Overview of Internet Information Services 7.5
IIS is one of the most widely
deployed Web servers in the world. IIS is used by thousands of
organizations to serve Web sites on intranets, extranets, and the
Internet. IIS not only provides support for hosting basic Web sites but
also advanced Web applications using technologies such as ASP.NET and
PHP. IIS additionally provides the following features:
Support for running multiple Web sites on a single host
A common administrative interface using Server Manager and PowerShell
Support for SSL-based Web sites using certificates from internal and public PKIs
Delegation of permissions giving Web developers limited access to servers hosting Web applications
Modular installation providing a greater level of security and reduced attack surface
Rich media services allowing organizations to provide streaming media via the Web.
Microsoft has included the following features in IIS 7.5 to further enhance the Windows Web server:
Request Filtering Module
The Request Filtering Module
is introduced as an add-on extension for IIS 7.0 to allow administrators
to block Web requests that are deemed harmful. Request filtering
provides additional security to IIS by limiting the types of requests
and commands that can be sent to IIS via the Web browser. IIS 7.5 now
includes the module as a standard part of the Web server role.
Best Practices Analyzer
IIS 7.5 now includes a BPA.
You should run the BPA after initial configuration and on a regular
basis thereafter to ensure that your IIS deployment is healthy and
optimally configured.
PowerShell Module
As with most roles in
Windows Server 2008 R2, IIS 7.5 includes a PowerShell Module allowing
administrators to perform most administrative functions from the
PowerShell command line. Administrators can use PowerShell to quickly
perform IIS administrative tasks as well as automate the configuration
of IIS for fast and standardized deployment of IIS Web servers.
Support for managed service accounts
Windows Server 2008 R2 Active Directory allows administrators to
create managed service accounts. Managed service accounts allow
administrators to change the password of a service account
without having to update each service using that particular account.
IIS 7.5 application pools provide support for managed service accounts.
For example, an IIS application pool could be running under the account
IIS_Service. For security purposes, an administrator needs to change the
password on this account. The administrator simply has to change the
password of the Active Directory account. Once the password has been
changed, the IIS application pool will automatically update the password
field to reflect the new password without administrator interaction.
Planning to Deploy IIS 7.5 Web Servers
Prior to installing IIS 7.5,
you will want to properly plan for the deployment. There are several
important items you will need to take into consideration. These include:
Web technology used —Will the Web server support applications based upon ASP.NET, PHP, or some other development platform?
Security requirements
—Will your Web sites and applications use SSL? If so, will you need
public or private certificates? What types of authentication methods are
required for your applications?
Resource requirements
—How much memory and CPU will the Web application require? How much
disk space will be used by the application files? How much network
bandwidth will be needed to ensure acceptable performance for users? Is
the application compatible with 64 bit hardware?
Server configuration
—Do you want to use a full server install or core install? What types
of logging need to be enabled for the Web site or application? Who will
manage the Web server and will they do so by logging onto the server or
via remote management tools?
Backup and disaster recovery
—In the event of a Web server failure, how will you recover the system?
Does your deployment require high availability and load balancing?
You will want to spend
ample time planning your IIS deployment to ensure that it can properly
support Web sites and applications that will be supported by the Web
servers within your organization. Be sure to document the configuration
and use standards when configuring IIS. After you complete your
deployment, be sure to run the BPA to verify your configuration.
Installing and Configuring IIS 7.5
IIS 7.5 is installed using the same process as
installing other roles in Windows Server 2008 R2. In this exercise, we
will explore the process to install IIS 7.5:
1. | Open Server Manager and select the Roles node. Then click the Add Roles link in the middle pane. This will launch the Add Roles Wizard. Click Next to continue.
|
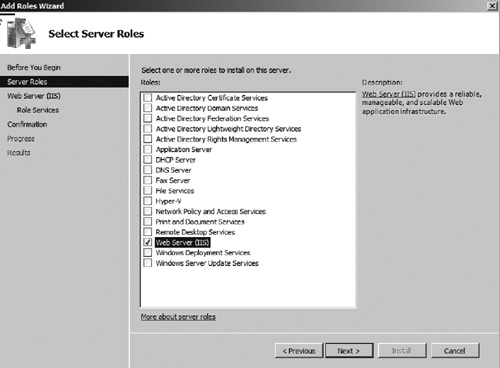
2. | Select the Web Server (IIS) role as seen in Figure 1. Then click Next.
|
3. | This will take you to the IIS summary page. Click Next.
|
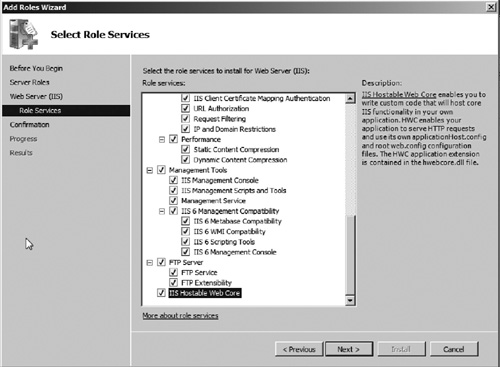
4. | You
now must select the role services you wish to use. Starting with IIS
7.0, Windows only installs the components that are required to provide
the requested functionality. This provides a reduced attack surface for
IIS making it more secure overall. For the purposes of this exercise and
other exercises in this article, we will select all role services. When
installing your production deployment, you should select only the role
services required to support your Web sites and applications. After selecting the role services (see Figure 2), click Next to continue.
|
5. | Verify your selections on the summary page, then click Install. This will install the IIS role and the role services you selected in step 4. You can later add or remove role services by selecting the add role services or remove role services links, respectively.
|
6. | When installation is completed, click Close to close the Add Roles Wizard.
|
The IIS 7.5 role has now been
added to the Windows Server 2008 R2 server. You can access the IIS
management console from within Server Manager by selecting the node Roles | Web Server (IIS) | Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager as seen in Figure 3.

|
IIS 6.0 Manager
While installing IIS role
services, you may notice that the IIS 6.0 Manager is listed. This is
available as a role service to support applications that require IIS 6.0
services. For example, some applications such as Microsoft Exchange
2007 were released prior to IIS 7.0 and 7.5 thus require IIS 6.0
components to function properly. To support these types of applications,
install the IIS 6.0 role services.
|
After you have installed IIS,
there are a few postconfiguration steps you may want to perform
immediately. For example, IIS logs are saved in the directory
%SystemDrive%\InetPub\logs\LogFiles by default. However, using this
default directory could allow IIS logs to fill up the operating
system drive if left unchecked over time, causing the OS to become
unstable. To help remediate this risk, you can move the log files to a
separate drive or partition. To configure the log file location, perform
the following:
1. | Open Server Manager and select the node Roles | Web Server (IIS) | Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
|
2. | In the middle pane, select the Web server as seen in Figure 4.

|
3. | In the features view, scroll down until you see the Logging option as seen in Figure 5. Double-click the Logging option to open the logging configuration window.

|
4. | Change the directory to the new location you would like the logs to be stored (see Figure 6), then click Apply.

|
|
IIS Logs
Depending on Web site
traffic, IIS Logs can become very large consuming a lot of space on Web
servers. You may want to write a script or bat file to regularly purge
old IIS logs from the server.
|
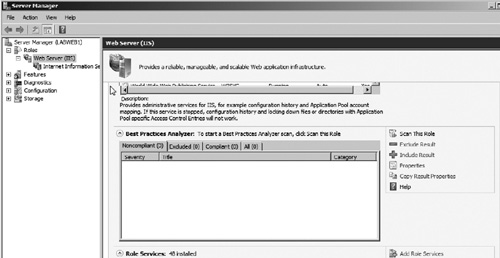
Another
task you may want to perform after installing IIS is to run the BPA.
The BPA can be accessed from Server Manager by performing the following:
1. | Open Server Manager and select the node Roles | Web Server (IIS)
|
2. | Scroll down the middle pane until you see the BPA as seen in Figure 7.
|
3. | Click the Scan Role link to begin the BPA scan process.
|
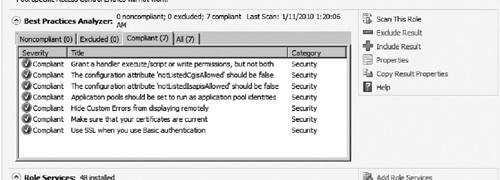
4. | The results will be listed as seen in Figure 8.
If any settings are noncompliant, review the warning and remediation
steps to bring the server into compliance. After resolving the issue,
rescan the system. You may also want to run the BPA when you set up and
configure new Web sites.
|