Network mapping, a feature that was new in Windows Vista, uses the Link
Layer Topology Discovery (LLTD) protocol to find the other computers
and devices on your network, and then displays them in a schematic
representation. To display the map, in Network And Sharing Center click See Full Map. Figure 1 shows an example.
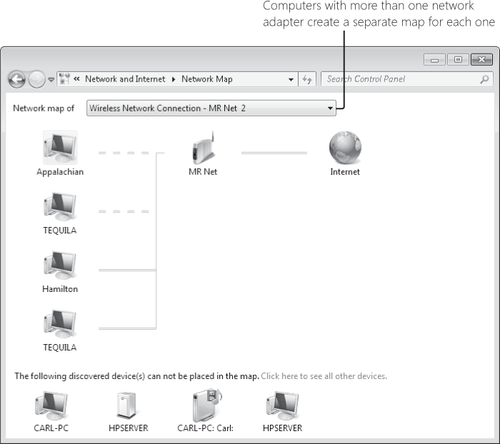
Network
mapping works with wired and wireless networks, but only on private
(home or work) network locations; by default, you can't view a map of a
domain-based network or a public network. LLTD maps only the computers in a single subnet—the typical setup in a home or small office.
You might notice that
some computers and devices are shown separately at the bottom of the
window, or they might be missing altogether. (For example, the Hpserver
device at the bottom of the display shown in Figure 19-2 is a server running Windows Home Server, which supports UPnP but not LLTD.)
This occurs because not all operating systems and devices include LLTD
support, or because the devices might not be configured properly.
|
By making changes through Group Policy, you can enable network mapping on domains, public networks, or both. To make this change, follow these steps:
At
a command prompt, type gpedit.msc to open the Local Group Policy
Editor. (The Local Group Policy Editor is available on computers running
the Professional, Enterprise, or Ultimate edition of Windows 7. These
are also the only editions that can join a domain.) Navigate to Computer Configuration\Administrative Templates\Network\ Link-Layer Topology Discovery. Double-click the Turn On Mapper I/O (LLTDIO) Driver policy.
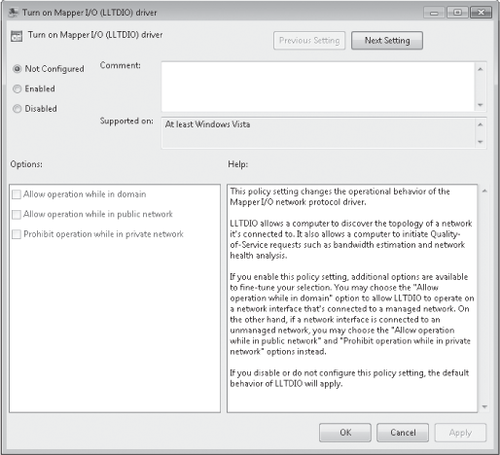
Select Enabled, and then select Allow Operation While In Domain. Repeat the selections for the Turn On Responder (RSPNDR) Driver policy setting, and then click OK.
Note that, depending on the size of the network, creating a network
map on a domain-based network can be inordinately slow, which is why it
is disabled by default. Note also that you can use these same policy
settings to enable network
mapping on a public network and, if you want, disable network mapping
on a private network. For security and convenience, we don't recommend
either of these options.
|
Devices shown at the bottom generally fall into one of the following categories:
Computers running Windows XP
LLTD is installed by default in Windows 7 and Windows Vista, but it is not included in earlier Windows versions. An LLTD client is available for
Windows XP, and it should be available through Windows Update. (To find
out if it's installed, look at the properties for the network
connection and see if LLTD appears in the list of installed protocols.)
You can download and install the protocol without Windows Update; for
details, see Knowledge Base article 922120 (w7io.com/1902). Note that if you have already installed Service Pack 3 for Windows XP, you'll need the hotfix available from w7io.com/1905. LLTD is not currently available for other versions of Windows.
Other network devices LLTD (along with another network discovery–related technology, Plug and Play Extensions, or PnP-X) is part of the Windows
Rally technologies, an initiative for network hardware devices that
gained steam in 2006. Devices that include LLTD support became widely
available in 2007 and later, but earlier devices are not fully
recognized by Network Map. Most devices sold in recent years support UPnP, which should get the device somewhere in the map window; however, Network Map displays only limited information about the device and offers only limited control of the device.
Configuration problems
In Network And Sharing Center, be sure that your network is not
identified as a public network, and be sure that network discovery is
turned on. In Network Connections, view the properties of your network
connection and be sure that two LLTD-related protocols, Link
Layer Topology Discovery Mapper I/O Driver and Link Layer Topology
Discovery Responder, are installed and enabled (that is, their check
boxes are selected). Whether you use Windows Firewall or another
firewall, be sure it has an exception enabled for file and printer
sharing.
|
It's possible to use the LLTD client for Windows XP on Windows Server 2003, as described in Windows IT Pro magazine (w7io.com/1903), and on Windows Home Server (which is based on Windows Server 2003), as described by Microsoft MVP Donavon West (w7io.com/1904).
These workarounds are not supported by Microsoft, so apply them with
caution. (Be sure you have a current backup and set a restore point.)
|
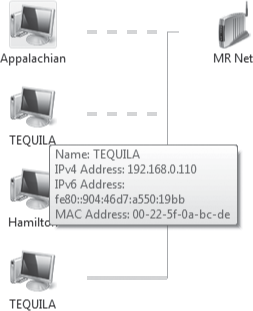
Network
Map is more than a pretty picture. If you hover the mouse pointer over a
computer or other device, you get more information about the device,
including information such as its IPv4 and IPv6 addresses and its Media
Access Control (MAC) address.
Network
infrastructure devices (such as routers) that include Wi-Fi Protected
Setup support offer a menu of choices when you right-click them, usually
including one that leads to the device's configuration page.
Right-clicking a computer icon displays relevant options for that
computer, such as connecting to it using Remote Desktop Connection. For
computers and other devices with shared resources, you can double-click
them in Network Map to open them, just as you can in the Network folder.
Network
Map, like the "mini-map" in Network And Sharing Center, indicates
broken network connections with an X. Click Diagnose And Repair to
attempt a solution.