Creating an NLB Cluster
Before an NLB cluster can
be created, a few bits of information are required. The NLB cluster is
actually clustering based on a defined IP address, the DNS name, and the
TCP/IP ports that will be used. Each NLB cluster node can also be
configured with multiple network cards. Each card can be associated with
a different NLB cluster and a single card can support multiple
clusters, but each cluster must have a different DNS name and IP
address(es). One configuration that cannot be performed is creating a
single NLB cluster that uses multiple network adapters in a single node.
To designate multiple adapters for a single NLB cluster, third-party
network teaming software must be loaded prior to configuring the NLB
cluster; the cluster will use the Virtual Team Network adapter and the
teamed physical adapters should not be configured with NLB. For this
example, a new NLB cluster will be created for the name www.companyabc.com using the IP address of 192.168.206.50. To create an NLB cluster, perform the following steps:
1. | Log
on to a Windows Server 2008 R2 system with an account that has local
administrator rights and that has the NLB feature already installed.
| 2. | Click Start, click All Programs, click Administrative Tools, and select Network Load Balancing Manager.
| 3. | When the Network Load Balancing Manager console opens, click the Cluster menu, and select New to create a new cluster.
| 4. | When
the New Cluster window opens, type in the name of the first server that
will be added to the new NLB cluster, and click Connect. If the server
is a remote system and cannot be contacted, ensure that the Inbound
Remote Administration exception has been enabled in the remote system’s
firewall.
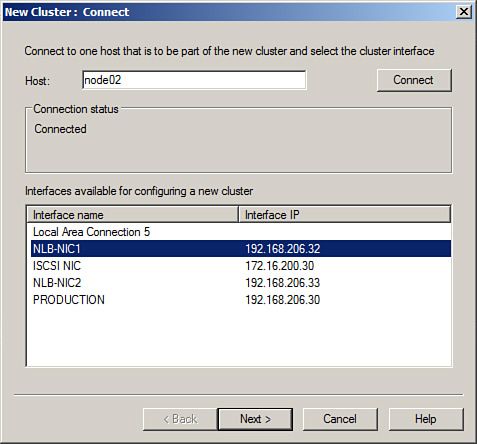
| 5. | When
the server is contacted, each of the network adapters will be listed,
select the adapter that will be used for the NLB cluster, as shown in Figure 1, and click Next.
| 6. | On
the Host Parameters page, accept the defaults of giving this first
server the Host ID of 1 and select the dedicated IP address that will be
used when communication is received for the NLB cluster IP address,
which will be specified next. Click Next to continue.
| 7. | On
the Cluster IP Addresses page, click the Add button to specify an IPv4
address and subnet mask or an IPv6 address to use for the NLB cluster,
and click OK. For our example, we will use the IPv4 configuration of
192.168.206.50/255.255.255.0.
| 8. | Back on the Cluster IP Addresses page, add additional cluster IP addresses as required, and click Next to continue.
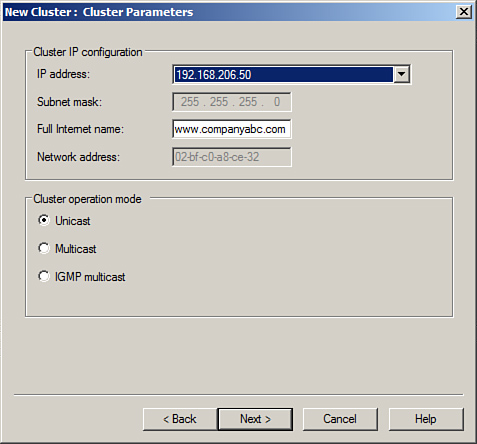
| 9. | On
the Clusters Parameters page, enter the fully qualified DNS name that
is associated with the IP address specified on the previous page, and
select whether it will be used for Unicast traffic, Multicast traffic,
or IGMP Multicast. This choice depends on the network communication of
the service or application that will be used in this NLB cluster. For
this example, we are creating an NLB cluster for standard web traffic,
so we will use www.companyabc.com as the Internet name and select Unicast as the cluster operation mode, as shown in Figure 2.
| 10. | If
multiple IP addresses were defined on the previous page, the IP address
can be chosen from the IP address drop-down list, and the Internet name
and cluster operation mode can be defined for each additional address.
When all the IP addresses have had their properties defined, click Next
to continue.
| 11. | On
the Port Rules page, a default rule is precreated that allows all
traffic on all ports to be load-balanced across the NLB cluster between
the cluster IP address and the dedicated IP address of the local
server’s dedicated IP address. Select this rule and click the Remove
button to delete it.
| 12. | Click the Add button to create a new port rule.
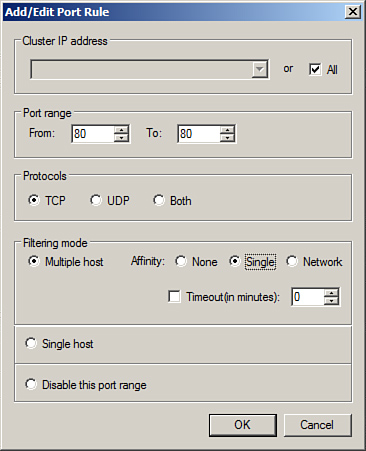
| 13. | When
the Add/Edit Port Rule window opens, type in the starting and ending
port range, for example 80 and 80 for a single HTTP port rule, but do
not close the window.
| 14. | Under protocols, select the TCP option button, but do not close the window.
| 15. | In the Filtering Mode section, select Multiple Host, and select Single Affinity, but do not close the window.
| 16. | Finally, review the settings, and click OK to create the port rule, as shown in Figure 3.
| 17. | Back on the Port Rules page, click the Add button to create an additional port rule.
| 18. | Specify
the starting port as 0 and the ending port as 79, select Both for the
protocol’s configuration, select the Disable This Port Range Filtering
mode, and click OK to create the rule.
| 19. | Back in the Port Rules page, click the Add button to create one more port rule.
| 20. | Specify
the starting port as 81 and the ending port as 65535, select Both for
the protocol’s configuration, select the Disable This Port Range
Filtering mode, and click OK to create the rule.
| 21. | Back on the Port Rules page, review the list of port rules and if the rules look correct, click Finish.
| 22. | Back
in the Network Load Balancing Manager window, the cluster will be
created and brought online. The cluster IP addresses are automatically
added to the TCP properties of the designated network adapter. Close the
NLB Manager and log off of the server.
|
Adding Additional Nodes to an Existing NLB Cluster
After an NLB cluster is
created, additional nodes can be added to it. To add nodes to an
existing cluster, perform the following steps:
1. | Log on to the Windows Server 2008 R2 system with an account that has local administrator rights.
| 2. | Click Start, click All Programs, click Administrative Tools, and select Network Load Balancing Manager.
| 3. | When the Network Load Balancing Manager console opens, click the Cluster menu, and select Connect to Existing.
| 4. | When
the Connect page opens, type in the hostname of a cluster node in the
cluster that will have nodes added to it. For this example, the hostname
is NODE02. Type in NODE02 and click Connect to retrieve a list of all
NLB clusters running on the specified host.
| 5. | In the Clusters section of the Connect page, select the cluster that will be loaded into the management console, and click Next.
| 6. | Back
in the Network Load Balancing Manager window, in the tree pane, select
and right-click the cluster, and select Add Host to Cluster.
| 7. | When
the Connect page opens, type in the hostname of the Windows Server 2008
R2 system that will be added to the cluster, and click Connect.
| 8. | After
the system is connected, a list of all of the available network
adapters is shown. Select the desired adapter to use for the NLB
cluster, and click Next.
| 9. | On
the Host Parameters page, review the details of the page, and click
Next to continue. The default settings should be sufficient unless the
Host ID needs to be changed or if multiple IP addresses are already
bound to the adapter; select the desired IP address to use for dedicated
NLB cluster communication, and click Next to continue.
| 10. | On
the Port Rules page, the existing port rules for the cluster are
listed. Unless this node will handle different traffic on this cluster,
accept the defaults and click Finish.
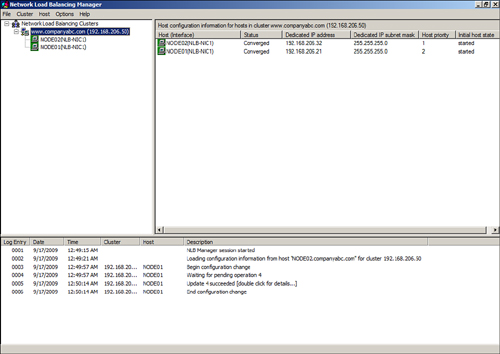
| 11. | The
node will be added to the cluster and if the node addition is
successful, both nodes will be listed under the cluster with a green
background, as shown in Figure 4.
| 12. | Close the Network Load Balancing Manager and log off of the server. |
|