In beta at the time of this writing,
Microsoft Forefront Client Security (FCS) is enterprise security
software that provides protection from malware in addition to many other
threats. While Windows Defender is designed for consumers and small
businesses, FCS is designed to be deployed throughout large networks and
managed efficiently. As shown in Figure 1, you can use FCS to centrally manage client security.
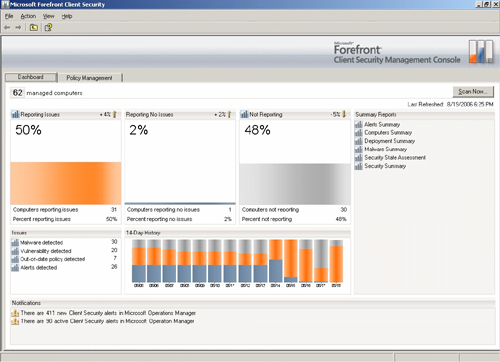
Microsoft Forefront products are designed to
provide defense-in-depth by protecting desktops, laptops, and server
operating systems. Forefront currently consists of the following
products:
Microsoft Forefront Client Security
Microsoft Forefront Security for Exchange Server (formerly called Microsoft Antigen for Exchange)
Microsoft Forefront Security for SharePoint (formerly called Antigen for SharePoint)
Microsoft Forefront Security for Office Communications Server (formerly called Antigen for Instant Messaging)
Microsoft Internet Security and Acceleration (ISA) Server 2006
Of these products, only FCS would be deployed to
Windows Vista or Windows XP client computers. The other products would
typically be deployed on servers to protect applications, networks, and
infrastructure.
Enterprise management of anti-malware software is useful for:
Centralized policy management.
Alerting and reporting on malware threats in your environment.
Comprehensive insight into the security state of your environment, including patch status and up-to-date signatures.
FCS provides a simple user interface for creating
policies that you can automatically distribute to organizational units
(OUs) and security groups by using Group Policy objects. Clients also
centrally report their status so that administrators can view the
overall status of client security in the enterprise, as shown in Figure 2.
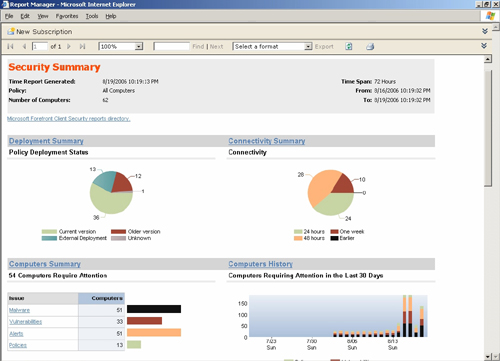
With FCS, administrators can view statistics
ranging from domain-wide to specific groups of computers or individual
computers to understand the impact of specific threats. In other words,
if malware does infect computers in your organization, you can easily
discover the infection, isolate the affected computers, and then take
steps to resolve the problems.
FCS also provides a client-side user interface.
Similar to Windows Defender, FCS can warn users if an application
attempts to make potentially malicious changes, or if it detects known
malware attempting to run. The key differences between Defender and FCS
are:
FCS is centrally managed
FCS is designed for use in medium and large networks. Administrators
can use the central management console to view a summary of current
threats and vulnerabilities, computers that need to be updated, and
computers that are currently having security problems. Windows Defender
is designed for home computers and small offices only, and threats must
be managed on local computers.
FCS is highly configurable
You can configure automated responses to alerts, and, for example,
prevent users from running known malware instead of giving them the
opportunity to override a warning as they can do with Windows Defender.
FCS protects against all types of malware
Windows Defender is designed to protect against spyware. Forefront
protects against spyware, viruses, rootkits, worms, and Trojan horses.
If you use Windows Defender, you need another application to protect
against the additional threats.
FCS can protect a wider variety of Windows platforms
FCS is designed to protect Windows 2000, Windows XP, Windows Server
2003, and Windows Vista computers. Windows Defender can only protect
Windows XP and Windows Vista computers.
Like Windows Defender, FCS supports using WSUS to
distribute updated signatures to client computers, but FCS also
supports using third-party software distribution systems. For more
information about FCS, visit http://www.microsoft.com/forefront/.
Note
Microsoft offers a
third client security solution: Windows Live OneCare. Windows Live
OneCare is designed to help protect home computers and small businesses
with antivirus, antispyware, improved firewall software, performance
monitoring, and backup and restore assistance. For more information,
visit http://www.windowsonecare.com/. |