Server
Manager is a new tool that provides a central location for managing all
the roles and features that Windows Server 2008 R2 provides. This
console gives an administrator access to the complete operational
status, monitoring tools, and configuration tools for the entire server
in a convenient single console.
Server Manager enables the administrator to do the following:
- Add and remove roles and features from the server
- Monitor and manage the server
- Administer the roles and features on the server
In effect, Server Manager is a
one-stop shop for all the administrator management and monitoring needs.
The features of Server Manager are available via the Server Manager
console.
Selecting the server name in the
folder tree will show the Server Manager main window in the Details
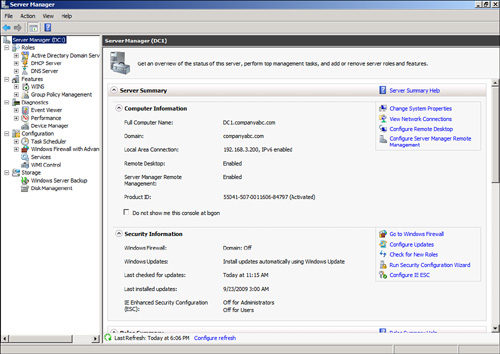
pane. This consists of several section windows. The Server Summary
window (shown in Figure 1)
shows computer information such as the computer name, networking
information, and if Remote Desktop is enabled. It also shows security
information, such as if Windows Firewall is enabled and the Windows
Updates status. The window also has active links that enable the
administrator to launch wizards to change the configuration or get help.
Server
Manager launches automatically when the Initial Configuration Wizard is
closed and each time a user logs on to the server.
The next sections discuss the components and features of Server Manager.
Server Manager Roles and Features
The Roles Summary and Feature Summary windows, shown in Figure 2,
show which roles and features are installed. In the Roles Summary
window, the status of the roles can be seen as well. As can be seen in
the figure, the Active Directory Domain Services role and the DNS Server
role have information icons, indicating that there are informational
messages. If there were problems with the roles, these would change to
warning or critical icons. The summary windows also include links to add
or remove roles and features, as well as to access context-sensitive
help.
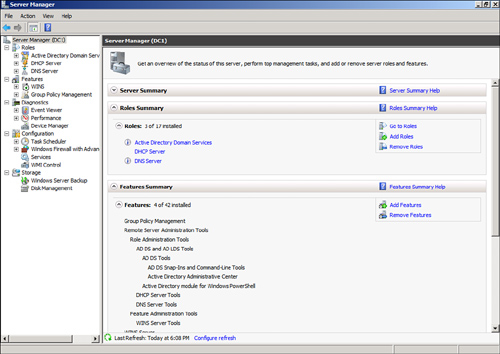
Server Manager Roles Page
The Server Manager
console has a folder tree dedicated to the roles of the server.
Selecting the Roles folder in the console tree shows a summary of the
roles installed on the server, as well as a summary page for each of the
roles. The summary page for each role shows the role status, such as
the status of the system services and the events for the role.
However, selecting the
folder for a specific role shows the Server Manager role-specific page
for that role. The role-specific pages are dedicated to the role and
contain operational information about the role. The following sections
discuss the sections included in the role-specific page.
Events Section
There
is a problem with going to the full Event Viewer and seeing all the
events for all roles, services, and the operating system. There is
usually so much information that it ends up overloading the
administrator, making it difficult to see real problems. The Events
section in the role-specific page addresses this by only presenting the
role-specific events.
From the Events
section, the administrator can see a summary of the events that pertain
to the role, review the details of the events, and filter the events as
needed. The default filter shows only events in the last 24 hours, but
this can be adjusted via the Filter Events control.
The full Event Viewer can also be launched from this section.
System Services Section
The System Services section
lists the services that the role depends on and their status. It also
describes each service and includes control links to Stop, Start,
Restart, and configure Preferences.
The Preferences control
enables the administrator to adjust the monitored services. For example,
if an administrator determines that the Windows Time service is
essential to the role of the Active Directory Domain Services server
(that is, the domain controller), that service can be monitored by
checking it in the Preferences section.
Role Services Section
The Role Services section shows
which of the role services that are available for the role have been
installed. There are also links to add or remove the role services.
A
nice feature of this section is that when a role service is selected, a
brief description is shown of what the role service is for. This
includes a link to get more information on the role service.
Advanced Tools Section
In the case of some roles,
there will be an Advanced Tools section with a list of tools that help
support the role. This includes both command-line tools and MMC consoles
with brief explanations of their functions.
In the case of the
Active Directory Domain Services role (which, by far, has the most
advanced tools of any role), there are 21 different tools in the
section, including the following:
AD DS Tools— These are tools such as the AD Domains and Trusts console, the ADSI Edit console, and the NTDSUTIL tool.
Directory Services Tools— These include DSADD, DSGET, and DSMGMT tools.
Networking and Other Tools— These include such tools as NSLOOKUP and W32TM.
The tools can be launched
by clicking on the active links. In the case of console tools, the
console will be launched. In the case of command-line tools, the tool
will be launched with the help option to display the options for the
tool.
For example, after installing
the Active Directory Domain Services role on a server, you can use the
Advanced Tools section to launch DCPROMO to complete the configuration
of the domain services.
Resources and Support Section
The Resources and Support
section is an extremely useful section. It provides a brief
recommendation on configurations, best practices, and links to
resources.
The recommendations are
listed in a window; highlighting the recommendation shows a brief
explanation of the recommendation with a link to a more detailed
explanation. This is great for researching the recommendations. The
section also includes links to online resources, such as the appropriate
TechCenter and Community Center for the role.
For example, the Resources and Support section for the Active Directory Domain Services role (shown in Figure 3)
includes over 18 different recommendations on installation. One of the
recommendations is Improve Active Directory Redundancy by Adding Another
Domain Controller. Highlighting this recommendation shows a brief
paragraph explaining the recommendation and includes a link to get more
detailed information on the recommendation.
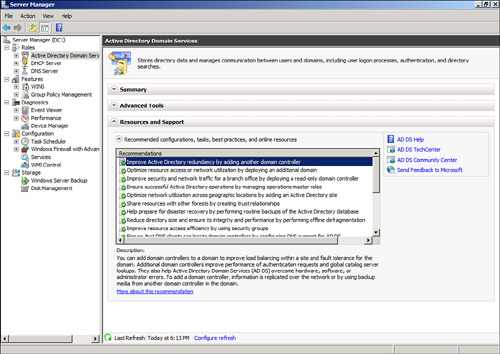
An important note is that these recommendations are static and don’t adjust to changes in the environment.
Tools Folders
For each of the role folders
in the Server Manager folder tree, there are subfolders that are the MMC
snap-ins for the role. This is a cool feature that makes it easy to
access the tools from within Server Manager without having to search for the tools in the Administrative Tools folder.
For example, the Active
Directory Domain Services role has two tools folders: the Active
Directory Users and Computers snap-in and the Active Directory Sites and
Services snap-in, shown in Figure 4.
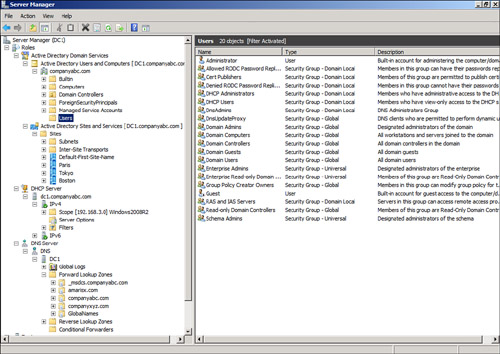
As can be seen in the figure,
these are the same full-featured snap-ins that can be launched from the
Administrative Tools folder. The Users container is selected in the
figure, and contents of the container can be seen.
For the other roles on the server (the DHCP Server role and DNS Server role), the respective tools can be seen as well.
Server Manager Features Page
The Features page shows a
summary of the installed features. There are active links to add and
remove features, as well as a link to get help.
In the case of some
features, there will be a folder under the Features folder that is the
MMC snap-in for the feature. For example, the Active Directory Domain
Services role automatically installs the Group Policy Management
feature. This places the Group Policy Management Console under the
Features folder.