A firewall
is a service on a computer or a device that isolates your computer from
unsolicited network traffic and can be used to control the type and
destination of outbound traffic sent from your computer.
Included with Windows Vista is
your very own personal firewall called Windows Firewall. Windows
Firewall acts as a boundary between your computer and the networks that
your computer connects to.
By default, the
Windows Firewall restricts almost all inbound traffic and notifies you
of almost all your outbound traffic. Because you may have several
different network interfaces on your computer, like a wired connection, a
wireless connection and even a modem, you may be connected to different
networks on these different network interfaces. Windows Firewall can be
configured differently on each of your network interfaces.
You may also connect your
computer to different locations, like your network at home, to the
Internet at a hotspot in a café, or to the network at your job. Windows
Firewall provides different profiles for these three different types of
networks that you may connect to. This allows for a great deal of
flexibility and control as to how your computer will interact with
different networks, using different network interfaces.
Tip
Firewalls typically
default to deny all traffic, both inbound and outbound, and then you
must configure exceptions, or allow rules, to permit traffic through the
firewall. These would be manually configured exceptions through your
firewall.
In addition to the
manually configured exceptions that allow traffic to flow to and from
your computer, as you enable services on the computer, the Windows
Firewall automatically adjusts itself to accommodate the desired
services. As you enable Remote Administration on the computer, for
example, Windows Firewall typically opens the correct ports (in this
case, port 3389) to allow the enabled service to function properly.
Exam Alert
If
you have a service enabled and it is not functioning properly, always
remember to double-check that the proper exceptions/ports have been
opened on the firewall.
You can customize Windows
Firewall by creating exceptions to the default “Blocked” configuration.
This “Allowed” traffic can be configured based on standard network
services provided by Windows Vista. Manually configured exceptions can
also be created based on the program, on the port number, or on the
protocol you want to allow.
Caution
A Word About Firewall Exceptions
Creating exceptions on a firewall is a potentially risky thing to do.
These exceptions must be carefully considered before implementation.
Every exception is a doorway for a bad guy to break into and compromise
your computer system. Generally speaking, the fewer openings in a
firewall, the stronger the security of the system. Implement exceptions
only when you really need to and after you’ve considered the potential
exposure.
You can access these settings
by opening the Network and Sharing Center from the Control Panel. In the
left pane you should see a hyperlink to Windows Firewall. Once there,
you can select the Change Settings hyperlink.
Tip
You also can access the Windows Firewall through the Windows Security Center or through the Control Panel > Security > Windows Firewall.
Alert
The General tab allows you to turn the firewall on, off, or to block all incoming connections, as shown in Figure 1.
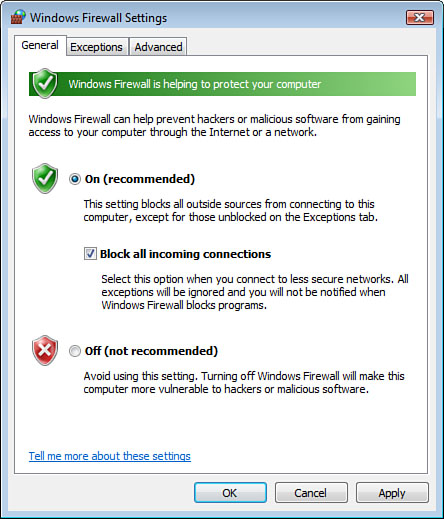
Caution
It is not recommended to turn
off the Windows Firewall unless you are running another firewall
application on the computer. This individual system firewall is
typically used in addition to enterprise network infrastructure
firewalls.
As stated earlier, an
exception is an opening in the firewall that allows a specified type of
network traffic through the firewall. On the Exceptions tab of the
firewall’s properties, you can select a program to be allowed through
the firewall, as shown in Figure 2.
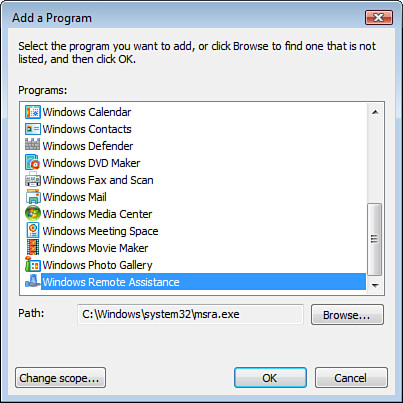
On the Advanced tab of the
firewall’s properties, you can enable or disable the firewall for each
network interface on the computer. This is also the place where you can
also reset the firewall’s settings back to their original default
configuration if you have lost track of the configuration changes you’ve
made to the firewall.
Caution
It is not recommended to disable
the firewall on any network interface. This would only be done under
rare circumstances, and only after careful consideration of the security
risks involved with such a configuration setting.
Windows Firewall with Advanced Security
For
a more granular level of control over the firewall, you can launch the
Windows Firewall with Advanced Security. You can locate this by clicking
Start > All Programs > Administrative Tools > Windows Firewall with Advanced Security.
The Windows Firewall
with Advanced Security provides notably more detail in the configuration
of the Windows Firewall. In this tool, Windows Firewall with Advanced
Security, you can fine-tune the firewall based on the three different
network profiles—Domain, Private, and Public—as well as individually
configure inbound rules and outbound rules, again based on program, port
number, or protocol.
You would configure the
Domain network profile to be active when your computer is connected to
the corporate network. The Private network profile should be used when
you are connected to your home network, and you should use the Public
network profile, the most restrictive profile, everyplace else.
Alert
The
Public network profile is the most restrictive profile. You want this
heightened security setting when you connect to networks that you don’t
know or don’t trust, like at a Starbucks or at an airport.
By selecting the Properties
link in the right pane, you can select to enable or disable the
firewall in each of these network profiles. For each of these network
connections, you can also configure Inbound Rules and Outbound Rules
based on program, port number, or windows services, or you can build
your own custom firewall rule, as shown in Figure 3.
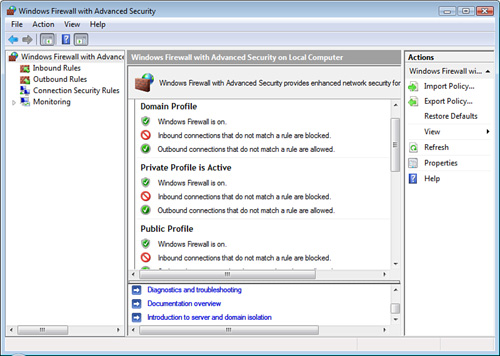
These more sophisticated
firewall rules and configuration available in the Windows Firewall with
Advanced Security are usually planned, designed, and implemented by
computer-savvy individuals with specialized needs and skills, or by
network administrators on the corporate network. For the typical home
user, the default firewall settings are usually acceptable, and the
Windows Firewall with Advanced Security is rarely used.
Alert
You
generally want the firewall enabled on each network interface, unless
you are connected to a well-trusted network, like a well-secured
corporate network.