Creating a Network Load Balancing cluster
After installing the NLB feature on each server that
will become a cluster node, you are ready to create a new cluster.
Perform the following to create a new NLB cluster:
1. | Open the Network Load Balancing Manager from Start | All Programs | Administrative Tools | Network Load Balancing Manager.
|
2. | Right click Network Load Balancing Clusters and select Create New Cluster (see Figure 3).
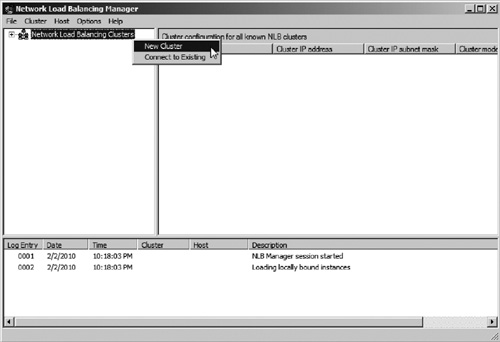
|
3. | Enter the hostname of the cluster node you wish to configure. Then click Connect (see Figure 4).
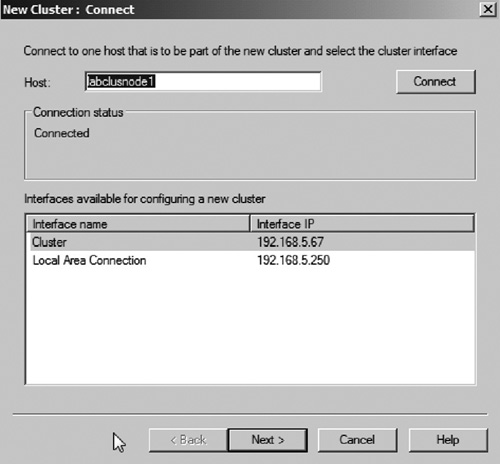
|
4. | Select
the interface that you want to use for the NLB cluster. Remember that
this has to be a dedicated network adapter if you plan on using unicast
mode. Select the interface you want to use, and then click Next.
|
5. | Select the IP address that you want to dedicate for cluster traffic. You also need to select the host priority (see Figure 5). The lower numbered node is the first to receive traffic. Then click Next.
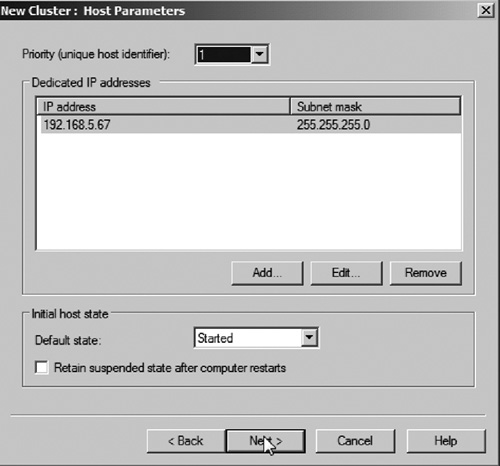
|
6. | Enter the cluster VIP address (see Figure 6).
This is the address that clients will use to connect to the cluster.
This IP will be shared among all nodes of the cluster. Then click Next.
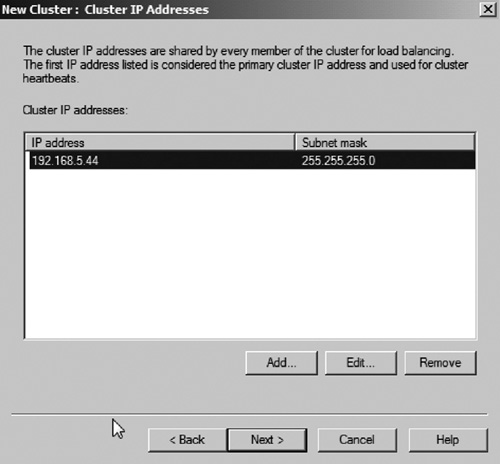
|
7. | You now need to configure the cluster operation mode (see Figure 7). You can use one of the following modes:
Unicast Multicast IGMP Multicast
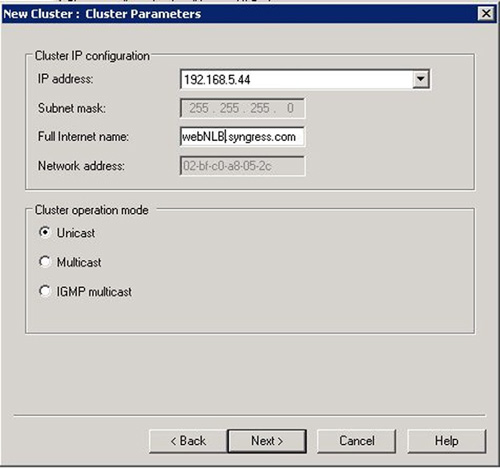
In addition to selecting the cluster operation mode, you can optionally
enter a FQDN that will be used to refer to the cluster IP. Click Next to continue. |
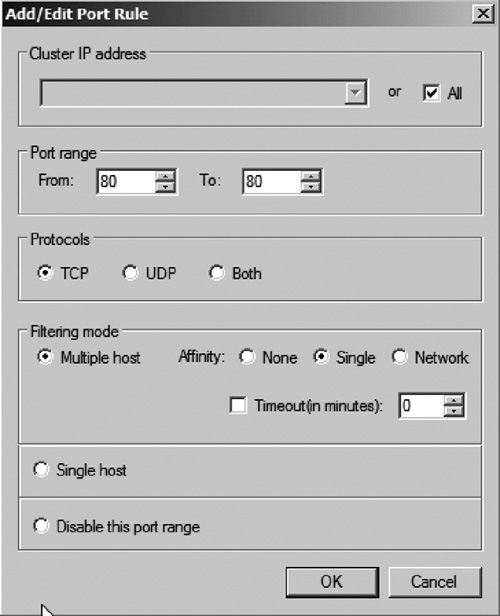
8. | You now need to configure the NLB ports range, protocols, and filtering mode (see Figure 8):
- Ports Range —This
is the range of ports that will be load balanced. You should limit this
range to the ports used by the application being load balanced. For
example, if you are load balancing an IIS Web site, you will more than
likely want to use ports 80 and 443.
- Protocols —Similar to port range, you need to select the protocols (TCP or UDP) used by the application being load balanced.
- Filtering Mode
—Filtering mode is used to help configure “stickyness.” Many
applications may require that once a session is initiated to a host the
client must continue to use the same host to complete certain
transactions. For example, an ecommerce site could host a checkout
process. The application may require that you remain on the same host
to perform the checkout. To help ensure that this session “sticks” to
the same host, you can use filtering. By choosing Multiple host and
setting affinity to single, NLB
will ensure that as long as the client comes from the same IP address,
it will remain on the same node for the duration of the session. By
setting affinity to Network, NLB will ensure that the client’s network,
subnetted to a class C, will continue the session on the same host.
This is useful if the clients are NAT’d behind firewall with multiple
public IP addresses.
|
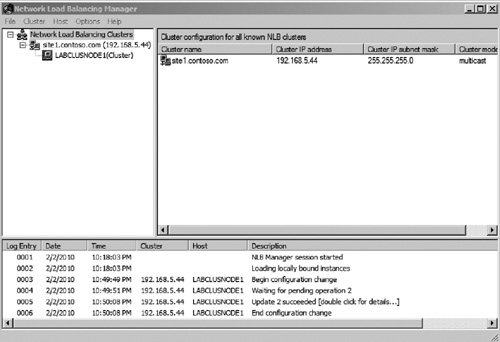
After configuring port rules and filtering, click Finish
to complete the setup of the NLB cluster. You will see several
configuration steps taking place in the Network Load Balancer Manager.
When the configuration is complete, you should see a newly set up NLB
cluster similar to Figure 9.
Adding an additional node to the NLB cluster
After
initial setup, you will need to add the rest of the nodes to the
cluster. To add additional nodes, perform the following within Network
Load Balancer Manager:
1. | Right click the cluster and select the option to Add Host to Cluster.
|
2. | Enter the server name of the host you wish to add as a node and click Connect.
|
3. | Select the interface you wish to use for the cluster, and then click Next.
|
4. | Select the priority of the new node, and then select the IP address to be used for cluster traffic. Then click Next.
|
5. | Verify that the port and affinity configuration matches that of the other node. These options should be grayed out. Then click Finish.
|
The Network Load Balancer Manger should perform a few configuration steps and then add the second node to the cluster.
You can now test the cluster by accessing
the NLB cluster IP address. If you want to verify NLB functionality and
that failover is working properly, you can shut down one of the nodes.
You should still be able to access the application or Web site on the
cluster IP address.