Configuring IPv6 in Windows Vista Using the User Interface
To configure the IPv6 settings for a network connection in Windows Vista using the user interface, follow these steps:
1. | Open the Network And Sharing Center in Control Panel.
|
2. | Click Manage Network Connections, and then double-click the connection you want to configure.
|
3. | Click the Properties button and respond to the UAC prompt.
|
4. | Select
Internet Protocol Version 6 (TCP/IPv6) and click Properties to open the
Internet Protocol Version 6 (TCP/IPv6) Properties sheet (see Figure 1).
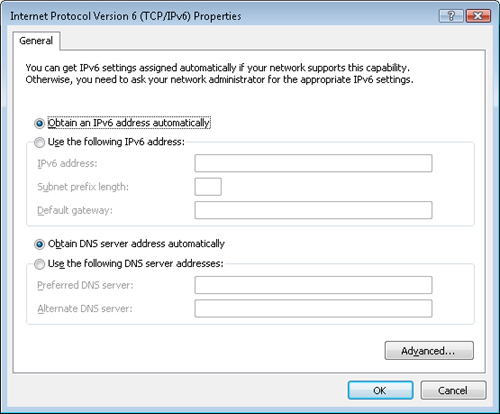
|
5. | Configure the IPv6 settings for the network connection as desired.
|
By default, the IPv6 settings for a network connection are configured as follows:
Obtain An IPv6 Address Automatically
This specifies that the physical or logical interface associated with
this connection uses stateful or stateless address autoconfiguration to
obtain its IPv6 address.
Obtain DNS Server Address Automatically
This specifies that the physical or logical interface associated with
this connection uses stateful address autoconfiguration (DHCPv6) to
obtain the IPv6 addresses of preferred and alternate DNS servers.
By
selecting Use The Following IPv6 Address, you can manually configure
the IPv6 address settings for a network connection by specifying the
following:
IPv6 Address
Type the unicast IPv6 address you want to assign to the physical or
logical interface associated with this connection in colon-hexadecimal
form. If you need to assign additional unicast IPv6 addresses to the
interface, click the Advanced button and then select the IP Settings
tab.
Subnet Prefix Length
Type the subnet prefix length for the IPv6 address you assigned to the
physical or logical interface associated with this connection. For
unicast IPv6 addresses, the subnet prefix length should always be
specified as 64.
Default Gateway
Type the unicast IPv6 address of the default gateway for the local IPv6
subnet in colon-hexadecimal form. If you need to specify additional
default gateways, click the Advanced button and then select the IP
Settings tab.
By selecting Use
The Following DNS Server Addresses, you can manually specify IPv6
addresses for a preferred and an alternate DNS server to be used by
your connection. If you need to specify additional alternate DNS
servers, click the Advanced button and then select the DNS tab. The
remaining settings on the DNS tab have similar functionality to those
used for configuring IPv4 address settings.
Note
The Advanced TCP/IP Settings does not have a WINS tab because IPv6 does not use NetBIOS for name resolution. |