Windows Server Update
Services Server (WSUS)
In a corporate environment, with dozens,
hundreds, or even thousands of client computers, administrators need
more control over the updating system. Microsoft provides, free of
charge, the Windows Server Update Services (WSUS)
server. At the time of this writing, the latest version of WSUS was
version 3.0.
This service allows an
administrator to download all updates to a corporate WSUS server, so
only one copy of each update must be downloaded for the company, not a
copy for each client. After the updates are downloaded, the
administrators can test each one to avoid hardware and software
conflicts and then can approve the update for distribution to the client
computers. The distribution of updates to the client can be fine-tuned
by organizing the computers into groups, based on hardware, software, or
any other consideration, like security level. Different updates can be
approved for different computer groups. The WSUS service also monitors
the delivered updates and logs, which computers successfully received
and installed which updates.
Clients are then configured
to download their updates from their local intranet WSUS server. This
minimizes bandwidth consumption by downloading updates once to the WSUS
server, instead of downloading a copy of every update for every client.
Another tool to aid this
process in the corporate environment is Active Directory and the
powerful GPO. The client’s updated system can be completely configured
by GPO. This overrules any settings that may have been configured on the
client computer, and it disables any further local configuration of the
update system.
Alert
Some
of the more important client settings that can be configured by GPO for
the WSUS systems are as follows:
Enable automatic updating, with options for various levels
of automatic updates, as shown in Figure 4
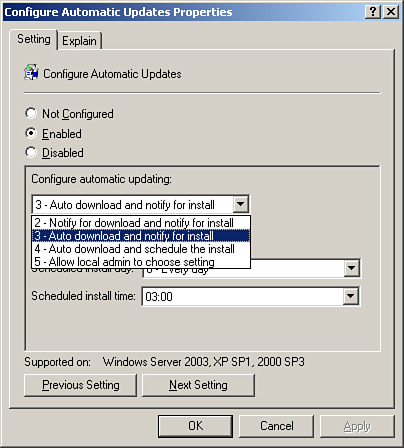
When to
install the updates, as shown in Figure 4
Which
intranet WSUS server to pull downloads from, as shown in Figure 5
(intranet update service for detecting updates)
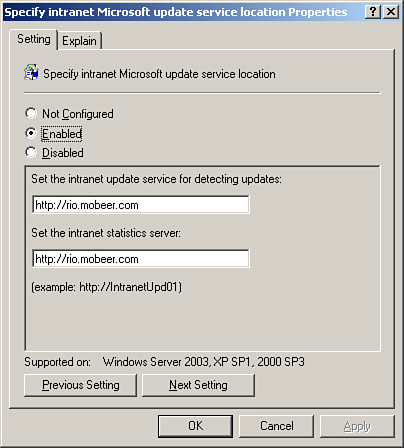
Which intranet WSUS server to report statistics to,
as shown in Figure 5 (set the intranet statistics server)
Assign
the computer to a WSUS Computer Group for approval of updates to
specific groups of computers
Auto-reboot configuration,
after update installation if the update requires a system reboot
and
more!
WSUS uses the
Internet Information Services server to deploy the updates. To increase
security for the update system, you can configure the WSUS website to
use HTTPS, which is HTTP over SSL, an encrypted channel between the
website and the client. You could also configure a VPN, such as IPSec,
to secure this communication.
While
the client’s firewall is probably already allowing traffic over port
443 for SSL, it probably is not allowing UDP port 500 for an IPSec
tunnel. If you did have an IPSec VPN between the client computer and the
WSUS server, you would need to configure an exception on the client’s
firewall to allow this IPSec traffic that is carrying the updates.