Presentation Model Elements
The two
types of presentation elements include rich client model elements and
Web client model elements. The rich client element categories, Forms and
Reports, are located under the AOT root node, and the Web client
element categories, Web Forms and Web Reports, are under the Web node.
Presentation elements are form, report, menu, or menu item definitions
for either a Windows client application, called a rich client
application, or a Windows SharePoint Services client application, called
a Web client application. Both types of clients have a control layout
feature called IntelliMorph. IntelliMorph automatically lays out
presentation controls based on model element property and security
settings. Presentation controls are automatically supplied with database
and calculated data when their data source elements are associated with
database or temporary table fields.
Rich Client Model Elements
Figure 3
illustrates the rich client elements and their relationships.
Configuration key and security key elements can be associated with menu
and menu item elements. This association prevents users from executing
application code that doesn’t have a license key or an active
configuration key.
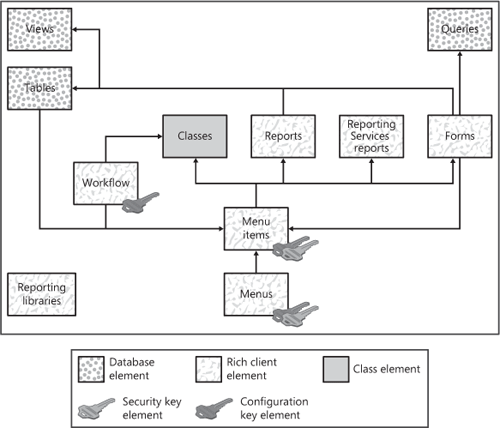
Table elements can also
be associated with menu item elements. Each table element definition
includes an optional display menu item element reference that, by
convention, launches a form presentation control that renders the data
from the database table in a grid control. The Dynamics AX runtime also
automatically adds a Go To The Main Table Form menu item to a drop-down
menu that appears when a user right-clicks a grid cell whose associated
table column has a foreign key relationship with another table. The
Dynamics AX runtime uses the referenced table’s menu item element to
launch the form that renders the data from the foreign key table.
Menu
elements define logical menu item groupings. Menu definitions can
include submenu elements and other menu elements. The menu element named
MainMenu defines the menu entries for the Dynamics AX navigation pane.
As a new feature in Dynamics AX 2009, menus can also work as a
hyperlink. This is modeled by specifying a menu item.
Menu item
elements define hyperlinks labeled for display, action, and output that
the Dynamics AX runtime uses to instantiate and execute reports,
Reporting Services reports, business logic objects (defined by using
class elements), and forms. When rendering forms and reports, the
Dynamics AX runtime ignores menu items that are disabled by
configuration keys, security keys, or role-based access permissions.
Form
elements define a presentation control with which users insert, update,
and read database data. A form definition includes a data source and a
design element that defines the controls that must be rendered on the
form as well as their data source mappings. A form is launched when a
user clicks a display menu item control, such as a button. Data sources
on a form can be table, view, or query elements.
Report elements
define a presentation control that renders database and calculated data
in a page layout format. A report can be sent to the screen, a printer, a
printer archive, an e-mail account, or the file system. A report
definition includes a data source and a design element that define the
output-only controls that must be rendered on the report as well as
their data source mappings. A report is launched when a user clicks an
output menu item control, such as a button.
Report libraries are
a logical grouping of Reporting Services reports, data sources, style
templates, layout templates, and images. Each report library represents a
single Dynamics AX Reports Library project. You can edit an existing
report library or create a new one using Microsoft Visual Studio 2008 if
you have the Dynamics AX Reporting Tools component installed. Reporting
Services reports that are part of a report library in the AOT can be
associated with menu items.
Workflow
elements define workflow documents and event handlers by using class
elements. Workflow elements define the workflow tasks, such as approve
and reject, by associating the tasks with menu items. When a form is
workflow enabled, it automatically renders controls supporting the user
in performing the tasks in the workflow.
Web Client Model Elements
Figure 4
illustrates the Web client model elements used to define Enterprise
Portal. You can associate configuration key and security key elements
with Web menu items and Web content elements to ensure that code without
license keys are an active configuration key that can’t be executed.
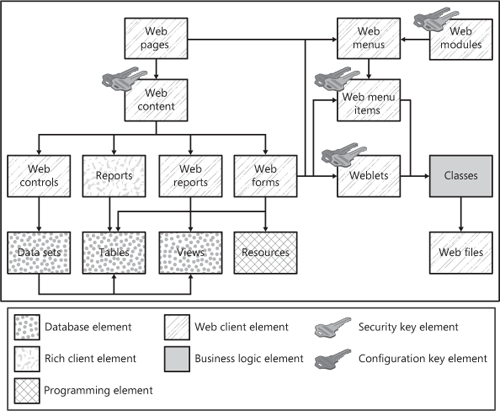
Web
menu elements define logical Web menu item groupings. Web menu
definitions can include submenu application elements and other Web menu
application elements. Web menu items are rendered as hyperlinks on Web
pages.
Web menu item
elements define hyperlinks containing URLs and class labels that the
Dynamics AX runtime environment uses to navigate between Web pages and
to generate Web pages, respectively. Web module elements define the site
structure. The Web modules are created as subsites under one parent
home site in Windows SharePoint Services.
Web file elements
define file references to components required by Windows SharePoint
Services. These components include site definitions, templates, and Web
part installation files. The MorphX IDE saves these files to a specified
Web server at deployment time.
Data
set elements define the data sources used by the Web user controls.
They offer a rich programming model in the AOT for defining data access,
validation, calculation, and so on. The data set elements also expose
business data to Web user controls through standard ASP.NET data binding
via the AxDataSource control.
Web control elements
store the Web user control’s markup and code-behind files. You can
create Web user controls in Visual Studio 2008 and add them directly to
the AOT by using the Dynamics AX Visual Studio add-in. Web user controls
define the user interface for interacting with business data.
Data sets, Web controls,
and report libraries are the elements used by the newly architected,
ASP.NET-based Enterprise Portal framework. (The Enterprise Portal
framework has been rewritten for Dynamics AX 2009. These elements replace the X++-based Enterprise Portal framework
(supported in deprecated mode in Dynamics AX 2009), which uses Weblet,
Web form, and Web report elements.
Weblet elements
define references to class application elements that extend the Weblet
class definition. Weblet objects return HTML documents whose format is
governed by input parameters.
Web form
elements define Web presentation controls with which users insert,
update, and read database data. A Web form definition includes a data
source and a design element that defines the controls that must be
rendered on the Web form, as well as their data source mappings. A Web
form is generated when a Web page hosting the Web form is generated.
Web report elements
define Web presentation controls that render database and calculated
data in a Web format. A report definition includes a data source and a
design element that define the output-only controls that must be
rendered on the report, as well as their data source mappings. A Web
report is generated when a Web page hosting the Web form is generated.
Web content elements
define managed, display, and output elements that reference Web user
control, Web form, Web report, and (rich) report elements for their
content.
Web page elements define the composition of an HTML document element that comprises Web content elements and Web menu elements.