File and Print Services Changes
Windows Server 2008 R2
introduces some new features and enhancements for file and print
services. These new features provide better security, stability, and
end-user experience. In this section, we will explore some of these new
features and how you might use them on your network.
Read-only DFSR Replicas
Windows
Server 2008 R2 allows administrators to set DFS Replication
(DFSR)-based replicated folders to read-only. Using this feature, you
can set up a central share with read-write access and provide read-only
replicas to remote servers. This can allow administrators to easily
publish files to various geographic locations, but ensure that remote
users are only viewing files and cannot make updates to the remote
copies.
File Classification Infrastructure
File classification is a new
feature included in Windows Server 2008 R2. File Classification
Infrastructure (FCI) allows administrators to classify files based upon
folder or file type. Using these classification capabilities,
administrators can then run reports or set retention policies on the
file classes. Additionally, Windows Server 2008 R2 can automatically
move files to an archive location after their retention periods have
expired. This feature is added by installing the Windows Server 2008 R2
role service.
Print driver isolation
Windows Server 2008 R2
introduces a new print server reliability feature. Print driver
isolation ensures that print driver functions run within their own
processes. Prior to Windows Server 2008 R2, the driver functions and
Windows print spooler ran in the same Windows process. If a poorly
developed print driver crashed, it could bring down the entire print
spooler service, resulting in the entire print server being unavailable.
Using print driver isolation, an unreliable print driver no longer has
any impact on the print spooler’s process. This ensures that the print
server remains online in the event an unreliable print driver fails.
Network scanner management
The
new distribute scan management features in Windows Server 2008 R2
provide management and workflow features for network-based scanners.
Using scan management, you can administer network scanners across your
network from a single-pane-of-glass interface. Additionally, you can
setup network scanners to perform workflow functions for scan jobs. For
example, a user could log on to a network scanner and scan a legal
document. The network scanner could then send the document to a scan
management server, which could then route the document to a file server
or SharePoint document library automatically.
Internet Information Server Changes
With
the release of Windows Server 2008 R2, Microsoft has included a dot
release of Internet Information Server (IIS) bringing the version to
7.5. IIS 7.5 on Windows Server 2008 R2 includes new administrative and
security enhancements to further evolve and secure the popular Web
server.
Request Filtering Module
The Request Filtering Module
is introduced as an add-on extension for IIS 7.0 to allow administrators
to block Web requests deemed harmful. Request filtering provides
additional security to IIS by limiting the types of requests and
commands that can be sent to IIS via the Web browser. IIS 7.5 now
includes the module as a standard part of the Web server role.
Best Practices Analyzer
IIS 7.5 now includes a BPA. You
should run the BPA after initial configuration and on a regular basis
thereafter to ensure that your IIS deployment is healthy and optimally
configured.
PowerShell module
As with most roles in
Windows Server 2008 R2, IIS 7.5 includes a PowerShell module allowing
administrators to perform most administrative functions from the
PowerShell command line. Administrators can use PowerShell to quickly
perform IIS administrative tasks as well as automate the configuration
of IIS for fast and standardized deployment of IIS Web servers.
Support for managed service accounts
Windows Server 2008 R2 AD allows administrators to create managed
service accounts. Managed service accounts allow administrators to
change the password of a service account without having to update each
service using that particular account. IIS 7.5 application pools provide
support for managed service accounts. For example, an IIS application
pool could be running under the account IIS_Service. For security
purposes, an administrator needs to change the password on this account.
The administrator simply has to change the password of the AD account.
Once the password has been changed, the IIS application pool will
automatically update the password field to reflect the new password
without administrator interaction.
Hostable Web core
The
IIS engine itself can be hosted by other systems and applications. This
gives developers the ability to include Web server functionality within
their applications without having to write their own server. By using
APIs they can leverage IIS directly inside their application code.
.NET support on server core installs
Windows
Server 2008 R1 allowed IIS to be installed on a core install but did
not support .NET. Windows Server 2008 R2 and IIS 7.5 now support the use
of .NET in IIS Web applications running on a server core install of the
operating system. .NET Framework versions 2.0, 3.0, 3.5.1, and 4.0 are
supported.
Hyper-V Changes
Windows Server 2008 R2
includes several new enhancements to Hyper-V virtualization services.
These enhancements include Live Migration, hot addition and removal of
virtual disks, new processor features, and support for jumbo frames on
virtual machines (VMs).
Live Migration
Windows Server 2008 R2 includes a
much-welcomed feature to enhance the process of moving VMs from one
Hyper-V host to another. Windows Server 2008 R1 includes a feature known
as Quick Migration, which suspends VMs and quickly transfers them to
another host. This process does, however, cause a brief outage to any
VMs being moved. When using quick migration to move a VM, some
applications on that VM may time-out and need to be restarted due to
their sensitivity to network or machine disruptions.
Live Migration allows
Hyper-V to overcome these limitations when moving VMs by removing the
need for them to be temporarily suspended, thus removing downtime for
applications running on the VM being moved. Live Migration uses a
process to transfer memory pages from the current host to the
destination host and then simply transfers ownership of the VM’s virtual
disks to the destination host. The Live Migration process is depicted
in Figure 1.
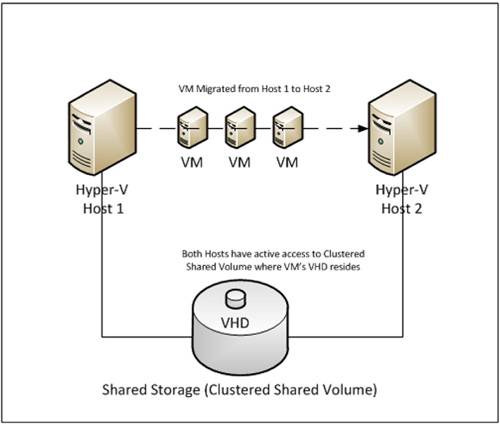
Live Migration allows
administrators to add easily, on the fly, new hosts to a Hyper-V cluster
and instantly increase resources needed for VM workloads. Live
Migration can also be used to allow administrators to service hosts
during normal business hours without impacting business services
and applications. For example, an administrator might want to add
additional memory to a Hyper-V host. He could use Live Migration to move
any active VMs from the host to another host in the cluster. He could
then turn off the host to add additional memory. After adding memory,
the administrator could use Live Migration to move the VM workloads back
to the host.
Live Migration requires
that Hyper-V be deployed on a Windows Server 2008 R2 Failover Cluster.
Additionally, Live Migration requires a dedicated network adapter on
each Hyper-V host for migration traffic. It is also recommended that
processors on all hosts are from the same manufacturer and of the same
processor family. This ensures that all processor features can be used.
|
Live Migration and Hyper-V processor compatibility mode
Though it is recommended that
all hosts in a Hyper-V cluster have the same processors, Windows Server
2008 R2 Hyper-V includes a new feature known as processor compatibility
mode. Processor compatibility mode allows you to include computers with
various processor types in a Hyper-V cluster. Processor compatibility
mode turns off the features of newer processors so that all processors
in the cluster use the same features as the processor with the least
number of features. This allows you to add older hosts to Hyper-V
clusters and will also cause newer hosts to run with a reduced set of
processor features.
|
Processor enhancements
Windows Server 2008 R2
Hyper-V includes several new processor enhancements, including support
for 32 processor cores per physical host. Hyper-V can also take
advantage of Windows Server 2008 R2 Core Parking features. Hyper-V moves
VM CPU loads to the fewest required number of processor cores and
allows Windows to suspend the cores not being used. As workloads require
more CPU resources, the cores are no longer suspended and Hyper-V moves
VM workloads to those cores.
Storage enhancements
Windows
Server 2008 R2 Hyper-V adds new storage features that allow
administrators to easily add and remove VM storage. Hyper-V now allows
administrators to add or remove virtual and physical storage hot, while
the VM is still running. This feature allows administrators to easily
reconfigure VM storage without requiring downtime. For example, assume
that a production SQL server needs additional storage space for more
databases. As the administrator, you can add a new virtual disk drive to
store new databases without taking the server offline.