Working with Virtual Hard Disks
Virtual hard disks have
been around since virtual machines appeared on the scene in the late
1990s. Windows Server 2008 R2 can create and directly attach Microsoft
virtual hard disks or VHD files. VHD files are used in Windows Server
2008 and Windows Server 2008 R2 Hyper-V guest machines, as well as
Microsoft Virtual Server 2005 and Microsoft Virtual PC, although not all
VHD versions are 100% interchangeable. Starting with Windows Server
2008 R2, VHD files can be easily created and attached to the host
operating system using Disk Manager. To create and attach a new VHD
file, perform the following steps:
1. | Log on to the Windows Server 2008 R2 system with an account with administrator privileges.
|
2. | Click Start, click All Programs, click Administrative Tools, and select Server Manager.
|
3. | In the tree pane, double-click the Storage node, and select Disk Management.
|
4. | Right-click Disk Management and select Create VHD.
|
5. | In the Create and Attach Virtual Hard Disk window, click Browse to select the volume and folder to place the new VHD file.
|
6. | In
the Browse Virtual Disk Files window, locate the correct volume and
folder, type in the name of the new VHD file, and click Save.
|
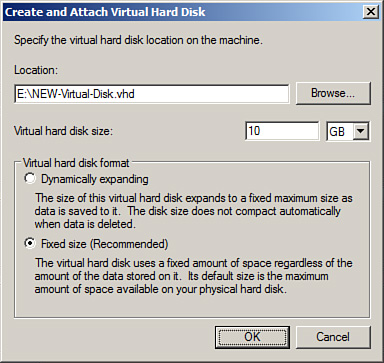
7. | Back
in the Create and Attach Virtual Hard Disk window, enter the size of
the new virtual hard disk and pull down the menu to select MB, GB, or
TB. For our example, we will create a 10GB file on the E: drive called
NEW-Virtual-Disk.vhd.
|
8. | In
the Create and Attach Virtual Hard Disk window, after the location,
name, and size of the new virtual disk are defined, select the Fixed
Size option button to create the file and allocate all the space to
file, as shown in Figure 6, and click OK to create the new virtual hard disk.
|
9. | Once
the process completes, scroll down in the Disk Management tasks pane to
locate the new virtual hard disk, which should be listed as the last
disk and should be listed as Unknown and Not Initialized. Right-click
the disk in the left section of the tasks pane and select Initialize
Disk.
|
10. | In
the Initialize Disk window, choose to create an MBR partition style for
the disk, ensure that the correct disk is checked in the window, and
click OK to initialize the disk.
|
11. | Once
initialized, the disk will be listed as basic and online. Right-click
the unallocated space in the tasks pane and select New Simple Volume.
|
12. | Follow the steps to format the disk as NTFS and assign a drive letter.
|
13. | Once
the process has completed, the virtual hard disk will be available in
My Computer and Windows Explorer just as any other local drive.
|
14. | Once
the usage of the disk is complete, from within Disk Manager,
right-click the attached virtual hard disk and select Detach VHD.
|
15. | In
the Detach Virtual Hard Disk window, the disk that was selected will be
listed; if the virtual hard disk file will be used again, do not check
the box to delete the virtual disk as part of detaching it. Click OK to
detach the disk.
|
Once the virtual hard disk is
detached, if the disk was not deleted, it can be copied to any other
Windows Server 2008 R2 system and mounted or attached to the host
operating system or a Hyper-V guest virtual machine. One use of this new
feature is to easily preload software and files on virtual disks that
will be used for Hyper-V guest machines or to mount up virtual disk for
disk repair, data copies, backup, or a number of different functions.
To attach an existing
virtual disk to a Windows Server 2008 R2 system, the server
administrator can open Server Manager, right-click the Disk Management
node, and select Attach VHD, and then the administrator can choose to
attach the VHD in read-only mode to avoid changing or modifying any data
stored within the disk.