Practice: Using the Netdiag and Dcdiag Command-Line Utilities
The netdiag utility tests
network connectivity. The tool lets you specify a number of optional
parameters, such as /test: to run a specific test and /d: to specify a
domain. However, it is typically run either with no parameters or with
the /fix switch to repair minor errors and the /debug switch to give
detailed output. The output from the tool can be redirected to a text
file for analysis.
The dcdiag utility is
mainly used to test domain controller operation, but it also tests DNS
availability. If there is a problem with your Active Directory domain or
your DNS server, then Exchange Server 2003 will not install and dcdiag
can help troubleshoot the failure. The utility has a number of
parameters, all of which are optional. You can use the /s: switch to
specify a domain controller, the /u: switch to specify a user (by
username and domain name), and the /p: switch to specify a password. If
you do not supply any of these parameters, then the utility will test
the host on which it is run in the context of the logged in user. The
/fix switch fixes the Service Principal Names (SPNs) on the specified
domain controller, and the /test: switch allows you to specify
particular tests. All tests except DcPromo and RegisterInDNS must be run
on a domain controller.
See Also
Details
of the netdiag and dcdiag tests and parameters may be obtained from the
Windows Server 2003 help files. Search under “Support Tools.” |
In this practice, you
create files to hold the output of the tests, run the netdiag tests on a
normal system and on a faulty system, compare the outputs, and then do
the same with the dcdiag tests.
Exercise 1: Create Files to Hold the Test Output
To create files to hold the test output, perform the following steps:
1. | On Server01, create a new folder named C:\Tests.
|
2. | In the C:\Tests folder, create the following empty text files:
Netdiag1.txt Netdiag2.txt Dcdiag1.txt Dcdiag2.txt
|
Note
Some
administrators do not create the required folder and files before using
command-line utilities such as netdiag and dcdiag, because the
utilities create them automatically. However, not all command-line
utilities do this. Arguably, it is good practice to create files before
you run any utility that uses them. |
Exercise 2: Use Netdiag to Check Network Connectivity
To use netdiag to test network connectivity on Server01, perform the following steps:
1. | On Server01, open the Command console.
|
2. | Enter netdiag/debug/fix>c:\tests\netdiag1.txt.
|
3. | Open the Netdiag1.txt file using Microsoft Notepad.
|
4. | Read
the test output. Use the search function to find “Errors,” “Warning,”
or “Failed.” A section of the test output is shown in Figure 1.
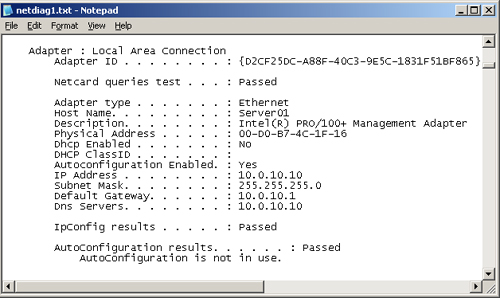
|
Exercise 3: Use Netdiag to Find a Connection Fault
To create a connection fault on Server01 and use netdiag to diagnose the fault, perform the following steps:
1. | On Server01, unplug the connector from Local Area Connection.
|
2. | Open the Command console.
|
3. | Enter netdiag/debug/fix>c:\tests\netdiag2.txt.
|
4. | Open the Netdiag2.txt file using Notepad.
|
5. | Read the test output. Use the search function to find “Fatal.” The relevant section of the test output is shown in Figure 2.
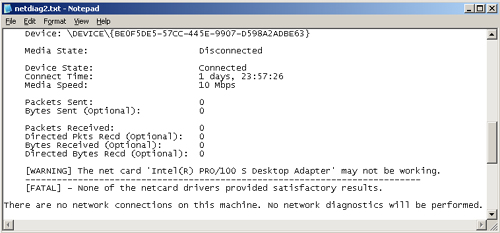
|
6. | Replace the network connector for Local Area Connection. Test the connection by pinging Server02.
|
Exercise 4: Use Dcdiag to Test Server02
In
this exercise, you run dcdiag from Server01 to test Server02. If
Server02 is not a domain controller on your test network, then test
Server01 instead. To test Server02 using dcdiag, perform the following
steps:
1. | On Server01, open the Command console.
|
2. | Enter dcdiag /s:server02 /n:contoso.com /u:contoso.com\administrator /p:* /v /f:c:\tests\dcdiag1.txt /fix.
|
3. | Enter the password for the contoso.com administrator when prompted. The test completes as shown in Figure 3.
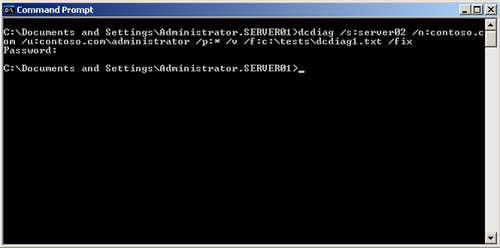
|
4. | Open the Dcdiag1.txt file using Notepad and read the results. A section of the test output is shown in Figure 4.
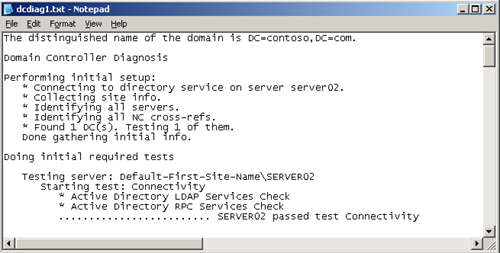
|
Exercise 5: Use Dcdiag to Detect a Fault on Server02
In this exercise, you
stop the DNS service on Server02 and then run dcdiag from Server01 to
test Server02. To use dcdiag to detect a fault on Server02, perform the
following steps:
1. | On Server02, open the DNS console, right-click SERVER02, and then click Stop.
|
2. | On Server01, open the Command console.
|
3. | Enter dcdiag /s:server02 /n:contoso.com /u:contoso.com\administrator/p:*/v/f:c:\tests\dcdiag2.txt/fix.
|
4. | Enter the password for the contoso.com administrator when prompted.
|
5. | Open the Dcdiag2.txt file using Notepad and read the results. The relevant section of the test output is shown in Figure 5.
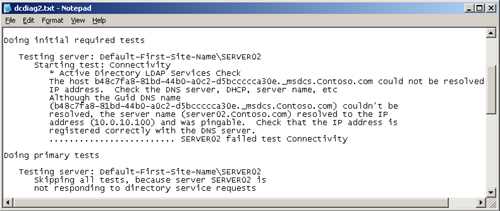
|
6. | Start the DNS service on Server02. |