2. Remote Desktop
Remote Desktop is a tool in
Windows 7 that allows you to take control of a remote computer's
keyboard, video, and mouse. This tool does not require someone to be
available to collaborate with you on the remote computer. While the
remote computer is being accessed, it remains locked and any actions
that are performed remotely will not be visible to the monitor that is
attached to the remote computer.
2.1. New/Updated Features
Windows 7 Remote Desktop is,
again, an enhanced version of the remote desktop functionality that has
been with us for many of the previous versions of Windows, both client
and server operating systems. Remote Desktop uses Remote Desktop
Protocol (RDP) to provide the data between a host and a client machine.
Windows 7 is using the latest version of RDP, RDP 7.0. Windows 7 Remote Desktop enhancements are as follows:
RDP Core Performance Enhancements
True Multi-Monitor Support
Direct 2D and Direct 3D 10.1 Application Support
Windows 7 Aero Support
Bi-directional Audio Support
Multimedia and Media Foundation Support
There are many uses for
Remote Desktop, but the most common use is that of the administrator
attempting to perform a task on an end user's machine (or server).
Another use is the end user
connecting to a machine from their home or on the road. If you have
noticed the enhancements of Remote Desktop (which are enhancements to
the RDP protocol), you can see that one of the main goals of enhancing
Remote Desktop is to make the user experience as comfortable and
seamless as possible.
|
I have mentioned many times
about using Remote Desktop for troubleshooting client computers. As an
administrator, I like to just take control of an end user machine and
fix it. Although this can be done in Remote Assistance, the end user is
required to allow us to have access and then can watch what we do. In
Remote Desktop, we just take control and close the interactive session
at the remote machine (yes, the remote end user can block us or take
over the session, but not if they want their problem solved).
But there are other uses as
well. We provide a server with resources to our clients, and that server
may need to be changed or updated on a regular basis (sometimes a
couple of changes in a day). Remote Desktop allows us to maintain our
server and database from wherever we are without impacting the clients
or other administrators.
|
2.2. Remote Desktop Connection Options
When connecting to a Remote
Desktop host machine, there are several options available to enhance the
client user session. The options allow configuration for general
settings, display options, local resource access, programs to be
executed on startup, the user experience, and advanced options for
security and Remote Desktop gateway access. The options are available by
selecting the Options button in the lower-left area of the initial
Remote Desktop connection screen. Figure 6 shows the options window both hidden and displayed.
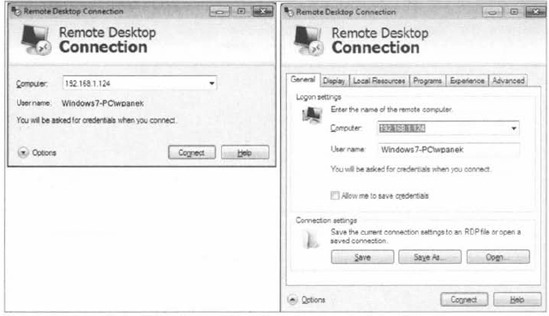
From the General tab, the
host computer and username can be selected. User credentials can be
saved from this tab as well. The connection settings can be saved to a
file or an existing RDP file can be opened from the General tab.
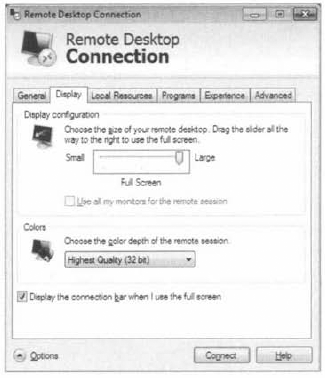
From the Display tab (Figure 7),
the size of the display screen can be chosen. This is also where the
option to use multiple monitors will be selected. The color depth (color
quality) is selected in the Display tab. The option to display the
connection bar when using full screen display is available here as well.
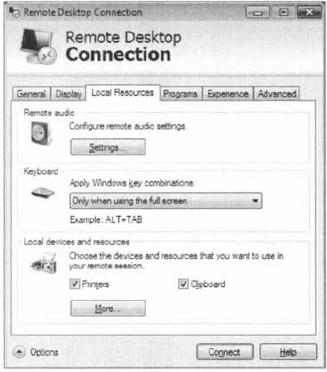
From the Local Resources tab (Figure 8), remote audio settings, keyboard settings, and local device and resource access can be configured.
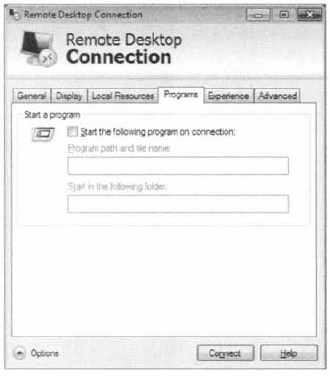
The Programs tab (Figure 9)
for Remote Desktop options allows the selection of a program to run at
connection startup. The program name and path are specified as well as a
startup folder if necessary.
The end user experience is
important to the overall success of using Remote Desktop in the user
environment. Remember, Remote Desktop can be used to provide a user with
the ability to connect to their machine and "remote in." The most
seamless environment from the user to the remote location is desirable,
but that will be dependent on the bandwidth available. The more
bandwidth, the more high-end features can be made available to the end
user.
This is also nice for the administrator who is working on an end user machine. The Experience tab (Figure 10) allows the configuration of the end user experience.
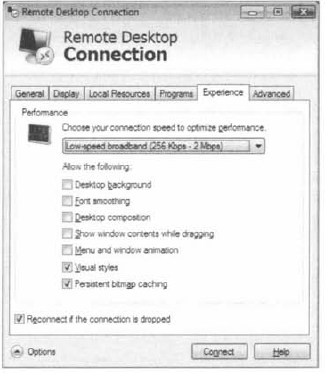
Controlling the
behavior of the Remote Desktop connection with regard to security is
configured on the Advanced tab of the Remote Desktop options dialog. The
Advanced tab also supports the configuration of a Remote Desktop
gateway to allow Remote Desktop connections to be established from any
Internet location through SSL. The user must still be authorized and the
Remote Desktop client must still be available.
Another way a Windows 7 user
can connect to a server is through the use of a virtual private network
(VPN) connection. In the next section, we will look at how to configure
a VPN connection on Windows 7.