1. Authorizing Administrative Actions
The
User Account Control is a very important part of Windows security and
is responsible for all those times a dialog box pops up asking you to
verify an action. Although the User Account Control is turned on by
default, people sometimes find it so annoying that they turn it off.
This action reduces your security and makes it much more difficult to
execute actions while you’re logged on as a Standard user.
Turn On the User Account Control
- 1. Log on to Windows as an Administrator.
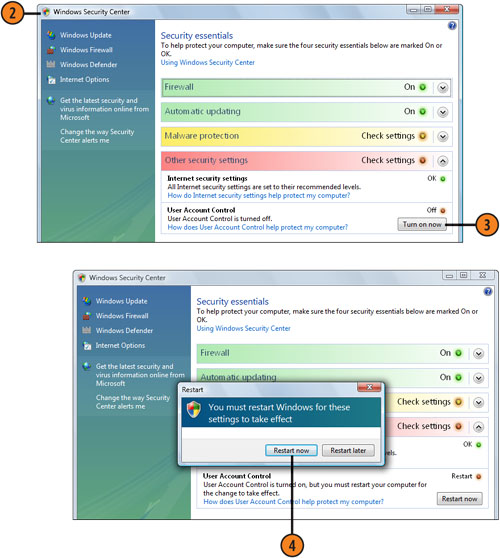
- 2. Click the Start button, choose Control Panel from the Start menu, and,
in the Security section, click Check This Computer’s Security Status to
display the Windows Security Center window.
- 3. If the User Account Control is shown as Off in the Other Security Settings section, click the Turn On Now button.
- 4. Click the Restart Now button to restart the computer.
- 5. Log on as a Standard user. When Windows requests your permission to
take an action, in the User Account Control dialog box, click an
Administrator account, enter the password for that account, and click
OK.
Tip There
are four types of situations that require authorization: Windows
settings that affect the computer system; running a program that’s
recognized (digitally signed) but that requires permission to affect the
system; running a program that isn’t recognized; and trying to run a
program that has been blocked from running by parental controls. |
2. Restricting Access to Web Content
If
you’re a parent, grandparent, guardian, or concerned relative or
friend, a child’s access to a computer is a huge source of worry.
Fortunately, you can restrict the type of content the child can access,
and, if several children have access to your computer, you can make
custom settings that are age-appropriate for each child’s account.
Set Up Parental Controls
- 1. If any of the individuals whose Web content you want to restrict are logged on, ask them to log off, or log them off yourself.
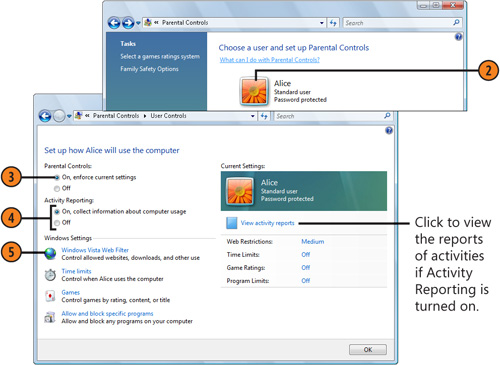
- 2. Click the Start button, choose Control Panel from the Start menu, and,
in the User Accounts And Family Safety section, click Set Up Parental
Controls For Any User. In the Parental Controls window that appears,
click the account to which you want to apply the controls. If the
individual doesn’t have an account, click Create A New User Account,
create a Standard account for that person, and click Create Account.
- 3. In the User Controls window, select the On, Enforce Current Settings
option to turn on the parental controls if they aren’t already turned
on.
- 4. Specify whether you want Windows Vista to keep a record of Web sites visited, games played, programs run, and so on.
- 5. Click Windows Vista Web Filter to display the Web Restrictions window.
Caution Make
sure that all Administrator accounts have passwords and that the person
whose access is being restricted doesn’t know or have access to a
password for any Administrator accounts. With Administrator permissions
to change settings, anyone can change or disable the parental controls. |
Control the Content
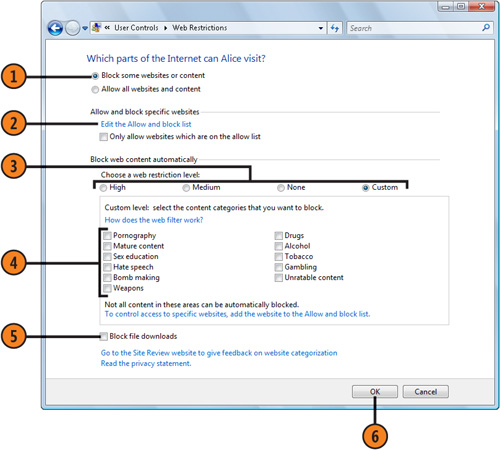
- 1. In the Web Restrictions window, select this option to enable specifying what content should be blocked.
- 2. If there are specific Web sites that you want to allow when they’re
normally blocked, or that you want to block when they’re normally
allowed, click this option, and add the relevant Web addresses to the
Allowed Websites or Blocked Websites list in the Allow Blocked Webpages
window. Click OK when you’ve finished.
- 3. Select a level of restrictions.
- 4. If you clicked the Custom option, select the check boxes for the type of content you want to block.
- 5. Select this check box if you don’t want to allow files to be downloaded from the Web.
- 6. Click OK, and then click OK in the User Controls window.
Tip You
can create a custom list of allowed and blocked Web sites and then use
the list to set the controls for each individual on any computer that’s
running Windows Vista. To do so, in the Allow Blocked Webpages window
where you created your list, click Export, and save the file. When
you’re setting up any additional parental controls, click Import in the
Allow Blocked Webpages window, and import the custom-list file you
previously saved. |
|