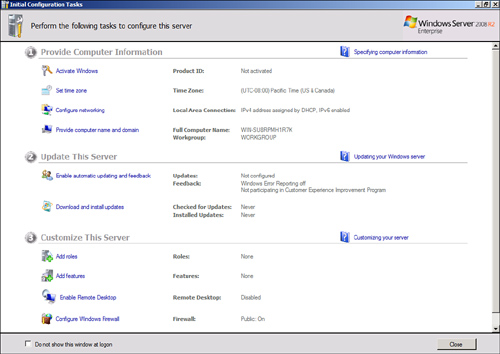
One of the features of Windows Server 2008 R2 is the Initial Configuration Tasks tool, shown in Figure 1.
Windows Server 2008 R2 streamlines the typical installation steps,
enabling an administrator to quickly set up a new server without having
to answer an endless stream of questions.
This
helps separate the tasks of installing the base operating system and
configuring the server, making the best use of the administrator’s time.
This will be a welcome relief to all the administrators who have sat
through a prior Windows version install, watching files get copied from
CD to the hard drive.
After the server operating
system has been installed, it will boot up into a secure state and be
ready for the initial configuration tasks. The initial configuration
tasks are broken into three general categories, as follows:
Provide Computer Information—
This section is where computer-specific information such as the
administrator password, time zone, network configuration, and computer
name are set.
Update This Server— This section of tasks is where the automatic update options are set and the updates are manually installed.
Customize This Server—
This section is where the roles and features for the computer are
added, as well as configuring the remote desktop and the firewall.
The initial configuration settings are stripped down and basic (as shown in Table 1),
with little or no security. For example, the latest security updates
have not been applied and the system is not configured to download them
automatically. Thus, the Windows Firewall is enabled by default to
protect the server from network access until the initial configuration
is completed and the Remote Desktop feature is turned off.
Table 1. Default Configuration Settings
| Setting | Default Configuration |
|---|
| Time zone | Pacific Time (GMT-8) is the time zone set by default. |
| Computer name | The
computer name is randomly assigned during installation. Administrators
can modify the computer name by using commands in the Initial
Configuration Tasks Wizard. |
| Domain membership | The computer is not joined to a domain by default; it is joined to a workgroup named WORKGROUP. |
| Windows Update | Windows Update is turned off by default. |
| Network connections | All network connections are set to obtain IP addresses automatically by using DHCP. |
| Windows Firewall | Windows Firewall is turned on by default. |
| Roles installed | No role or features are installed by default. |
Each of the settings can
be configured via wizards that launch from the Initial Configuration
Tasks, making it easy to configure the server. Once the initial
configuration is completed, there is a check box in the Initial
Configuration Tasks console that will prevent it from launching
automatically.
Note
Once
the Initial Configuration Tasks console is closed, there is no menu
option to launch it again. If you need to use the console again (for
example, if it was closed accidentally), the tool can be launched
manually by opening a command prompt and running the command oobe.exe. The “oobe” stands for Out-Of-Box Experience.