6. The noindex Class
One way SharePoint 2010 allows administrators and developers to manage noise in the search engine is by implementing the noindex
class value in the HTML of the page. Of course, this works only for web
pages or other content written with HTML. Many web pages are largely
based on the same templates. These templates include branding and
navigation so every web page looks the same or similar and has a similar
navigational structure. This is friendly and familiar to web-browsing
end users. However, a large number of the important terms for the
organization appear on every document. That generates noise in the
search engine. Adding this class value to tags in the HTML will tell the
crawler not to index the content of those tags and focus only on the
terms that appear in the "content" section of the web page.
To include the noindex
class, simply find the tag that holds the content that should not be
indexed. This is usually a header, footer, news Web Part, or navigation.
Add the following values to that tag:
class="noindex"
It should be noted that some nested tags will require their own noindex class to respect the rule. Here is a typical example:
...
<div class="noindex">
<table>
<tr>
<td style="text-align:right;line-height:70%;">
<a href=http://www.prosharepointsearch.com/about.html">About Us</a>
</td>
</tr>
...
7. Popularity (Click-Through)
Although not something that an
administrator can actively modify to improve search, click-through
relevancy adjustments can improve search without any administrative
influence. This "social search" capability records a number of all the
clicks for a given query with the document of choice. This document's
ranking value is then, over time, increased to improve its ranking. This
is an advantage insofar as the search engine learns based on the
experience and knowledge of the end users. It relies on the fact that
the end users know what they are looking for in respect to the query
they made to find it. And they would naturally click the only document
that is the correct one for their query. In actual practicality, this is
probably not totally true. Users will click in and out of different
documents, looking for the right one. This may or may not adversely
affect ranking. However, over thousands, if not hundreds of thousands of
queries, a useful pattern should emerge that will help ranking, not
hinder it.
Should ranking appear to
degrade over time, the Search service application can be removed and a
new index, database, and ranking values applied to start again. At this
point, there is no other way to manually affect this mechanism.
8. Social Tagging
Social tagging is a
mechanism in SharePoint to allow users to personalize the content by
adding tags to it. The tags can be anything the user wants and are
unique to him or her. The tags can affect relevancy as well, helping
content be handled by search. The term folksonomy is often applied to
this type of user-generated tagging, and it is becoming more and more
prevalent on web sites on the Internet. The concept is of a
user-generated taxonomy that grows with user experience. Folksonomies
can be a useful way to share interests and identify socially interesting
concepts but should not be left as the core method for tagging and
managing documents' taxonomies. A more managed structure should always
be available for end users.
9. The Ratings Column
Although not technically
part of adjusting relevancy, the ratings column can allow users to
filter on results, along with the other search refinement mechanisms to
find documents that are considered valuable by other users. The ratings
column is a feature in SharePoint that will allow users to give
documents in a given library or items in a list a rating by clicking
from one to five stars in a column beside the document. Although this
may seem trivial in an organization where all documents have value and
purpose, if a given list or library is a collection of information on a
given topic, the ratings column can allow users to rate and filter based
on that what best represents that topic. The rating values can also be
displayed on the results page to allow users to quickly identify which
documents were ranked useful by their colleagues.
9.1. Adding a Ratings Column
To add a ratings column to a list or library follow these steps:
Activate
the feature at the farm using PowerShell if it isn't already active.
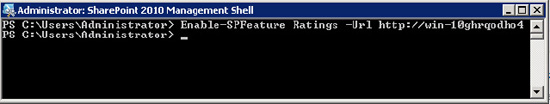
Open the SharePoint 2010 Management Shell and call the following (Figure 5):
Enable-SPFeature Ratings -Url http://server/site/subsite
NOTE
SharePoint Team Server
Administration (STSADM) is still supported for those more comfortable
with it. To enable the feature, run STSADM, which is found in c:\Program Files\Common Files\Microsoft Shared\Web Server Extensions\14\BIN. Find STSADM.exe, and drag it into a command prompt window with the following parameters: STSADM.exe –o activatefeature –name ratings –url http://server/site.
Navigate to the library or list in question, and click the Library tab in the ribbon.
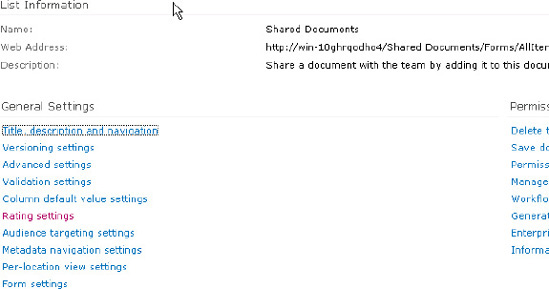
Choose Library Settings in the ribbon, and click "Rating settings" under General Settings (Figure 6).
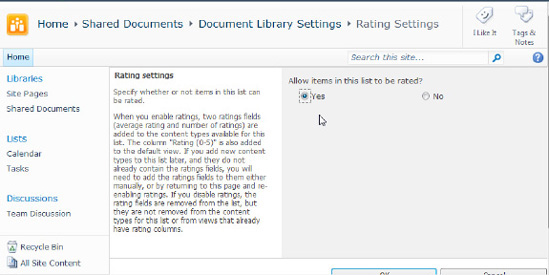
Select Yes under "Allow items in this list to be rated?" (Figure 7). SharePoint will automatically apply the ratings column to the library or list.
Find the AverageRating crawled property (ows_AverageRating) as shown in Figure 8.
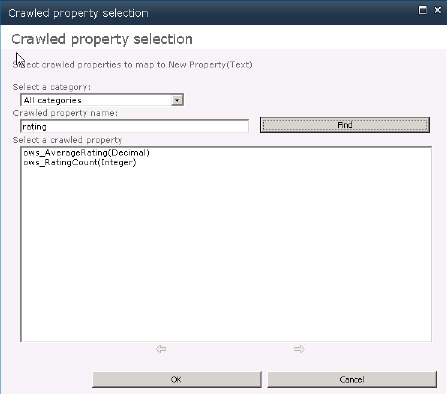
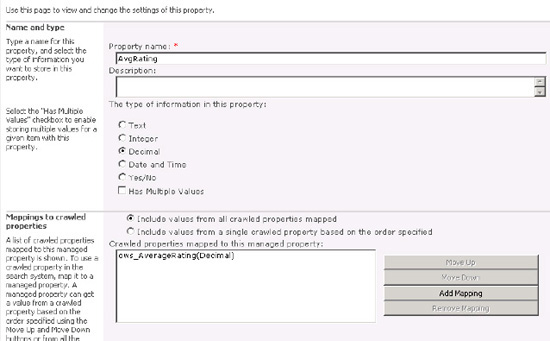
Create a property called AvgRating, and map ows_AverageRating to it. It should be a decimal property.
On
the crawled property pages that can be accessed by clicking the crawled
property in the Metadata Property Mappings page, check "Include values
for this property in the search index".
NOTE
Make sure that the
property has its values included in the search index. This flag can be
set on the crawled property's page. See Figure 9.
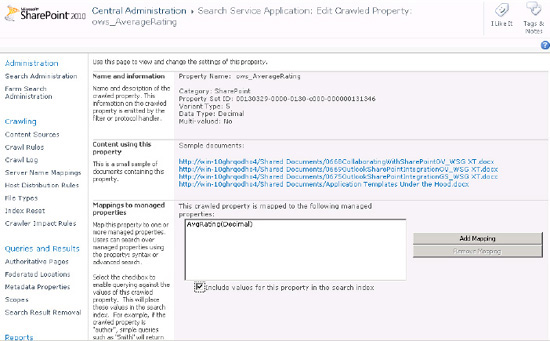
Figures 19 and 10 are two views of the same mapping, one from the crawled property and one (Figure 10)
from the mapped property, which is the one we will eventually call from
the user interface. One must be set for mapping the crawled property
and the other to include its values in the search index.
9.2. Displaying Ratings in the Results
The next thing to do is to make
this rating value visible in the result list. This will help users
identify which documents are rated higher by their peers.
To add the ratings values to display on the results page, do the following:
Navigate to the search results page, and edit the page.
Edit the core search results Web Part.
On the right, expand the Display Properties section, and uncheck Use Location Visualization.
Add
the new column to be fetched from the index. Call it <Column
Name="AvgRating"/> and place it anywhere in the list as long as it is
after the first <Columns> tag and after the closing columns tag
and doesn't interfere with the existing entries.
Click
XSL Editor. You can now add the XSLT template to control how the stars
will be displayed. You should place this in the search results where you
want the ratings displayed. A natural place to put it is beside the
title. To do this, find the srch-Title3
div tag. Just before this div section closes is the end of the title.
It is in the middle of the XSLT and has two closing div tags. Place a
call to the template before these closing div tags, as shown in Listing 1.
Save, click OK on the Web Part editing pane, and stop editing the page.
Example 1. XSLT to display the rating stars<!-- Ratings -->
<xsl:text> </xsl:text> <xsl:choose>
<xsl:when test="avgrating > 0 and avgrating < .75">
<span class="ms-currentRating"><img class="ms-rating_0_5"
src="/_layouts/Images/Ratings.png" alt="Current average rating is half a star."/></span>
</xsl:when>
<xsl:when test="avgrating >= .75 and avgrating < 1.25">
<span class="ms-currentRating"><img class="ms-rating_1"
src="/_layouts/Images/Ratings.png" alt="Current average rating is 1 stars."/></span>
</xsl:when>
<xsl:when test="avgrating >= 1.25 and avgrating < 1.75">
<span class="ms-currentRating"><img class="ms-rating_1_5"
src="/_layouts/Images/Ratings.png" alt="Current average rating is 1.5 stars."/></span>
</xsl:when>
<xsl:when test="avgrating >= 1.75 and avgrating < 2.25">
<span class="ms-currentRating"><img class="ms-rating_2"
src="/_layouts/Images/Ratings.png" alt="Current average rating is 2 stars."/></span>
</xsl:when>
<xsl:when test="avgrating >= 2.25 and avgrating < 2.75">
<span class="ms-currentRating"><img class="ms-rating_2_5"
src="/_layouts/Images/Ratings.png" alt="Current average rating is 2.5 stars."/></span>
</xsl:when>
<xsl:when test="avgrating >= 2.75 and avgrating < 3.25">
<span class="ms-currentRating"><img class="ms-rating_3"
src="/_layouts/Images/Ratings.png" alt="Current average rating is 3 stars."/></span>
</xsl:when>
<xsl:when test="avgrating >= 3.25 and avgrating < 3.75">
<span class="ms-currentRating"><img class="ms-rating_3_5"
src="/_layouts/Images/Ratings.png" alt="Current average rating is 3.5 stars."/></span>
</xsl:when>
<xsl:when test="avgrating >= 3.75 and avgrating < 4.25">
<span class="ms-currentRating"><img class="ms-rating_4"
src="/_layouts/Images/Ratings.png" alt="Current average rating is 4 stars."/></span>
</xsl:when>
<xsl:when test="avgrating >= 4.25 and avgrating < 4.75">
<span class="ms-currentRating"><img class="ms-rating_4_5"
src="/_layouts/Images/Ratings.png" alt="Current average rating is 4.5 stars."/></span>
</xsl:when>
<xsl:when test="avgrating >= 4.75">
<span class="ms-currentRating"><img class="ms-rating_5"v
src="/_layouts/Images/Ratings.png" alt="Current average rating is 5 stars."/></span>
</xsl:when>
<xsl:otherwise>
<b>Not yet rated</b>
<br/>
</xsl:otherwise>
</xsl:choose>
<!-- Ratings End -->
|
The ratings should now appear on the result list. See Figure 11. This XSLT will check the value of the AvgRating
property you have mapped and compare it with ranges between every half
unit, starting at three-fourths. This will allow for half ratings based
on the decimal values of the ows_AverageRating property, which is an average of all accumulated ratings.
The XSLT uses the built-in image Ratings.png,
which is actually a larger image of all ratings stars, and sets them to
be displayed using the built-in cascading style sheet (CSS). If the
default CSS is changed, the ratings images will not display correctly.
There are certainly more clever ways to create this XSLT, but this is a
simple start to set the ratings value on the result template.
