Software Restrictions
The next major area of GPO category is in Software
Restrictions. These GPOs are used to deny all executables except those
specifically allowed using the Restricted Default Rule, or used to allow
all executables and then disallow specific executables using the
Unrestricted Default Rule. These GPO settings are located in the GPO
under Computer Configuration > Windows Settings > Security
Settings > Software Restriction Policies.
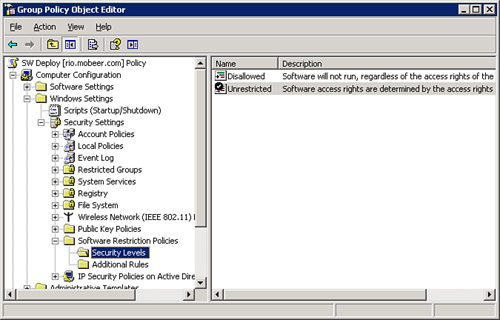
By default, the
execution of applications is configured as Unrestricted, as shown in Figure 3. Application execution is intended to be
controlled by the access permissions (share and NTFS) of the user on the
executable.
You can configure permissions to keep users from
executing applications. You need to do this on each computer where the
application resides, a huge task in a large environment. Or you can do
it much more easily and on a larger scale by creating a GPO with
Software Restriction Rules and then link them appropriately.
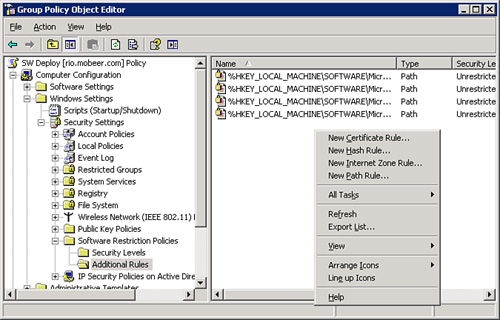
Four types of Software
Restriction Policy Rules can be used to modify the Default Rule:
Certificate Rule— A digital signature embedded within the
executable file.
Hash Rule— A numeric
fingerprint of the executable file.
Internet Zone Rule—
From tab. They include Internet, Local Intranet, Trusted Sites, and
Restricted Sites.
Path Rule— The
local path or UNC path to the executable file.
These rules are shown in Figure 4.
These rules often get
applied in combinations, and it can get tricky to figure out which GPOs
will effectively restrict which applications. As GPOs get processed on
the computer, the Software Restriction GPOs are evaluated and then are
prioritized in the following order:
1. | Certificate
Rule—Strongest
|
2. | Hash Rule
|
3. | Path Rule
|
4. | Internet Zone Rule
|
5. | Default Rule—Weakest
|
Exam
Alert
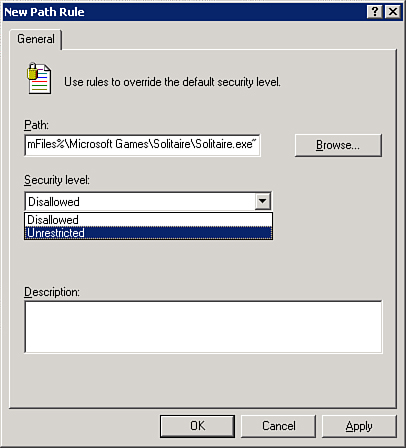
If an application fails to run due to Software
Restrictions, you might need to add a new Unrestricted Rule of higher
priority. An example would be that your OU is configured with a Default
Rule set to Restricted. For any application to run, you must configure
an Unrestricted Rule of higher priority, such as a Path Rule, as shown
in Figure 5.
Alert
With
Path Rules, you may use wildcards within the path statement itself.
The
more specific the path, the higher priority it receives when there is a
conflict between Path Rules. You can use a single question mark to
represent a wildcard for a single character, one question mark per
character, or you can use an asterisk as a wildcard to represent any
number of characters in the path statement.
For
example, the use of \\Server?? in a
Path Rule would satisfy all servers named \\Server00 through \\Server99,
as well as \\Serveraa through \\ServerZZ. The use of the asterisk as a wildcard in a Path
Rule might look like *.vbs, to allow or
restrict all VBS scripts wherever they may be located.