For more advanced performance monitoring, Windows XP
offers the System Monitor tool, which you can get to by selecting Start,
Run, typing perfmon.msc, and clicking OK. The System Monitor appears, as shown in Figure 1.
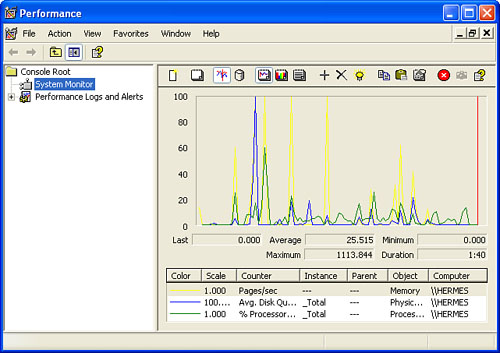
System Monitor’s job
is to provide you with real-time reports on how various system settings
and components are performing. Each item is called a counter
and the displayed counters are listed at the bottom of the window. Each
counter is assigned a different colored line, and that color
corresponds to the colored lines shown in the graph. Note, too, that you
can get specific numbers for a counter—the most recent value, the
average, the minimum, and the maximum—by clicking a counter and reading
the boxes just below the graphs.
The
idea is that you should configure System Monitor to show the processes
you’re interested in (page file size, free memory, and so on) and then
keep System Monitor running while you perform your normal chores. By
examining the System Monitor readouts from time to time, you gain an
appreciation of what is typical on your system. Then, if you run into
performance problems, you can check System Monitor to see whether you’ve
run into any bottlenecks or anomalies.
By default,
System Monitor shows only the Kernel Processor Usage setting, which
tells you the percentage of time the processor is busy. To add another
setting to the System Monitor window, follow these steps:
1. | Right-click a counter and then click Add Counters. The Add Counters dialog box appears.
|
2. | Use the Performance Object list to select a counter category (such as Memory, Paging File, or Processor).
|
3. | Activate the Select Counters from List option.
|
4. | Select the counter you want and then click Add. If you need more information about the item, click the Explain button.
|
5. | Repeat step 4 to add any other counters you want to monitor.
|
6. | Click OK.
|