5. How to Troubleshoot Joining or Logging on to a Domain
Administrators often
encounter problems when joining a computer running Windows to an AD DS
domain. Additionally, users might receive error messages about domain
controllers being unavailable when trying to log on to their computer
with a domain account.
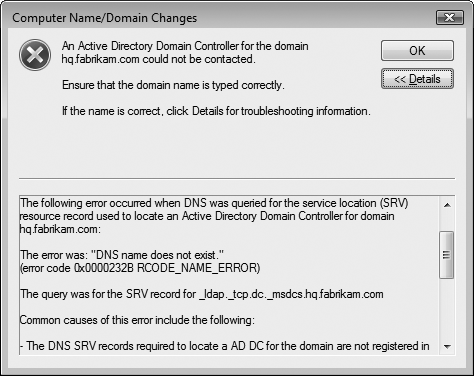
The first step in troubleshooting
domain join problems is to click Details in the Computer Name/Domain
Changes dialog box to view the error information. For example, the error
shown in Figure 4
indicates that the DNS server does not have a DNS entry for the domain
controller. If you want to view this error information after closing the
Computer Name/Domain Changes dialog box, open the
%WinDir%\Debug\Dcdiag.txt log file.
5.1. How to Analyze the NetSetup.Log file
If the Computer Name/Domain
Changes dialog box does not reveal the source of the problem, view the
%WinDir%\Debug\Netsetup.log file. This log details the process of
joining a domain as well as the details of any problems encountered. For
best results, compare a log file generated on
a computer that successfully joined your domain to a computer that
failed to join the domain. For example, the following entry indicates
that the computer successfully located the hq.contoso.com domain controller (note the return value of 0x0).
-----------------------------------------------------------------
NetpValidateName: checking to see if 'HQ.CONTOSO.COM' is valid as type 3 name
NetpCheckDomainNameIsValid [ Exists ] for 'HQ.CONTOSO.COM' returned 0x0
NetpValidateName: name 'HQ.CONTOSO.COM' is valid for type 3
-----------------------------------------------------------------
The following entry
indicates that the computer failed to locate the hq.fabrikam.com domain
controller (note the return value of 0x54b).
-----------------------------------------------------------------
NetpValidateName: checking to see if 'hq.fabrikam.com' is valid as type 3 name
NetpCheckDomainNameIsValid for hq.fabrikam.com returned 0x54b, last error is 0x3e5
NetpCheckDomainNameIsValid [ Exists ] for 'hq.fabrikam.com' returned 0x54b
-----------------------------------------------------------------
If you see this type of name
resolution failure during an unattended setup but you are able to
manually join a domain, verify that clients are receiving a valid DHCP
configuration. Specifically, verify that the DNS server addresses are
correct and that the identified DNS servers contain service location
(SRV) resource records for your domain controllers in the format _ldap._tcp.dc._msdcs.DNSDomainName.
If you see an error
resembling the following, it indicates that the computer was previously
joined to a domain using the same computer name but a different account.
Joining the domain might fail because the administrative user account
does not have permission
to modify the existing account. To work around the problem, change the
computer name, have the computer account deleted from the domain, or use
the original user account to join the computer to the domain.
NetpManageMachineAccountWithSid: NetUserAdd on '\\hq.contoso.com' for
'43L2251A2-55$' failed: 0x8b0
04/06 06:36:20 SamOpenUser on 3386585 failed with 0xc0000022
If you see an error
resembling the following, it indicates that the client could not
establish a Server Message Block (SMB) session to the domain controller
to manage the client computer account. One possible cause of this issue
is missing WINS registrations for a domain controller.
NetUseAdd to \\ntdev-dc-02.ntdev.corp.microsoft.com\IPC$ returned 53
To reproduce this problem (and test whether you have fixed it), open a command prompt and run the following command.
net use \\<server from above>\ipc$ /u:<account used for join> <password>
To determine whether the edition of Windows supports joining a domain, search for the keyword NetpDomainJoinLicensingCheck (most recent entries are at the bottom of the log file). If the ulLicenseValue
is anything other than 1, it indicates that the edition of Windows
cannot join a domain. To join a domain, a computer must be running the
Windows 7 Professional, Windows 7 Enterprise, or Windows 7 Ultimate
operating systems. The following shows a log file entry for a computer
running a supported version of Windows (as indicated by ulLicenseValue=1).
NetpDomainJoinLicensingCheck: ulLicenseValue=1, Status: 0x0
5.2. How to Verify Requirements for Joining a Domain
To join or log on to a domain
successfully, you must meet several different requirements. When
troubleshooting a problem joining a domain, verify each of these
requirements:
The client computer must be able to resolve the IP address for a domain controller
In most enterprise networks, client computers receive an IP address
assignment from a DHCP server, and the DHCP server provides addresses
for AD DS–enabled DNS servers that can resolve the domain controller IP
address. If another DNS server is configured, you should update the
client computer's IP configuration to use an AD DS–enabled DNS server.
If this is not possible, you can add two records to your existing DNS
server that resolve to a domain controller's IP address:
The _ldap._tcp.dc._msdcs.DNSDomainName SRV resource record, which identifies the name of the domain controller that hosts the AD DS domain. DNSDomainName is the DNS name of the AD DS domain the computer is attempting to join.
A corresponding
address (A) resource record that identifies the IP address for the
domain controller listed in the _ldap._tcp.dc._msdcs.DNSDomainName SRV resource record.
The client computer must be able to exchange traffic with the domain controller on several different TCP and UDP ports These ports include:
TCP port 135 for RPC traffic
TCP port 389 and UDP port 389 for LDAP traffic
TCP port 636 for LDAP over SSL traffic
TCP port 3268 for LDAP Global Catalog (GC) traffic
TCP port 3269 for LDAP GC SSL traffic
TCP port 53 and UDP port 53 for DNS traffic
TCP port 88 and UDP port 88 for Kerberos traffic
TCP port 445 for SMB (also known as CIFS) traffic
The administrator must have privileges to add a computer to a domain Administrators who add a computer to a domain must have the Add Workstations To Domain user right.
The computer must be running Windows 7 Professional, Windows 7 Enterprise, or Windows 7 Ultimate Windows 7 Starter, Windows 7 Home Basic, and Windows 7 Home Premium operating systems cannot join a domain.
6. How to Troubleshoot Network Discovery
With Network
Discovery, users can browse shared network resources from the Network
window. On private networks, this is convenient because users can
connect to resources without knowing the names of other computers on the
network. On public networks, however, Network Discovery is a security
concern because it will announce the presence of the computer on the
public network and users might use it to connect to a potentially
malicious computer.
For these reasons, Network
Discovery is enabled on private networks but disabled on public networks
by default. When connected to an AD DS domain, Network Discovery is
controlled by Group Policy settings but is disabled by default.
Therefore, if the Network window does not display shared resources on
the local network, it is almost certainly because Network Discovery is
disabled. To remedy this, follow these steps (all of which require
administrator privileges and can increase your computer's exposure to
security attacks):
Verify that the Function Discovery Provider Host service is running.
Verify that Windows Firewall has exceptions enabled for Network Discovery.
Change the type of network from public to private. Alternatively, you can manually enable Network Discovery by opening the Network And Sharing Center window and enabling Network Discovery.