Because Web-based applications rely on HTTP to
connect browsers to servers and HTML to represent the state of the
application, ASP.NET is essentially a disconnected architecture. When an
application needs to use session
state, the runtime needs a way of tracking the origin of the requests
it receives so that it can associate data with a particular client.
ASP.NET offers three options for tracking the session ID—by cookies, the
URL, or device profiles.
1. Tracking Session State with Cookies
This is the default
option for an ASP.NET Web site. In this scenario, ASP.NET generates a
hard-to-guess identifier and uses it to store a new Session
object. You can see the session identifier come through the cookie
collection if you have tracing turned on. Notice how ASP.NET stores the
session ID in a request cookie. The tracing information also reveals the
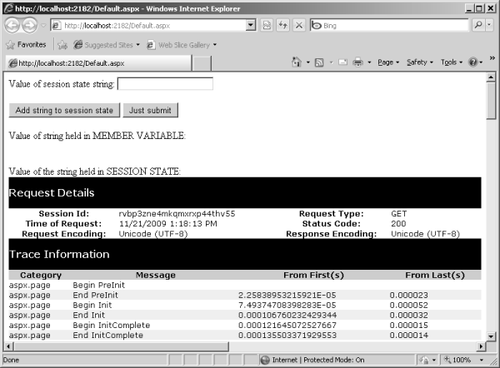
names and the values of the session variables. The following graphic
shows the session ID in the request details section of the trace:
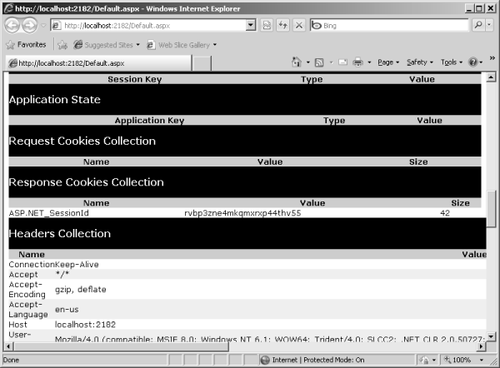
The following graphic shows tracing information, indicating the session ID is just another cookie:
2. Tracking Session State with the URL
The other main option is to
track session state by embedding the session ID as part of the request
string. This is useful if you think your clients will turn off cookies
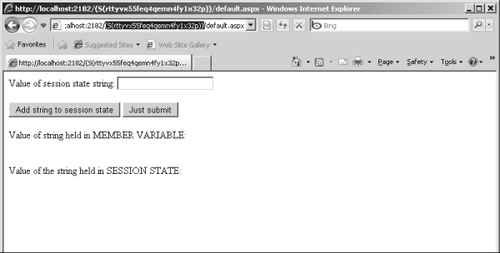
(thereby disabling cookie-based session state tracking). Notice that the navigation URL has the session ID embedded in it:
3. Using AutoDetect
When you use AutoDetect, the ASP.NET runtime determines whether the client browser has cookies turned on. If cookies are turned on, the session identifier is passed around as a cookie. If not, the session identifier is stored in the URL.
4. Applying Device Profiles
The UseDeviceProfile option tells ASP.NET to determine whether the browser supports cookies based on the SupportsRedirectWithCookie property of the HttpBrowserCapabilities object set up for the request. Requests that flip this bit to true cause session identifier values to be passed as cookies. Requests that flip this bit to false cause session identifiers to be passed in the URL.
5. Session State Timeouts
The timeout
configuration setting manages the lifetime of the session. The lifetime
of the session is the length of time in minutes a session can remain
idle before ASP.NET abandons it and renders the session ID invalid. The
maximum value is 525,601 minutes (one year), and the default is 20.