7. How to Troubleshoot File and Printer Sharing
Several different factors can
cause problems with connecting to shared files and printers (which use
the same communications protocols):
Windows Firewall or another software firewall is blocking traffic at the client or server. A network firewall between the client and server is blocking traffic. The client is providing invalid credentials, and the server is rejecting the client's connection attempt. Name resolution problems prevent the client from obtaining the server's IP address.
First, start troubleshooting
from the client computer. If the server is a computer running Windows 7
and you have administrator access to it, you can also troubleshoot from
the server. The two sections that follow assume that the client and
server belong to a domain.
7.1. How to Troubleshoot File and Printer Sharing from the Client
Follow these steps to troubleshoot problems connecting to shared files and printers:
If
you can connect to the shared folder but receive an Access Is Denied
message when attempting to open the folder, your user account has
permission to access the share but lacks NTFS File System (NTFS)
permissions for the folder. Contact the server administrator to grant
the necessary NTFS file permissions. Verify that you can resolve the server's name correctly. At a command prompt, type ping hostname.
If Ping displays an IP address, as shown here, you can resolve the
server's name correctly. It does not matter whether the server replies
to the pings. If this step fails, it indicates a name resolution
problem. Contact your AD DS or DNS administrator. ping server
Pinging server [10.1.42.22] with 32 bytes of data:
Attempt
to connect using the server's IP address, as identified in the previous
step, rather than the server's host name. For example, instead of
connecting to \\server\printer, you might connect to \\10.1.42.22\printer. From a command prompt, attempt to establish a connection to a server using the net use
\\ip_address command. If it succeeds, you have sufficient network
connectivity, but your user account lacks privileges to connect to the
folder or printer share. Have the server administrator grant your
account the necessary share permissions. Share permissions are separate
from NTFS file permissions. Use
Telnet or PortQry to test whether your computer can connect to TCP port
445 of the remote computer. If you cannot connect using TCP port 445,
test TCP port 139. For instructions on how to test for connectivity
using a specific port. If you cannot connect using either TCP port
139 or TCP port 445, verify that File And Printer Sharing is enabled on
the server. Then, verify that the server has a firewall exception for
TCP ports 139 and 445 or that an exception in Windows Firewall is
enabled for File And Printer Sharing. Attempt
to connect to the server using an account with administrative
credentials on the server. If you can connect with a different account,
your normal account lacks sufficient credentials. Have the server
administrator grant your account the necessary privileges. Depending on
the server configuration, you might be able to identify authentication
problems by viewing the Security Event Log. However, logon failure
auditing must be enabled on the server for the events to be available.
If you are still unable to connect, continue troubleshooting from the server. If you do not have access to the server, contact the server administrator for assistance.
7.2. How to Troubleshoot File and Printer Sharing from the Server
To troubleshoot file
and printer sharing from a server running Windows 7 that is sharing the
folder or printer, follow these steps:
Verify
that the folder or printer is shared. Right-click the object and then
click Sharing. If it does not indicate that the object is already
shared, share the object and then attempt to connect from the client. If you are sharing a folder and it is not already shared, right-click the folder and click Share. In the File
Sharing Wizard, click Change Sharing Permissions. If the File Sharing
Wizard does not appear, the Server service is not running. Continue with
the next step. Otherwise, verify that the user account attempting to
connect to the share appears on the list or that the user account is a
member of a group that appears on the list. If the account is not on the
list, add it to the list. Click Share and then click Done. Verify that the Server service is running. The Server service should be started and set to start automatically for file and printer sharing to work. Verify
that users have the necessary permission to access the resources.
Right-click the object and then click Properties. In the Properties
dialog box, click the Security tab. Verify that the user account
attempting to connect to the share appears on the list, or that the user
account is a member of a group that appears on the list. If the account
is not on the list, add it to the list. Check the Windows Firewall exceptions to verify that it is configured properly by following these steps: Click Start and then click Control Panel. Click Security and then click Windows Firewall. In the Windows Firewall dialog box, note the Network Location. Click Change Settings. In
the Windows Firewall Settings dialog box, click the Exceptions tab.
Verify that the File And Printer Sharing check box is selected. If
the File And Printer Sharing exception is enabled, it applies only for
the current network profile. For example, if Windows Firewall indicated
your Network Location was Domain Network, you might not have the File
And Printer Sharing exception enabled when connected to private or
public networks. Additionally, Windows Firewall will, by default, allow
file and printer sharing traffic from the local network only when
connected to a private or public network.
8. How to Troubleshoot Wireless Networks
Wireless networks are now very
common. However, users often have problems connecting to wireless
networks, because these networks are more complex than wired networks.
To troubleshoot problems connecting to a wireless network, follow these
steps.
Verify
that the wireless network adapter is installed and has an active
driver. From Network And Sharing Center, click Change Adapter Settings.
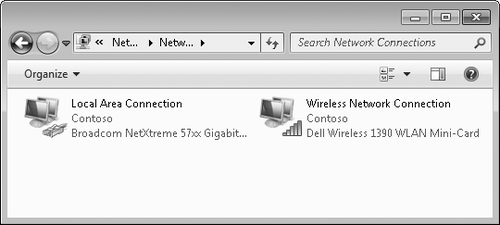
If your wireless network connection does not appear as shown in Figure 5, your network adapter or driver is not installed.
If
a wireless network adapter is installed, right-click it in Network
Connections and then click Diagnose. Follow the prompts that appear.
Windows might be able to diagnose the problem. |
Network Diagnostics
Tim Rains, Program Manager
Windows Networking
Network Diagnostics is
capable of diagnosing more than 180 different issues related to wireless
networking. To get the most from network diagnostics for wireless
networks, ensure that you are using native WiFi drivers instead of
legacy WiFi drivers. To determine which type of driver(s) is installed
on a system, run the following command at a command prompt.
netsh wlan show drivers
In the resulting output, look
for the line labeled "Type." It should be either legacy WiFi Driver or
Native Wi-Fi Driver. If a legacy WiFi driver is installed, contact the
manufacturer of the wireless network adapter to see whether a native
WiFi driver for the adapter is available.
|
Open
Event Viewer and view the System Event Log. Filter events to view only
those events with a Source of Diagnostics-Networking. Examine recent
events and analyze the information provided by the Windows Troubleshooting Platform for the possible source of the problem. Verify
that wireless networking is enabled on your computer. To save power,
most portable computers have the ability to disable the wireless network
radio. Often, this is controlled by a physical switch on the computer.
Other times, you must press a special, computer-specific key combination
(such as Fn+F2) to enable or disable the radio. If the wireless radio
is disabled, the network adapter will appear in Network Connections but
it will not be able to view any wireless networks. If
the wireless network adapter shows Not Connected, attempt to connect to
a wireless network. Within Network Connections, right-click the Network
Adapter and then click Connect. In the Connect To A Network dialog box,
click a wireless network and then click Connect. If
the wireless network is security enabled and you are prompted for the
passcode but cannot connect (or the wireless adapter indefinitely shows a
status of Identifying or Connected With Limited Access), verify that
you typed the passcode correctly. Disconnect from the network and
reconnect using the correct passcode. If
you are still unable to connect to a wireless network, perform a
wireless network trace and examine the details of the report for a
possible cause of the problem.
If the wireless network adapter
shows the name of a wireless network (rather than Not Connected), you
are currently connected to a wireless network. This does not, however,
necessarily assign you an IP address configuration, grant you access to
other computers on the network, or grant you access to the Internet.
First, disable and re-enable the network adapter by right-clicking it,
clicking Disable, right-clicking it again, and then clicking Enable.
Then, reconnect to your wireless network. If problems persist, move the
computer closer to the wireless access point to determine whether the
problem is related to signal strength. Wireless networks have limited
range, and different computers can have different types of antennas and
therefore different ranges. 9. How to Troubleshoot Firewall Problems
Many attacks are initiated
across network connections. To reduce the impact of those attacks,
Windows Firewall by default blocks unrequested, unapproved incoming
traffic and unapproved outgoing traffic. Although Windows Firewall will
not typically cause application problems, it has the potential to block
legitimate traffic if not properly configured. When troubleshooting
application connectivity issues, you will often need to examine and
possibly modify the client's or server's Windows Firewall configuration.
Misconfiguring Windows
Firewall can cause several different types of connectivity problems. On a
computer running Windows 7 that is acting as the client, Windows
Firewall might block outgoing communications for the application (though
blocking outgoing communications is not enabled by default). On a
computer running Windows 7 that is acting as the server (for example, a
computer that is sharing a folder), Windows Firewall misconfiguration
might cause any of the following problems:
Windows Firewall blocks all incoming traffic for the application. Windows Firewall allows incoming traffic for the LAN but blocks incoming traffic for other networks. Windows
Firewall allows incoming traffic when connected to a domain network but
blocks incoming traffic when connected to a public or private network.
The symptoms of client- or server-side firewall misconfiguration are the same: application communication fails. To make troubleshooting
more complex, network firewalls can cause the same symptoms. Answer the
following questions to help identify the source of the problem:
Can
you connect to the server from other clients on the same network? If
the answer is yes, you have a server-side firewall configuration problem
that is probably related to the configured scope of a firewall
exception. If adjusting
the scope of the firewall exception does not solve the problem, it is
probably caused by a network firewall, and you should contact your
network administrators for further assistance. Can
you connect to the server when the client is connected to one type of
network location (such as a home network or a domain network), but not
when it is connected to a different type of network location? If the
answer is yes, you have a client-side firewall configuration problem
that is probably caused by having an exception configured for only one
network location type. Can
other clients on the same network connect to the server using the same
application? If the answer is yes, you have a client-side firewall
configuration problem that is probably caused by having a rule that
blocks outgoing traffic for the application. Can
the client connect to other servers using the same application? If the
answer is yes, you have a server-side firewall configuration problem,
and the server needs a firewall exception added. If adding an
exception does not solve the problem, it is probably caused by a network
firewall, and you should contact your network administrators for
further assistance.
|