4. System Services
The Security Settings =>
System Services node can be used to enforce the startup mode and
permissions for any service. Startup modes can be configured as
Automatic, Manual, or Disabled through this node. The newer Automatic
(Delayed Start) startup mode is not available through the System
Services node.
The benefit of using the
System Services node is that you can control the startup mode of
services and which accounts can start services. For example, your
organization may decide that they don't want most users to use the
Encrypting File System (EFS).
Figure 10 shows how this can be modified. When Disabled is selected, the service will not be able to start.
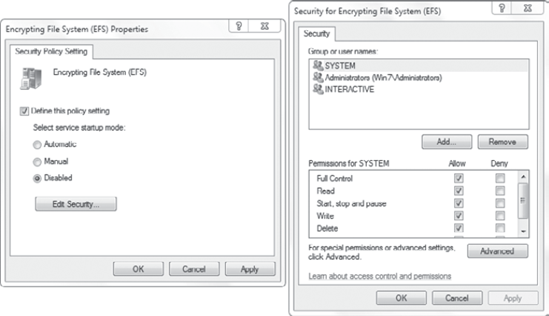
It's also possible to configure
it to Manual and then configure permissions so that only users in
specific groups can manipulate the service. If you click the Edit
Security button, you can manipulate the permissions.
|
Hardening a system means that
you are making it more secure than the default installation. Although
Windows 7 starts out more secure than previous operating systems, it can
still be tweaked to make it even more secure for your organization.
Many organizations identify
the services that aren't needed and take steps to disable them. If the
service is disabled in the Default Domain Policy, it will be disabled
for all systems in the domain.
By disabling unneeded services,
you are reducing the attack surface of a system. If malware is
programmed to attack a specific service, but the service is disabled,
the malware cannot attack. Disabling unneeded services makes you less
susceptible to possible attacks.
|
5. Removable Storage Access Policy
Removable storage devices such
as USB flash drives represent a significant risk within a corporate
environment. It's very easy for employees to transport malware
unknowingly from their home computer to their work computer with flash
drives. In addition, with a USB drive, users can easily copy a
significant amount of data in a short period of time.
Because of the risks, many organizations restrict the use of USB flash drives and other removable media. You can use a Removable Storage Access policy to enforce this corporate policy.
Windows includes several
Group Policy settings that can be configured to restrict the use of
removable media. These settings are located in the Computer
Configuration => Policies => Administrative Templates => System => Removable Storage Access node.
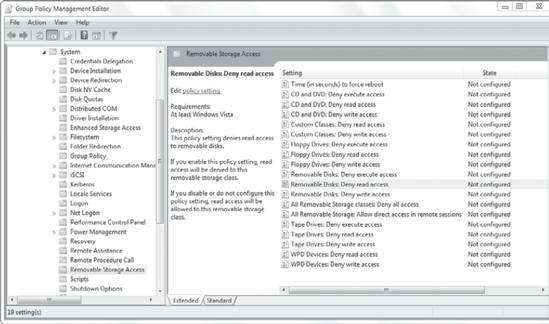
Figure 11 shows the Removal Storage Access node with the Removal Disks: Deny Read Access selection highlighted.
Notice that you can
configure an access policy for different types of devices. You can also
deny all access to any removable device with the All Removal Storage
Classes: Deny All Access setting. Each of the individual removable
devices has three access rights that can be denied:
Deny Execute Access
This prevents any
executable files from running directly from the device. Many malware
programs attempt to run as soon as the device is plugged in. This
setting can be used to help prevent this common malware attack. Deny
Execute Access is available only on Windows 7. It is not available on
Windows Vista.
Deny Read Access
This prevents data from being read from the device. Deny Read Access is available on Windows Vista and Windows 7 computers.
Deny Write Access
This prevents data from being written to the device. Deny Write Access is available on Windows Vista and Windows 7 computers.
NOTE
WPD devices are
listed in the Removable Storage Access policy. WPD is short for Windows
Portable Devices. These can include media players, cell phones, and
other small portable devices.
If any of these access rights
are changed, they will not take effect until the system is restarted.
The Time (In Seconds) To Force Reboot setting can be configured to force
a system to reboot if any of these rights are changed.