The concept of cross-references in Dynamics AX is
simple. If an element uses another element, the reference is recorded.
Cross-references allow you to determine which elements a particular
element uses as well as which elements other elements are using.
Dynamics AX provides the Cross-reference tool to access and manage
cross-reference information.
You must update the
Cross-reference tool regularly to ensure accuracy. The update typically
takes several hours. The footprint in your database is about 1 gigabyte
for the standard application.
You can update the
Cross-reference tool by going to the Microsoft Dynamics AX drop-down
menu and then pointing to Tools\Development
Tools\Cross-reference\Periodic\Update. Updating the Cross-reference tool
also compiles the entire AOT because the compiler emits cross-reference
information.
Tip
Keeping
the Cross-reference tool up to date is important if you want to rely on
its information. If you work in a shared development environment, you
share cross-reference information with your team members. Updating the
Cross-reference tool nightly is a good approach for a shared
environment. If you work in a local development environment, you can
keep the Cross-reference tool up to date by enabling cross-referencing
when compiling. This option does slow down the compilation, however.
Another option is to manually update cross-references for the elements
in a project. You can do so by right-clicking the project, pointing to
Add-Ins, pointing to Cross-reference, and then clicking Update. |
In addition to the main cross-reference information, two smaller cross-reference subsystems exist:
Data model This
cross-reference subsystem stores information about relationships
between tables. It is primarily used by the query form and the Reverse
Engineering tool.
Type hierarchy
This cross-reference subsystem stores information about class and data
type inheritance. It is used only in the Application Hierarchy Tree. The
Application Hierarchy Tree is available from the Microsoft Dynamics AX
drop-down menu, at Tools\ Development Tools\Application Hierarchy Tree.
The cross-reference
information the Cross-reference tool collects is quite complete. The
following list shows the kinds of elements it cross-references.
(Cross-reference information for elements followed by an asterisk is new
in Dynamics AX 2009.) You can find the following list of
cross-referenced elements and their values by opening the AOT, expanding
the System Documentation node, and clicking Enums and then xRefKind.
BasicType
Class
ClassInstanceMethod
ClassStaticMethod
ClrType
ClrTypeMethod
ConfigurationKey
Dataset*
Enum
Enumerator
ExtendedType
Form*
Job*
Label
LicenseCode
Map
MapField
MapInstanceMethod
MapStaticMethod
Menu*
MenuItemAction
MenuItemDisplay
MenuItemOutput
Predefined (system functions)
Query*
Report*
SecurityKey
Table
TableField
TableIndex
TableInstanceMethod
TableStaticMethod
WebActionItem
WebDisplayContentItem
WebForm*
WebManagedContentItem*
WebMenu*
WebModule*
WebOutputContentItem
WebReport*
WebUrlItem
When
the Cross-reference tool is updated, it scans all metadata and X++ code
for references to elements of the kinds listed here.
Tip
It’s
a good idea to use intrinsic functions when referring to elements in
X++ code. An intrinsic function can evaluate to either an element name
or an ID. The intrinsic functions are named <ElementKind>Str or <ElementKind>Num,
respectively. Using intrinsic functions provides two benefits: you have
compile-time verification that the element you reference actually
exists, and the reference is picked up by the Cross-reference tool.
Also, there is no run-time overhead. An example follows. // Prints ID of MyClass, such as 50001
print classNum(myClass);
// Prints "MyClass"
print classStr(myClass);
// No compile check or cross-reference
print "MyClass";
|
|
The primary function of
the Cross-reference tool is to determine where a particular element is
being used. Here are a couple of scenarios:
You want to
find usage examples. If the product documentation doesn’t help, you can
use the Cross-reference tool to find real implementation examples.
You
need to perform an impact analysis. If you’re changing an element, you
need to know which other elements are affected by your change.
To access usage
information, right-click any element in the AOT, point to Add-Ins, point
to Cross-reference, and then click Used By. If the option isn’t
available, either the element isn’t used or that cross-reference hasn’t
been updated.
Figure 1 shows where the prompt method is used on the RunBaseBatch class.
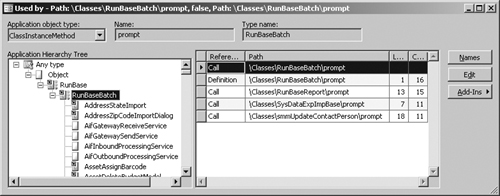
When
you view cross-references for a class method, the Application Hierarchy
Tree is visible, allowing you to see whether the same method is used on
a parent or subclass. For types that don’t support inheritance, such as
tables, table methods, and table fields, the Application Hierarchy Tree
is hidden.