The focus so far has been on ensuring that
your computers are properly activated. However, what happens when
activation can't be obtained or maintained? The general result is that
the computer enters a grace period and then eventually into Reduced
Functionality Mode.
Computers can enter the grace period for several
reasons. Initially, the computer will be in a grace period immediately
following installation until activation can be performed. After initial
activation, MAK activated computers may enter their grace period if
substantial hardware changes are noticed. In this case, Windows assumes
it has been moved to new hardware and must reactivate to validate it is a
legal copy. KMS clients may enter a grace period if they fail to
reactivate 180 days following the last successful reactivation. While in
the grace period, the computer functions normally except for occasional
reminders that the computer needs to be activated.
Volume license editions of Windows will remain in
a grace period for up to 30 days. If hardware is significantly modified
on Retail or OEM licenses, the grace period is only three days. If
activation is not performed during the grace period, the computer will
see the Notification Experience (if Windows Vista Service Pack 1 or
later is installed) or Reduced Functionality Mode (if the computer does
not have Service Pack 1 or later installed).
1. Introducing the notifications-based experience
If a Windows Vista SP1 and Windows Server 2008
system are not activated within the grace period, persistent
notifications will alert users of the need to activate. While in the
notifications-based experience, the system will function normally, with
the following exceptions:
The desktop background will be black.
A KMS host cannot activate or renew KMS clients.
Windows Update installs only critical updates (optional updates and those marked as "Genuine Only" will not be made available).
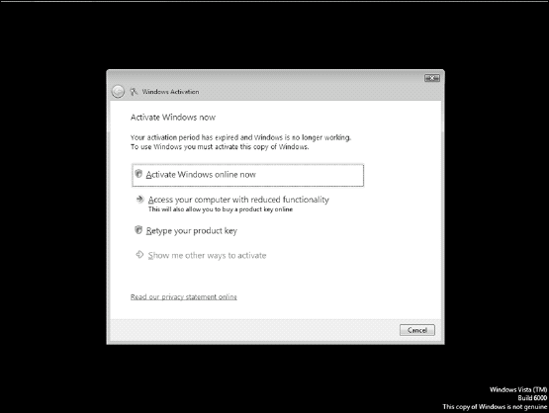
2. Experiencing Reduced Functionality Mode
Prior to Windows Vista SP1, if activation was
not performed during the grace period, the computer enters Reduced
Functionality Mode (RFM), shown in Figure 1.
There are two flavors of Reduced Functionality
Mode, depending upon the reason for entering RFM. If activation is not
performed after the initial grace period, reactivation isn't performed
at least 210 days after a KMS activation, or reactivation isn't
performed after significant hardware change, the computer will enter
out-of-grace RFM. In out-of-grace RFM the following limitations apply:
One hour logon time limit
No access to built-in games
No access to premium features (such as Aero, ReadyBoost, and BitLocker)
If the Windows Genuine Advantage program detects
a blocked key code or modified activation files, the computer will
enter non-genuine RFM. Non-genuine RFM includes the following
restrictions:
3. Resolving the notification experience and Reduced Functionality Mode
The first option is to activate Windows over the
Internet immediately. If the computer needs to be reloaded or was only a
test computer, you may reload the computer and format the hard drive to
gain another 30 days of initial grace period. If in RFM, and there is a
need to recover data from the workstation, it can be booted into Safe
Mode or the explorer.exe process can be launched manually to provide a standard desktop with which any necessary data may be moved.
It does occasionally happen where immediate
activation or reload are not options. The workaround in this situation
is to use the slmgr.vbs script to re-arm the computer. Similar to how Sysprep will reset the grace period back to 30 days, the slmgr.vbs
re-arm command performs the same function much quicker and without
resetting the network and licensing information. Keep in mind that a
computer may only be re-armed three times. Assuming that the computer
was imaged from a Syspreped image file, two more re-arms would be
allowed. For this reason, it is always recommended that image files be
Syspreped no more than twice before re-creating the image from scratch.
With a properly designed unattended answer file, that should be a
relatively simple process.
NOTE
An exception to the rule, Windows Vista Enterprise SP1 can be re-armed up to five times.