
previous section, clients connect to the default public folder database
on their mailbox store in order to obtain referrals for public folders
that are accessed. You can modify the default public folder database
that clients use.
To change the default public folder database that clients connect to, use the following steps in the EMC:
Open the EMC and browse to the Organization Configuration => Mailbox node in the Console tree.
Select the Database Management tab in the Work area.
Select the mailbox database that you want to modify the default public folder store for.
In the Actions pane, select the Properties option from the Action menu for the mailbox database that you have selected.
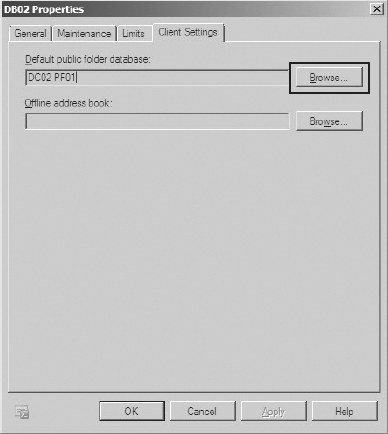
In the properties dialog box for the database, click the Client Settings tab.
Under
the Default Public Folder Database field, click the Browse button to
select a new default public folder database, as shown in Figure 9.
A
dialog box appears that lists the current public folder stores in the
organization. Choose the store that you want to use and click OK.
When back in the properties dialog box, click OK to make the changes and close the dialog box.
You can also modify the default public folder database using the EMS. You can make this change through the Set-MailboxDatabase cmdlet. When you run the command, specify the PublicFolderDatabase parameter and enter the name of the public store that you want to use. The following example shows how to use this command:
Set-MailboxDatabase DB02 -PublicFolderDatabase PF02