1. Post Deployment Tasks
Because OSD is part of ConfigMgr, deploying a
system does not necessarily end after deploying the image. This allows a
lot of flexibility in choosing what should and should not be part of an
image. This was a major point of emphasis for Microsoft when building
OSD into ConfigMgr 2007. Deploying an image is a relatively simple task;
the true power of OSD is its capability to perform pre- and
post-deployment tasks and allow you as the administrator to customize
them for your environment.
ConfigMgr Software Deployment
For those organizations without a robust
software deployment solution, the ability to include more things in the
reference image or create multiple reference images might be the only
way to deploy software and other customizations. ConfigMgr is a robust
software deployment platform, letting you distribute software and other
customizations in an automated and controllable way after deploying the
image.
You can implement customizations in many
different ways, including task sequence variables, static collection
membership, and dynamic collection membership.
Group Policy
One of the mistakes often made when creating a
reference image is to pack all the registry tweaks and customizations
into the image. This is a manual process using .reg files or scripts.
There are multiple problems with this approach:
The customizations are not enforced in any way. Users can undo or change the customization.
The
customization does not uniformly apply to all systems in an
organization, specifically those not deployed with OSD or those that
might have a different image on them.
Manual processes are subject to the skill and opinion of the person applying them.
Script
and .reg files are potentially difficult to maintain for those not
familiar with them, and you cannot change them after deploying the image
to a system.
Using group policies and preferences
have none of the disadvantages just listed. By using the built-in
policies or a customized ADM or ADMX file, you can change any Registry
setting and enforce it uniformly across the organization, using the
native Windows GUI policy editor.
2. Troubleshooting
Finding
and correcting problems in OSD is similar to fixing issues elsewhere in
ConfigMgr—look in the logs. The trick, as always, is to find the
correct log.
Operating System Deployment Home Page
The OSD home page is a good place to start
reviewing and troubleshooting deployments; you access it by selecting
the top-level Operating System Deployment node in the Configuration
Manager console. The right pane displays a list of all OSD deployments,
their status, and some valuable statistics including running, success,
and failure counts. Selecting a specific advertisement in the list
displays a summary graph to the right.
The bottom of this home page includes links to
other sections of OSD, valuable Web reports, and links to topics in the
help system.
Check Advertisement Status
Another valuable source of information is the
Advertisement Status node under System Status in the ConfigMgr console.
Each advertised task sequence has its own entry; these are no different
from advertised software distribution entries. Perform these steps:
1. | In the ConfigMgr MMC, select System Status -> Advertisement Status.
|
2. | Drill-down all the way on the tree node and right-click the corresponding site node in the right detail pane.
|
3. | From the resulting context-menu, choose Show messages -> All.
|
4. | Each
task in the task sequence has an entry along with other task sequence
status messages. Unfortunately, if the target system does not yet have a
ConfigMgr client agent installed, it cannot send status messages back
to ConfigMgr. The system caches the messages until there is an installed
agent.
|
The Smsts.log File
After checking advertisement status, the next
place to look is in the smsts.log on the target system. This log file
lives in various places depending on the stage of the deployment, as
listed in Table 1.
the smsts.log file is a detailed log of every task sequence-related
action that takes place on a target system. It usually indicates exactly
why a task sequence fails.
Table 1. Smsts.log Locations
| Deployment Finished? | Status | ConfigMgr Client Installed? | Location |
|---|
| No | Windows PE running | N/A | Windows temp folder on the RAM-disk—usually x:\windows\temp\smsts.log |
| No | Deployed OS running | Yes | Smstslog sub folder in the ConfigMgr client logging folder—usually %windir%\system32\ccm\logs\smstslog |
| No | Deployed OS running | No | Windows temp sub folder—usually %windir%\temp\smstslog |
| Yes | Windows PE running | N/A | Smstslog folder on the largest available volume |
| Yes | Deployed OS running | Yes | ConfigMgr client logging folder—usually %windir%\system32\ccm\logs |
| Yes | Deployed OS running | No | Windows temp folder—usually %windir%\Temp |
You might also want to check http://blogs.technet.com/inside_osd/archive/2007/12/13/troubleshooting-tips.aspx
for additional information. Steve Rachui of Microsoft discusses an
excellent method for copying the OSD log files, including smsts.log, at http://blogs.msdn.com/steverac/archive/2008/07/15/capturing-logs-during-failed-task-sequence-execution.aspx.
|
There
is no complete list of error codes that can be returned by a task
sequence. This is because ConfigMgr and OSD use a variety of tools and
Windows APIs to perform their work. Here are several suggestions in
diagnosing error codes:
A good place to start is the ever-handy
Trace32 log viewer. A built-in error lookup function in this tool
available from the menu, Tools -> Error Lookup, attempts to look up
an error number and return a friendly message. This message is often
informative and can lead you down the path to finding the actual issue. You can also find a list of common OSD-relevant error codes and possible solutions available on TechNet, at http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/bb735886.aspx.
|
Status Reports
Running task sequences send status messages back
to the server for each step in the task sequence. You can find the last
1,024 characters of stdout/stderr text from each action in these status
messages. You can use this information to remotely diagnose a task
sequence issue; this is particularly useful if an error occurred in
Windows PE and the debug shell is not enabled. The report History –
Specific task sequence advertisements run on a specific computer
provides a list of these status messages for a specific advertisement
and computer; you can open this report from the Reports node in the
ConfigMgr console.
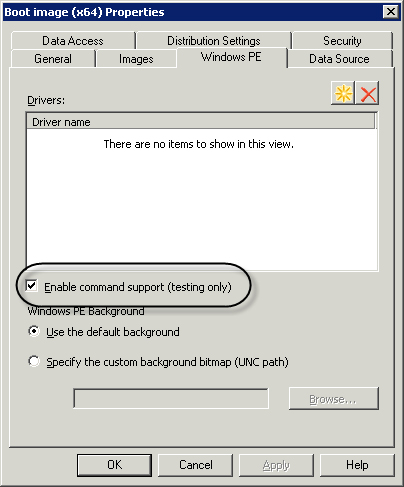
Command Line Support
A
highly recommended troubleshooting step is to enable command line
support in Windows PE. When enabled, you can start a separate command
line by pressing F8 while a target system is booted into Windows PE.
From this command line, you can launch Windows Notepad to view the
smsts.log file or otherwise inspect the target system. A common use of
this command line is to run ipconfig /all to verify that
network drivers have been loaded with proper configuration of IP-related
network information. To enable command line support, edit the
properties of your boot images by right-clicking them and selecting
Edit. Go to the Windows PE tab and check the option to Enable command
support, as highlighted in Figure 1.
It is possible for a user to
intentionally or unintentionally press F8 during the process and gain
access to the file system or subvert the process altogether. Because of
this, Microsoft recommends that you disable command line support for
production deployments.