Changing DCHP Server Status
You can use various tools
to start or stop the DHCP Server service: the DHCP console, the
command-line interface, and the Services console.
DHCP Console
Within the DHCP
console, the Action menu that appears when the server icon is selected
contains an All Tasks submenu that includes the options Start, Stop,
Pause, Resume, and Restart. This same Action menu and All Tasks submenu
also appear in the DHCP console when you right-click the DHCP server
icon.
To start or stop a DHCP server, complete the following steps:
1. | Open the DHCP console.
|
2. | In the console tree, select the applicable DHCP server.
|
3. | On the Action menu, point to All Tasks and then select one of the following:
To start the service, select Start. To stop the service, select Stop. To interrupt the service, select Pause. To continue a service after it has been paused, select Resume. To stop and then automatically restart the service, select Restart.
|
Command-Line Interface
You can also start,
stop, pause, and resume the DHCP Server service by executing the
following commands, respectively, at the command prompt.
Net Start Dhcpserver
Net Stop Dhcpserver
Net Pause Dhcpserver
Net Continue Dhcpserver
Services Console
The Services
console is a graphical administration tool that you can open by clicking
Start, selecting Administrative Tools, and then clicking Services. To
access controls for the DCHP Server service, double-click the DHCP
server node in the list of services in the details pane. This procedure
opens the DHCP Server Properties dialog box, shown in Figure 1.
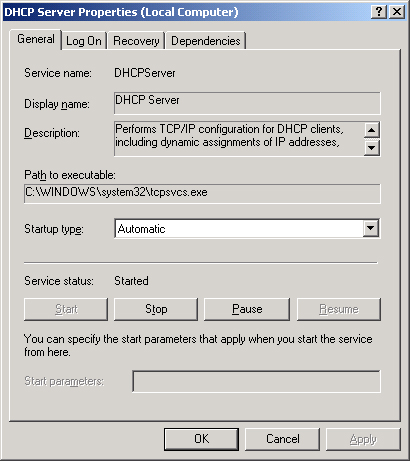
The
Services console offers an important addition to the Start, Stop,
Pause, and Resume controls available in both the DHCP console and the
command-line interface. In the Startup Type drop-down list, you can
select the Disabled option. When this option is selected, the service
cannot be started until the setting is changed. This setting is useful,
for example, when you need to move a DHCP database to another computer
and you want to ensure that the old server remains stopped even after
you perform the migration.
Note
If the service is running when you select the Disabled option, the setting applies after the next shutdown. |
Managing DHCP from a Command Line
Windows Server 2003
includes the Netshell (Netsh) command-line environment, which provides
an interface from which you can manage many functions and features of
your server. The Netsh commands for DHCP make up a fully equivalent
alternative to console-based management. Using this command-line tool
can be useful in the following situations:
When managing
DHCP servers in WANs, you can use commands at the Netsh command prompt
to perform administrative tasks across slow-speed network links.
When
managing a large number of DHCP servers, you can use commands in Batch
mode to automate recurring administrative tasks that need to be
performed for all DHCP servers.
To enter the Netsh
command-line environment, you simply execute the Netsh command at a
command prompt. This procedure opens the Netsh> prompt. To access the
DHCP administration interface, execute the DHCP command at the
Netsh> prompt to enter the dhcp context. This process is illustrated
here:
C:\>netsh
netsh>dhcp
netsh dhcp>
Note
You
do not need to step gradually into the various levels of Netsh prompts
to execute a Netsh command. For example, to view a DHCP server
configuration summary, you can simply open a command prompt and type the
following in one line: netsh dhcp server show all.
However, entering each context separately allows you—through the use of
the Help, List, or ? commands—to view a list of commands available
within each context. |
Although
the Netsh dhcp> prompt allows you to add, delete, and view DHCP
servers on your network, many more DHCP management controls are
accessible through the Netsh dhcp server> prompt and the Netsh dhcp
server scope> prompt. To access the Netsh dhcp server> prompt,
simply execute the Server command at the Netsh dhcp> prompt. To
access a Netsh dhcp server scope> prompt, enter the Scope <scope IP address> command at the Netsh dhcp server> prompt. This process is illustrated here:
netsh>dhcp
netsh dhcp>server
netsh dhcp server>scope 192.168.0.0
Changed the current scope context to 192.168.0.0 scope.
netsh dhcp server scope>
At any given prompt,
you should use the Help, List, or ? command to view the full list of
commands available within each context. To learn about usage associated
with any particular command, you can use the Help, List, or ? command
after any given command. For example, to learn about the options
available with the Set command, you can enter set help at a prompt within any Netsh context.
You can also use Windows Server 2003 online help to learn more about the Netsh utility.
Note
To
manage a DHCP server by using the Netsh command line, you must be
logged on as a member of either the local Administrators group or the
local DHCP Administrators group on the applicable server computer. |
To use DHCP commands interactively at the command prompt, complete the following steps:
1. | Open a command prompt.
|
2. | Enter netsh.
|
3. | At the Netsh> command prompt, enter dhcp.
|
4. | At the Netsh dhcp> command prompt, enter either server <\\servername> or server <ip_address> for the server you want to manage. To manage the local server, simply type server.
|
5. | Once connected, you can use any supported Netshell command for DHCP.
Type /? or help to display the immediate DHCP subcommand menu, or enter list to list all Netshell subcommands available for use with DHCP.
|