3. Branding Internet Explorer
You can brand IE 8 by adding
custom graphics and text to Internet Explorer. The Internet Explorer
Administration Kit 8 (IEAK 8) can be used to customize the appearance of
IE. IEAK 8 allows you create an installation package to complete a full
installation of IE 8 or just modify the settings.
NOTE
The objectives for the 70-686
exam specifically mention branding of IE. You should be aware that the
IEAK can accomplish branding and much more.
Some of the branding capabilities available with IEAK 8 are these:
Use custom graphics in IE such as a company logo.
Customize the browser toolbar button.
Add icons for the Favorites list.
Modify the Autorun splash screen when IE is installed.
You can also modify many of the other settings for Internet Explorer. Figure 5 shows the Feature Selection screen from the IE Customization Wizard 8.
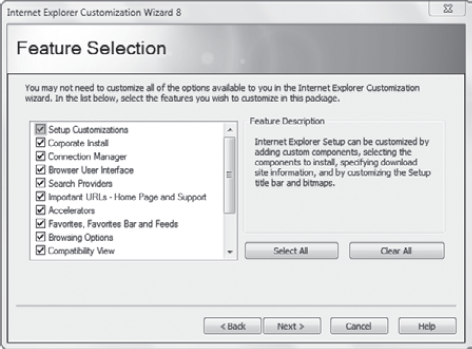
Once you start digging into
the capabilities of the IEAK, you'll soon realize you can do just about
anything that may be needed or desired in corporate network.
This section provided only
a high-level overview of the branding capabilities by using IEAK 8. For
more in-depth details, you can check out full documentation for IEAK 8
at http://technet.microsoft.com/library/cc817437.aspx.
4. Group Policy Settings
Group Policy settings are
applied and how to determine the scope and precedence of a GPO. This
section provides an overview of some of the relevant Group Policy
settings that apply to IE.
One of the great
strengths of Internet Explorer browsers over other browsers is that you
can manage them using Group Policy. If you add third-party browsers to
your network, you lose a significant amount of management capability. It
becomes very difficult to lock down any of the settings and ensure they
stay locked down.
Both the Computer
Configuration and User Configuration nodes have IE settings. Between the
two nodes, there are over 1,200 individual settings for IE.
Figure 6 shows the settings for the Computer Configuration node, and Figure 7
shows the settings for the User Configuration node. Many of the
settings are the same, but you can see that a few of the settings are
different. For example, the Computer Configuration node includes
Corporate Settings.
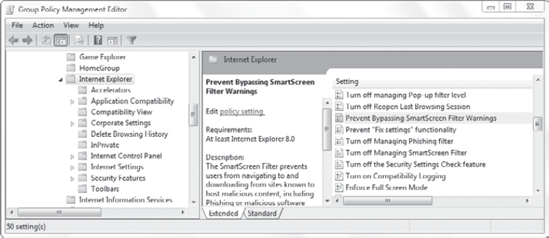
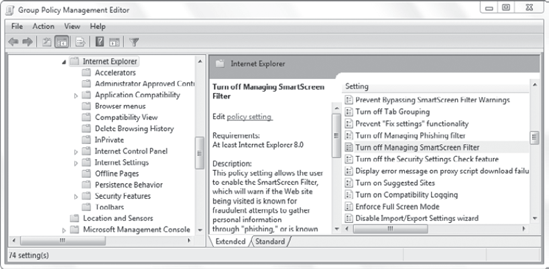
|
If you can't easily find the setting you're looking
for, right-click any node in Administrative Templates and select Filter
Options. Enter a keyword or key phrase such as "crash detection" and
click OK. Only the settings that match the search term will appear.
|
|
You can access these settings via Administrative Templates => Windows Components => Internet Explorer.
The full path for the Computer Configuration node is Computer Configuration => Policies => Administrative Templates => Windows Components => Internet Explorer. The full path for the User Configuration node is User Configuration => Policies => Administrative Templates => Windows Components => Internet Explorer.
On a local user system, you can
use local Group Policy, which can be accessed by clicking Start, typing
Group, and selecting Edit Group Policy. Use this path: Computer
Configuration => Administrative Templates => Windows Components => Internet Explorer or User Configuration => Administrative Templates => Windows Components => Internet Explorer.
Many of these settings apply to
earlier versions of IE. However, some of them apply only to IE 7 and IE
8, which came out with Windows Vista and Windows 7, respectively.
Some of the more notable settings are these:
Delete Browsing History
You can use this node to
control whether users can delete different types of data. Settings that
apply to at least IE 8 are as follows:
Prevent Deleting Cookies
Prevent Deleting Web Sites That The User Has Visited
Prevent Deleting InPrivate Filtering Data
Prevent Deleting Temporary Internet Files
Prevent Deleting Favorites Site Data
Configure Delete Browsing On Exit
Settings that apply to at least IE 7 are these:
-
Turn Off "Delete Browsing History" Functionality
Prevent Deleting Forms Data
Prevent Deleting Passwords
InPrivate
InPrivate mode is new to Windows 7 and IE 8. All of the
settings only apply to IE 8. The following settings are available:
Turn Off InPrivate Filtering
Turn Off InPrivate Browsing
Do Not Collect InPrivate Filtering Data
Disable Toolbars And Extensions When InPrivate Browsing Starts
InPrivate Filtering Threshold
Internet Settings / AutoComplete
This node includes one
setting that applies to at least IE 8: Turn Off Windows Search
AutoComplete. AutoComplete is used to fill in the URL for users.
Internet Control Panel
This node includes
two additional nodes: Advanced Page and Security Page. These settings
allow you to configure a significant number of settings for IE.
Security Features
This node includes
several other nodes that allow you to manage additional security
settings for IE with Group Policy. Combined with the Internet Control
Panel settings, you can configure just about all (if not all) of the
security settings needed for IE.