5. Configuring a Network Interface Card
One of the first steps to
ensure a system has connectivity is to verify the TCP/IP configuration.
You can check the TCP/IP configuration from the command line (using IPConfig) and configure it by accessing the properties of the network adapter.
IPConfig /all
will provide a lot more information. If the system has the wrong address, you can configure the
network adapter directly to assign a statically assigned IP address, or
it can be configured to receive the IP address from a DHCP server.
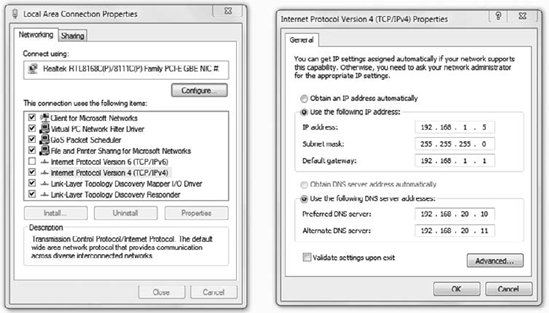
Figure 7
shows a NIC configured with a statically assigned IP address. The IP
address, subnet mask, default gateway, and DNS server addresses are all
entered manually. Alternatively, you could select the Obtain An IP
Address Automatically check box, indicating that the information is
being obtained from DHCP.
It's more common to use
DHCP in an enterprise. Statically assigning the TCP/IP configuration
information requires more administrative effort, which directly
translates into more cost.
Launch Control Panel by clicking Start => Control Panel. Click View Network Status And Tasks in the Network And Internet section. This will launch the Network and Sharing Center. Click Local Area Connection in the Connect Or Disconnect section of the Network and Sharing Center. On the Local Area Connection Status page, click Properties. Select Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4), and click the Properties button. Use the following information to configure a static IP address: If the IP address is configured as Obtain An IP Address Automatically, select Use The Following IP Address. Enter the IP address and subnet mask assigned to the client. Enter the IP address of the default gateway. Enter the IP address of the preferred DNS server.
To
configure the client to obtain an IP address from DHCP, select Obtain
An IP Address Automatically and Obtain DNS Server Address Automatically.
|
6. Using Proxy Servers
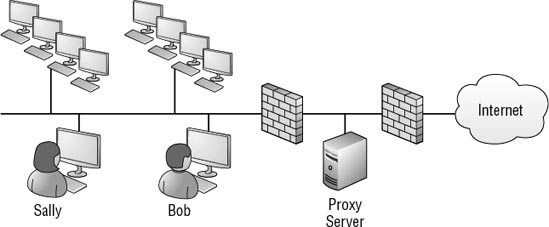
When a proxy server is used, user computers must be configured to use it. Consider Figure 8.
The proxy server is configured to accept all web-based requests from
the clients and forward these requests on the Internet. When the proxy
server receives a response from the Internet-based server, it forwards
the response to the client that sent the request.
NOTE
Microsoft's Internet
Security Accelerator (ISA) server application product can be used as a
proxy server, a firewall, or both. The next version is known as
Microsoft Forefront Threat Management Gateway 2010.
As an example, if Sally needed to
access Microsoft's TechNet site to do some research or download an
article, Sally's request would go through the proxy server.
Proxy servers provide two important benefits:
Caching
Data retrieved from
the Internet is cached on the server and can be served from cache if
requested by another user. For example, if Bob later needed to view the
same content from TechNet that Sally recently viewed, the proxy server
wouldn't need to retrieve the content via the Internet again. Instead,
the data Bob requested can be returned from cache.
Content filtering
Sites can be filtered
to restrict users from visiting certain sites. As an example, a company
may not want employees to access any gambling sites. The proxy server
can be configured with the addresses of blocked sites, and users who try
to access these sites will be blocked using URL filtering. Proxy
servers can also filter out malware.
NOTE
An enterprise may subscribe to
a list of sites based on categories such as gambling. These URL lists
are regularly updated by the company selling the subscription. This
provides the enterprise with an easy method of ensuring employees'
web-browsing habits using company resources comply with company
policies.
Figure 9 shows where Internet Explorer is commonly configured to use a proxy server. This can be configured locally or via Group Policy.
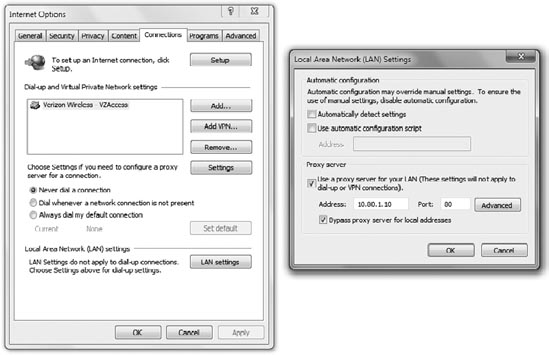
When setting this via Group Policy, use the User Configuration => Policies => Windows Settings => Internet Explorer Maintenance => Connection node. This node includes proxy settings that can be configured with the proxy server address.
Launch Internet Explorer. Select Tools => Internet Options. Tools is a drop-down menu on the far right of the Internet Explorer command bar. Select the Connections tab. Click the LAN Settings button. Select
the Use A Proxy Server For Your LAN check box. Enter the IP address for
the proxy server. Some proxy servers listen on port 80, whereas others
listen on port 8080, and it's possible to configure the proxy server to
listen on other ports. Enter the proper port number for your proxy
server. Click the Advanced button. Your display will look similar to the following graphic.
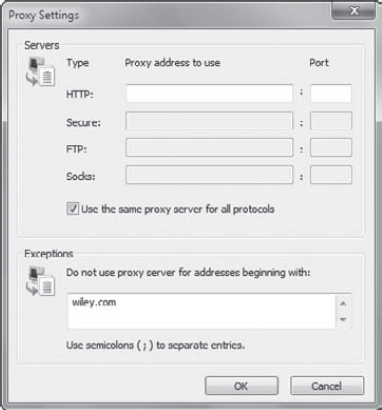
Notice that you
can select the Use The Same Proxy Server For All Protocols check box.
It's common for a single proxy server to handle the Internet traffic for
all protocols, so this is commonly selected. If
you don't want the proxy server used for specific sites, you can enter
the domain names in the bottom text box separated by semicolons. In the
graphic, the proxy server is configured with an exception so that it is
not used for sites with wiley.com in the address.
|