5.3. Performing the Telnet Test
At this point, you have Telnet installed and
configured, and the service is installed and configured. Follow these
steps to test the functionality of the trigger-start service:
Open the Event Viewer console in the Administrative Tools folder of the Control Panel. You'll see the Event Viewer window.
Open the Event Viewer\Windows Logs folder.
Right-click the System log entry and choose Clear Log from the Context menu. You'll see an Event Viewer dialog box.
Click Clear to clear the events in the Event Viewer.
Open
the Services console in the Administrative Tools folder of the Control
Panel. Right-click the Telnet entry and choose Start from the Context
menu. The Telnet service will start. Starting the Telnet service opens
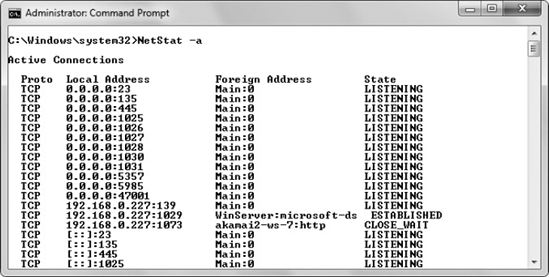
Port 23. You can verify this fact by typing NetStat –a at the command prompt and pressing Enter. The NetStat utility shows that the system is listening on Port 23, as shown in Figure 11. (Notice the 0.0.0.0:23 address entry on the first line of the output — the :23 part of the entry signifies Port 23.)
Wait
at least 60 seconds. Windows doesn't guarantee that a trigger-start
service will respond immediately to an event. In fact, you'll find that
the documentation makes a vague reference to a 60-second response time,
but Microsoft never makes it very clear. Depending on system load, a
trigger-start service may not even respond within 60 seconds, but it
will respond.
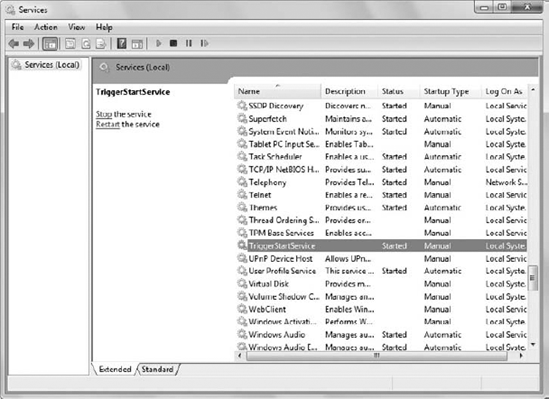
Choose Action =>
Refresh. You'll see that TriggerStartService has started. It will
remain started as long as the Telnet service is running, as shown in Figure 12.
Right-click
the Telnet service and choose Stop from the Context menu. The Telnet
service will stop. Verify that Port 23 is no longer open by typing NetStat –a at the command prompt and pressing Enter.
Wait at least 60 seconds.
Choose Action => Refresh. You'll see that TriggerStartService has stopped.
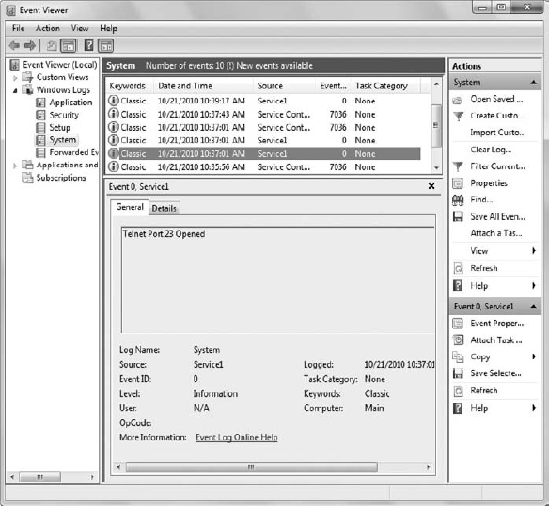
In the Event Viewer, make sure the System log is selected and choose Action  Refresh. You'll see a series of event log entries like those shown in Figure 1.
Refresh. You'll see a series of event log entries like those shown in Figure 1.
Beginning
with the oldest entry, view the entries one at a time. You'll see the
sequence of events that you've just tested with this procedure. The
event log will tell you that Telnet started, then TriggerStartService.
One of the entries will tell you that Port 23 has opened. Keep
following the entries, and you'll eventually see one where Port 23
closes after the Telnet service stops. Notice that the trigger-start
service starts and stops as the port opens and closes, but that Windows
doesn't act immediately — the action always requires some amount of
time.
At this point, you might want to uninstall
TriggerStartService. To perform this task, type InstallUtil /U
TriggerStartService.EXE and press Enter.