Create an InfoPath 2010 Add-In
You may use Visual Studio
2010 to create an InfoPath 2010 add-in that can be used within
InfoPath. The add-in is an application-level add-in that customizes the
InfoPath Designer experience. Two common uses of an InfoPath add-in are
to customize the ribbon and generate a custom task pane.
To create an InfoPath 2010 add-in, follow these steps:
1. | Launch Visual Studio 2010.
|
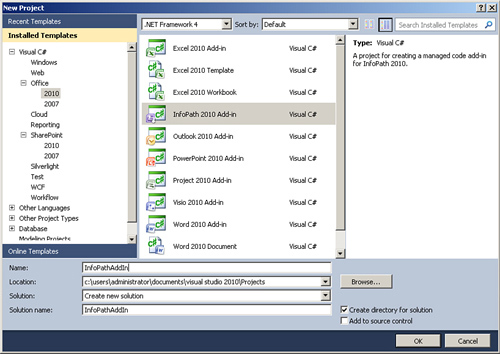
2. | Click File, New, Project. The New Project dialog appears.
|
3. | Navigate to Office, 2010 from the left-side Installed Templates navigation.
|
4. | Select the InfoPath 2010 Add-In project template, as shown in Figure 1.
|
5. | Click OK.
|
6. | Add user controls or classes as appropriate; see the next section for an example.
|
7. | Build the add-in project. The add-in is generated.
|
8. | Open InfoPath Designer 2010.
|
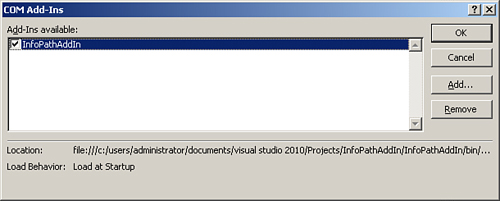
9. | Click the COM Add-Ins button on the Developer ribbon. The add-in is available and installed, as shown in Figure 2
|
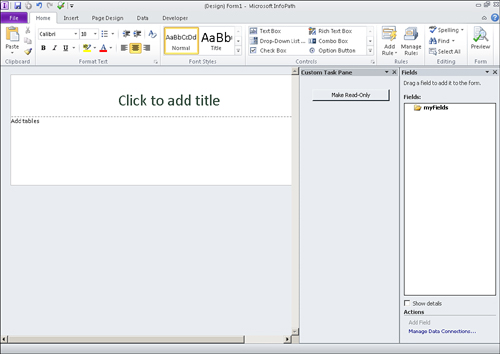
Create a Custom Task Pane
To create a new task pane, follow the steps for creating a new InfoPath 2010 add-in. Then perform these steps:
1. | Add a user control to your project.
|
2. | Add windows controls to your user control as needed. In this example, a user control named CustomTaskPaneControl is used.
|
3. | Add any code to handle options or selections.
|
4. | In the ThisAddIn class, add private variables to handle the user control and custom task pane, as shown in Listing 3.
|
5. | In the startup method of the ThisAddIn class, add code to instantiate the user control as a custom task pane, as shown in Listing 4.
Listing 3. Private Declarations
private CustomTaskPaneControl customTaskPaneControl;
private Microsoft.Office.Tools.CustomTaskPane customTaskPane;
|
Listing 4. Custom Task Pane Instantiation
customTaskPaneControl = new CustomTaskPaneControl();
customTaskPane = this.CustomTaskPanes.Add(customTaskPaneControl, "Custom
Task Pane");
customTaskPane.Visible = true;
|
|
6. | Build the project, and then launch InfoPath Designer 2010. The custom task pane appears as shown in Figure 3.
|