Troubleshooting
Updates
Automatic updates can fail for
many reasons. We’re going to look at a few of the more common failures
here and address how to recover from them to get the automatic update
process running again.
Time Synchronization
To authenticate the client
computer to the server computer, client requests typically use either
Kerberos tickets or digital certificates.
If the clock on the client
computer is too far out of sync from the intranet-based update server,
the Kerberos ticket mechanism that provides authentication services
between the client and resource server (in this case, the intranet-based
Windows Server Update Services server) fails. These Kerberos tickets
typically have only a five-minute lifetime. If the clocks on the client
and the resource server are out of sync, the just-issued ticket could be
expired already! The client would not be authorized to perform the
download of the updates from the intranet WSUS server because he
presented an expired Kerberos ticket to authenticate himself.
In the more extreme case of
the clocks being out of sync, the digital certificates used between the
client and the Internet-based Windows Update server at windowsupdate.com cause the certificate validation check to
fail, which also causes the client download of the updates to fail.
In both of these cases,
the solution is simple. Be sure your computer’s date and time are
synchronized to an Internet-based time server so that the client
computer’s clock agrees with the update server’s clock.
You can adjust the clock
manually or have it synchronize with its time master in the Clock,
Language, and Region applet in the Control Panel.
Corrupted Update Files
in the Updates Store
The Background
Intelligent Transfer Service (BITS)—currently version 3.0 in Windows
Vista—must be installed and be running on the WSUS server as well as the
WSUS client computers. Even though Windows Update uses BITS to help
with the downloading of updates to the client, periodically a downloaded
file may get corrupted in this process. This corrupted file can cause
the Windows Update download processes to stop working.
To get the Windows
Update download processes running again on the client computer, you may
have to remove from the client computer the update files that have been
downloaded.
If the Windows Update
system stalls, the first thing to try is to simply delete all temporary
files located in the two folders holding the update files that have been
downloaded. These may be the corrupted files causing the download
process to fail.
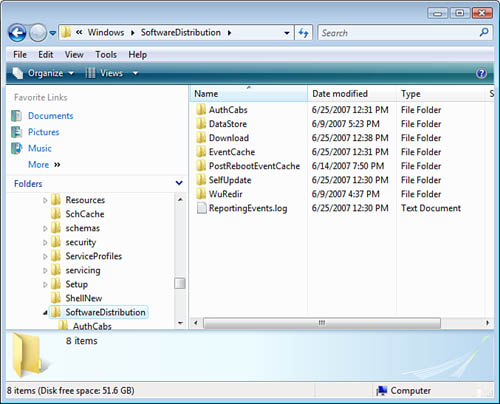
The two folders that hold the
update files are \Windows\SoftwareDistribution\DataStore (that holds the logs of updates) and \Windows\SoftwareDistribution\Download
(that holds the actual *.cab update files), as shown in Figure 6.
With the corrupted files gone,
the next time the update process initializes, the update process will
regenerate local files as required and then can restart downloading the
required updates.
If this first approach
doesn’t solve the problem, and the Windows Update system remains
stalled, the area of corruption may be in different folders than the Download
and DataStore folders. To perform a
more complete “refresh” of the update files, you need to perform the
following steps:
1. | Using the Services applet in the Computer
Management console, stop the Windows Update service by right-clicking it
and selecting Stop, as shown in Figure 7.

|
2. | Rename the
\Windows\SoftwareDistribution folder to \Windows\XXXSoftwareDistribution.
|
3. | Start the Windows Update service in the Services
applet.
|
This should cause the \SoftwareDistribution folder to be regenerated, and then the
Windows Update service will get a fresh start on the update process.