In this section, we will
discuss how the File Server Resource manager (FSRM) can be used to
provide additional features such as quotas, file screens, reporting, and
file classification services to your Windows file servers. The File
Server Resource Monitor first appeared in Windows Server 2003 and has
been carried on to Windows Server 2008 R2 adding new features along the
way. FSRM is an additional role service for the File Server role and can
be installed via Server Manager as seen in Figure 1.
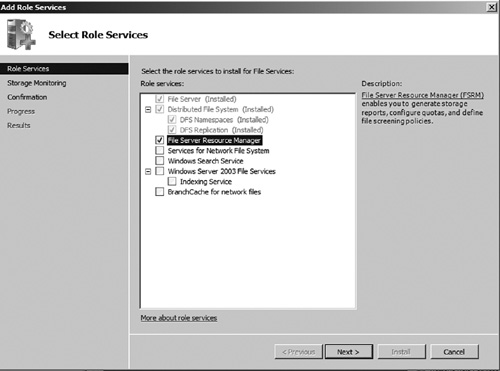
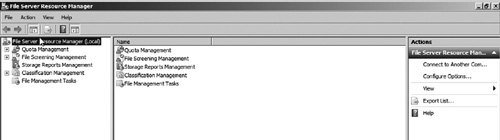
After the role service has been installed, the FSRM management console can be accessed via the Start Menu by selecting Start | Administrative Tools | File Server Resource Manager. As seen in Figure 2, the FSRM console is organized into five main sections:
Quota Management
File screening management
Storage reports management
Classification management
File management tasks
Quota management
Quota management allows administrators to allot soft
and hard quotas on folders within a volume. By using quotas, each user
is restricted to consuming a limited amount of disk space for a given
folder. This limit can be soft, meaning that the user is only warned
that they are exceeding their quota but will still be allowed to save
the file or the limit can be a hard quota, meaning that the user is not
allowed to save additional data to the folder once he has reached his
quota limit. Additionally, FSRM can e-mail users and administrators
informing them that they have exceeded their quotas. For example, you
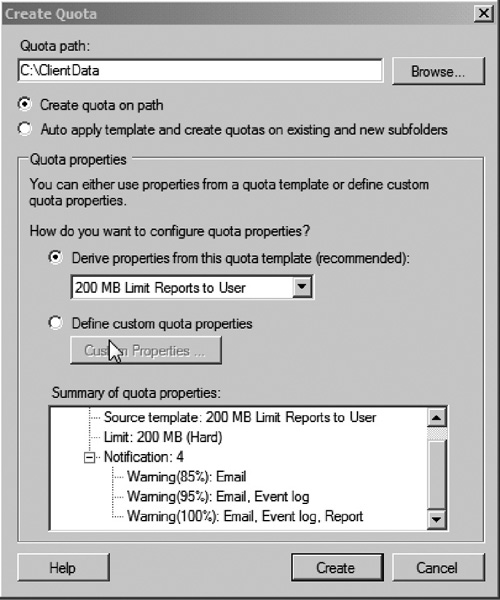
might want to set a 200-MB quota on the client data folder. You can use
FSRM to create a new quota on the path C:\ClientData and use the
predefined template 200 MB limit Reports to Users. This template will
limit each user to saving a maximum of 200 MB to the ClientData shared
folder and e-mail them warnings at 85%, 95%, and 100% quota usage levels
as seen in Figure 3.
|
Quota e-mail notifications
FSRM uses the E-mail Address field from Active
Directory user accounts to send users e-mail alerts regarding their
quota usage. If you do not populate this field with each user’s correct
e-mail address, they will not receive quota notifications.
|
File screening management
File screens allow
administrators to restrict the types of files saved to folders. For
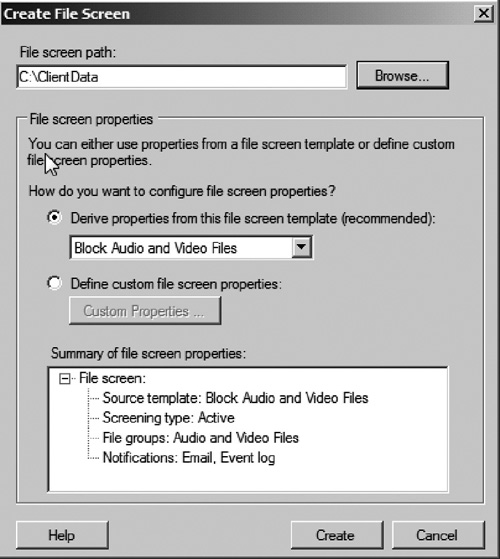
example, you may wish to prevent users from saving personal music files
such as MP3s to shared folders (see Figure 4).
File screens look at the file extension to determine whether the file
is allowed to be stored in a specific folder. Like quotas, FSRM can send
e-mail notifications to users if they attempt to violate a file screen
policy. FSRM file screening management comes with a few predefined
templates with common file extensions. You can also create your own
customized templates to meet your own needs. File screens can be set up
in active or passive mode. Active mode will prevent the restricted file
types from being saved to the folder, while passive mode only monitors
restricted file types.
Storage reports
FSRM provides some basic storage reporting for Windows file servers. These reports can be run ad hoc
or set to run on a scheduled basis. Additionally the reports can
automatically be e-mailed to administrators when they are generated.
FSRM provides nine report types. They are defined in Table 1.
Table 1. File Server Resource Manager Storage Reports
| Report | Definition |
|---|
| Duplicate files | This report will display all the files in the volume or folder that have duplicate copies. |
| File screening audit | This report will display all the files that violate a file screen for a folder or volume. |
| Files by file group | This report will display files and file counts by their group type such as text files, office files, image files, etc. |
| Files by owner | This
report displays files created/saved by the owner. This allows
administrators to easily identify users who are saving large amounts of
data on the file server. |
| Files by property | This
report displays files and file counts by their property values. This
helps identify specific property types that may be using large amounts
of disk space. |
| Large files | This
report will display files that are considered large. The minimum size
file is configurable with 5 MB being the default size to include in the
report. |
| Least recently accessed files | This
report will display the files in the folder or volume that have gone
the longest period without being accessed. This report provides
administrators a good way to review files that have not been accessed
for a long period of time. |
| Most recently accessed files | This
report will display files that have gone the shortest period of time
without being accessed. This report provides administrators the ability
to review files that are being used on a regular basis. |
| Quota usage | This
report will display quotas that exceed a specified disk space usage
level. This report includes a list of all users who have saved files in
the folder or volume and how much of their allocated quota they have
used. |
Classification management
Classification management is a new feature in Windows
Server 2008 R2 that can be used to classify files based upon rules or
folders in which they are stored. Using classification management, you
can provide better records management for files on your network.
File management tasks
File
management tasks is a new feature introduced with the release of Windows
Server 2008 R2. Using file management tasks, administrators can set up
scheduled operations to scan volumes and folders on file servers and
review specific file properties. Based upon rules defined for the
properties, the scheduled task can then move the file to a folder where
it can be archived, or custom command can be performed on the file. A
great example of using a file management task would be to move any files
not accessed in the last 180 days to an archive folder. An
administrator could then back up the archive folder and delete the files
from the server. This is known as a file expiration task. Additionally,
the file expiration task can e-mail a notification to the owner of
files that are about to be moved to the archive folder.