Scenario/Problem: Your company has an empty OU that is no longer required.
Solution: Delete an OU by using the Windows interface or the command line.
Delete an Organizational Unit by Using the Windows Interface
To delete an OU by using the Windows interface, perform the following steps:
1. | Log on to a domain controller or a member computer that has Windows Server 2008 RSAT installed.
|
2. | Click Start, click Administrative Tools, and then click Active Directory Users and Computers.
|
3. | In the console tree, right-click the OU you want to delete and select Delete.
|
4. | On the confirmation screen to delete the OU, shown in Figure 1, click Yes.
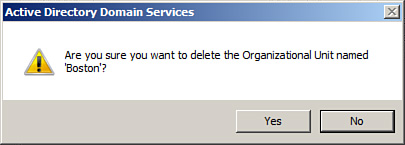
|
In
Windows Server 2008, the option to protect an OU from accidental
deletion is selected by default when the OU is created using Active
Directory Users and Computers. If you need to delete an OU, you must
ensure that the object is not protected from accidental deletion before
it can be deleted.
Delete an Organizational Unit by Using the Command Line
To delete an OU by using the command line, perform the following steps:
1. | Log on to a domain controller.
|
2. | Click Start, and click Command Prompt.
|
3. | In the Command Prompt window, type the following command and press Enter:
Dsrm "OU=Boston,DC=WS08DOMAIN01,DC=local"
(where "OU=Boston,DC=WS08DOMAIN01,DC=local" is the distinguished name of the OU you want to delete).
|
4. | Type Y on the confirmation to delete the OU and press Enter.
|
5. | Verify that the results of the dsrm command entered above returns dsrm succeeded, as shown in Figure 2.
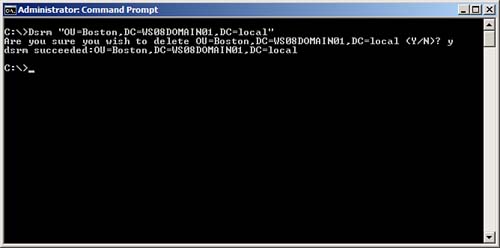 |