Securing Network
Traffic for Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) Access
IPSec is used to
secure network traffic between client and server computers, typically on
the corporate LAN, or over the Internet between two LANs.
You also need to protect
traffic when you connect to a computer using the Remote Desktop Protocol
(RDP). RDP, which runs over port 3389, allows you to connect to an RDP
server as if you were sitting in front of the local console on the
remote server.
Alert
A
Windows Vista computer can be the RDP server. This must be enabled on
the Remote tab of the System properties, as displayed in Figure 9.
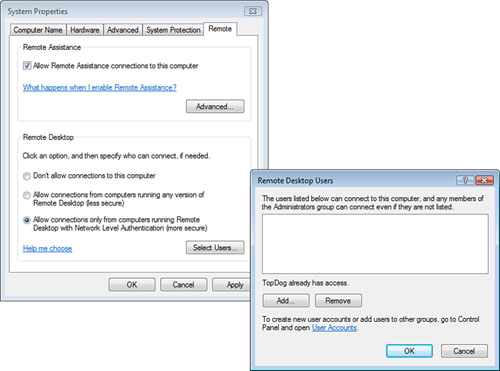
By clicking Select Users, you
can add users to the Remote Desktop Users group.
RDP traffic is encrypted
by default, and the RDP client must authenticate to the RDP server.
However, the strength of the encryption can be increased, and mutual
authentication of RDP client and server can be implemented. You do this on a Windows
Vista computer in the Local Security Policy or by GPO in an Active
Directory environment.
To set a required
encryption strength, you configure the Set Client Encryption level
setting.
The available settings are as follows:
High Level— Requires the use of 128-bit keys for
encryption. If the RDP server cannot do 128-bit encryption, the RDP
connection fails.
Low Level— Allows
the use of 56-bit keys for encryption. Use this setting if the RDP
server cannot use 128-bit keys for encryption.
Client Compatible— Negotiates for 128-bit keys first and rolls down
to 56-bit keys if the RDP server cannot use 128-bit keys.
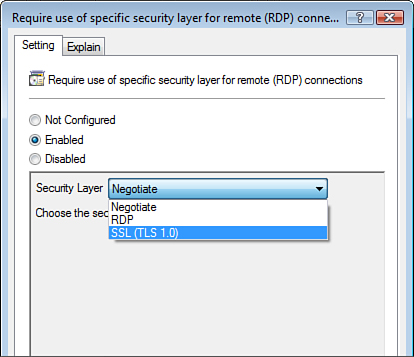
To require mutual
authentication, you can configure the Require Use of Specific Security
Layer for Remote (RDP) Connections setting. This implements SSL (Transport Layer Security, or TSL, 1.0)
mutual, certificate-based authentication of the RDP client and the RDP
server.
As shown in Figure 10,
the available settings are as follows:
Negotiate— Tries TLS 1.0 mutual authentication. If this
fails, this setting rolls down to use RDP authentication of the client
only.
RDP— Authenticates the client to the RDP server only.
Use this setting if the RDP server cannot perform TLS 1.0
authentication.
SSL (TLS 1.0)—
Requires both the client and RDP server to use TLS 1.0 authentication.
If either end of the connection cannot use TLS 1.0 to authenticate, the
connection fails.
Alert
To
summarize, the strongest settings for using the Remote Desktop Protocol
to connect to a Windows Vista computer are to require 128-bit key
strength on the encryption setting and require SSL (TLS 1.0) for mutual,
certificate-based authentication on the security layer for RDP
connections.