Occasionally, IE doesn't work as you'd expect. There are several steps you can take to check and troubleshoot different issues:
Check network and proxy settings.
Troubleshoot plug-ins and add-ons.
Restore IE original settings.
Disable Add-on Crash Detection.
Enable Compatibility View.
1. Check Network and Proxy Settings
If a user is unable to reach
any Internet sites, you should start with the basics. Make sure that the
client is able to reach other network resources. However, if you can
ping other network resources but can't access Internet resources with
IE, you should check the proxy settings.
You can access these settings from Tools =>
Internet Options. Select the Connections tab, and click the LAN
Settings button. If a proxy server is used in your network, ensure that
the correct address and port are configured. Figure 1 shows these settings.
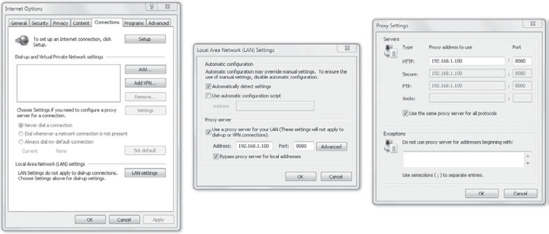
If you have different
proxy servers for different protocols, you can click the Advanced button
and configure different IP addresses for the different proxy servers.
However, it's common for a single proxy server to handle all the
protocols.
2. Troubleshoot Plug-ins and Add-ons
One of the strengths of IE
is that it can be extended with plug-ins and add-ons. These can add
significant capabilities to IE. However, unreliable plug-ins and add-ons
can make IE unstable.
IE supports four types of add-ons:
Toolbars and extensions
Search providers
Accelerators
InPrivate Filtering
If you suspect
that an add-on is causing instability problems with IE, you can launch
IE without any add-ons. If it's stable, you'll have verified that the
problem is caused by the add-on. Now, the challenge is determining which
add-on is causing the problem. You can do this with the Manage Add-ons
screen.
Figure 2 shows the Manage Add-ons screen with Toolbars And Extensions selected. You can select any of the add-ons and select Disable.
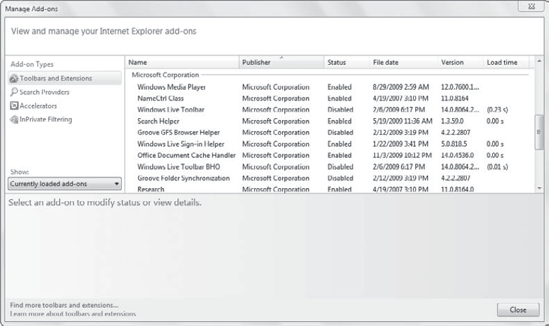
This display shows
another valuable piece of information. On the far right is the Load Time
column. If an add-on is causing problems, it will likely have a long
load time. Unfortunately, only the Toolbars And Extensions screen
includes the Load Time column.
You can launch an instance of IE in No Add-ons mode. Click Start => All Programs => Accessories => System Tools => Internet Explorer (No Add-ons). This will launch a page with text indicating that Internet Explorer is running without add-ons. Launch a regular instance of IE. Select Tools =>
Manage Add-ons. By default, the Toolbars And Extensions add-ons are
shown. You can select any of the add-ons and select Disable. Select
Search Providers. This screen shows the search providers that have been
added to IE. You can choose any of these and select Remove to remove it
completely. You can select one to be the default provider. Select
Accelerators. You can view all of the accelerators that have been added
to IE, disable them, or remove them. If any of the categories includes
more than one accelerator, you can also set one as the default.
|
3. Restore IE Original Settings
Occasionally, the settings
for IE can become changed so much that it is no longer reliable or
secure. This can be due either to a user experimenting with IE or to
modifications from malware.
You can completely reset
all of the IE settings and add-ons. This is a drastic step, but if IE
has become unreliable, it can be very useful.
Select Tools => Internet Options. Scroll
through the settings. The last category of settings is Security. Notice
that some settings are marked with an asterisk (*). If you change these
settings, they will take effect only after you restart IE. If
you want to restore all of the Advanced settings to what they were when
IE was first installed, click Restore Advanced Settings. Click the Reset button. Your display will look similar to the following graphic.
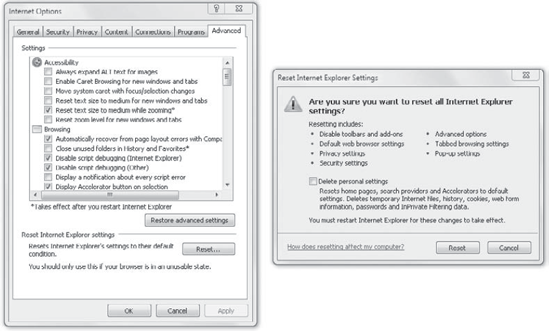
Notice that you can
use this to reset all IE settings. If you select the Delete Personal
Settings check box, IE will be returned exactly to how it was when it
was first installed. This is a drastic step but can be used if IE is no
longer running reliably.
|
4. Disable Add-on Crash Detection
By default, IE
will detect problematic add-ons and automatically disable them. However,
there may be times when you need the add-on to remain functional. This
could be for testing or until a solution is discovered.
If you want to ensure that the add-on is not disabled, you can modify
the following Group Policy setting: Administrative Templates => Windows Components => Internet Explorer => Turn Off Crash Detection. This setting is available in both the User Configuration and the Computer Configuration nodes.
5. Enable Compatibility View
The Hyper Text Markup Language
(HTML) has evolved quite a bit over the lifetime of the Internet.
Although there have been several standards published, not all websites
and even browsers consistently follow the same standards.
If IE detects that a web page is
not being displayed correctly, it will enable the Compatibility View
button on the Address bar. Figure 3 shows where the Compatibility View button appears in IE.

NOTE
The Compatibility View
button is not always available. It appears only when IE detects that the
display may be improved using the Compatibility View. For example, if a
metatag within the page indicates that the page is ready for IE 8, the
Compatibility View button doesn't appear.
When you click the button, IE
will display using compatibility settings. It will also add the site to
the Compatibility View Settings list. You can add and remove sites from
this list by manipulating the Compatibility View Settings. With IE
started, click Tools => Compatibility View Settings or Page => Compatibility View Settings.