Database availability
groups (DAGs) provide a high-availability solution without the complexities involved
in deploying failover clustering and a Storage Area Network. In its simplest form,
DAGs are collections of servers that can host up-to-date replicated copies of each
other’s mailbox databases that automatically failover without requiring
complicated cluster configuration. In this lesson, you will learn how to create a
DAG, add servers to the DAG, add and remove mailbox database copies, and configure
database copy lag and failover priority.
1. DAGs
A DAG is a collection of up to 16 Exchange Server 2010 Mailbox servers that
provide automatic mailbox database failover in the event of database, server, or
network failure. DAGs provide Exchange Mailbox servers with high availability
without requiring the expense or complexity of a Storage Area Network. Any
server in a DAG can host a copy of a mailbox database from any other server in
the DAG. DAGs allow for incremental deployment, which means that you can change
which servers are members of a DAG or which mailbox databases are being
replicated without having to re-create the DAG.
The Active Manager is the internal Exchange 2010 component responsible for
managing switchovers and failovers and runs on every server in a DAG. The Active
Manager detects failures of local resources and initiates failover. Active
Manager also forwards information to Client Access servers so that these servers
are aware which server in a DAG hosts the active copy a specific mailbox
database. Exchange administrators do not need to directly interact with the
Active Manager in order to manage DAGs.
2. Create DAGs
The DAG itself is a collection of up to 16 Exchange
Server 2010 Mailbox servers where there is less than a 250-millisecond (ms)
round-trip delay between any two servers. An Exchange Server 2010 organization
can host multiple DAGs, but a server can be a member of only one DAG. You must
create a DAG in the Exchange organization before you add members to the
DAG.
To create a new DAG using the Exchange Management Console (EMC), perform the
following general steps:
Select the Organization Configuration\Mailbox node in the EMC and then
click on New Database Availability Group on the Actions pane. This will
launch the New Database Availability Group dialog box.
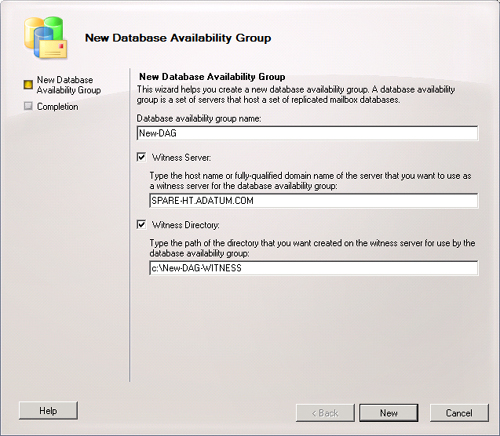
On the New Database Availability Group page, shown in Figure 1, enter a name for the DAG, the fully
qualified domain name of the witness server, and the directory on the
witness server that will be used to store witness data. Click
New.
A DAG name must be unique within the organization and can be up to 15
characters. You can assign an Internet Protocol version 4 (IPv4) or an IPv6
address to the DAG when using the Exchange Management Shell (EMS) or have those
addresses assigned automatically through DHCP, which is the default when you use
the EMC to create the DAG. To create a DAG using the EMS, use the
New-DatabaseAvailabilityGroup cmdlet. For example, to
create a new DAG named DAG-ALPHA with the virtual IP address 10.10.0.100 using
the witness server ht.adatum.com and the directory c:\witness, issue the
following command:
New-DatabaseAvailabilityGroup -Name DAG-ALPHA -DatabaseAvailabilityGroupIpAddresses
10.10.0.100 -WitnessServer 'ht.adatum.com' -WitnessDirectory 'c:\witness'
The witness server should be
a Hub Transport server that does not have the Mailbox role installed. It is
possible to configure other servers to function as DAG witnesses, Microsoft does not
recommend this alternate configuration. Witness servers should have the
following properties:
Witness server cannot be a member of a DAG.
Witness server must be a member of the same Active Directory forest as
the DAG.
Though a single server can function as a witness for multiple DAGs,
each DAG must have a unique witness directory.
If the witness server is not an Exchange Server 2010 server, it is
necessary to add the Exchange Trusted Subsystem universal security group
to the local Administrators group on the witness server.
If you do not specify a witness server during DAG creation, the DAG creation
process will search for a Hub Transport server that does not have the Mailbox
server role installed and will automatically create the default directory and
share, configuring it as the witness server. You can remove a DAG only if the
DAG has no members.
3. Add and Remove Servers from DAGs
Once a DAG exists, you are able to add Exchange Server 2010 Mailbox servers.
You can add a maximum of 16 Mailbox servers to a DAG. Adding a server to a DAG
automatically installs the Windows Failover Clustering feature. You can add a
server to a DAG only if the server’s IPv4 address information includes a
default gateway address.
A server must be running one of the following operating systems:
The Enterprise or Datacenter editions are required because these operating
systems support the Windows Failover Clustering feature. The Standard editions
of Windows Server 2008 and Windows Server 2008 R2 do not support the Windows
Failover Clustering feature. All servers in the DAG must be running the same
operating system. This means that you can have all DAG members running Windows
Server 2008 R2 or Windows Server 2008 with Service Pack 2, but you are unable to
have a mixture of these operating systems.
Perform the following general steps to add a Mailbox server to a DAG:
Select the Organization Configuration\Mailbox node in the EMC.
On the middle pane, select the Database Availability Groups tab and
then select the DAG to which you wish to add Mailbox servers. On the
Actions pane, click on Manage Database Availability Group.
In the Manage Database
Availability Group Membership dialog box, click Add. In the Select
Mailbox server dialog box, select the Mailbox server that you wish to
add to the DAG and then click OK.
You can also use this dialog box to remove servers from a DAG. Instead of
clicking add, select the server that you want to remove from the DAG and then
click on the red X icon to remove it. While you can add and remove DAG members
at any time, you can remove a server from a DAG only if there are no mailbox
database copies hosted on the server.
Use the Add-DatabaseAvailabilityGroupsServer cmdlet to
add a Mailbox server to a DAG. For example, to add the server MBX-ALPHA to DAG
DAG-ONE, issue the following command:
Add-DatabaseAvailabilityGroupServer -Identity DAG-ONE -MailboxServer MBX-ALPHA
Use the Remove-DatabaseAvailabilityGroupServer cmdlet to
remove a Mailbox server from a DAG. For example, to remove the server MBX-BETA
from DAG DAG-ONE, issue the following command:
RemoveDatabaseAvailabilityGroupServer -Identity DAG-ONE -MailboxServer MBX-BETA