Through Internet access, computers have a tremendous
amount of potential. Users can access a wide variety of Web sites,
ranging from informational to entertainment resources. Windows Vista
also provides a great platform for playing games. Although these
capabilities provide users with significant benefits, they can also come
at a cost. For example, it is often difficult to restrict which content
is accessible. For situations in which parents want to be able to
manage the types of content that their children can access, it can be
very difficult to create and enforce rules.
In this lesson, you’ll learn
how you can use the Parental Controls features in Windows Vista to
limit the types of access that are available to children. Although this
is the primary use for this feature, there are other applications. For
example, perhaps you might want to restrict some shared computers to
only specific Web sites or restrict the times during which users can
access them. Regardless of the purpose, Parental Controls are a good way
to help limit the types of content users can access.
Understanding Parental Controls
The Windows Vista
Parental Controls feature is designed to provide several different types
of restrictions on how children access programs and Web sites. It can
also control when they can use the computer. The specific types of
restrictions include the following:
Web Restrictions Managing which Web sites children can access
Time Limits Specifying when children are allowed to log on to the computer and how long they can use it
Games Controlling access to games and other entertainment software based on third-party content ratings
Allowing Or Blocking Programs Preventing children from running specific applications on the computer
You’ll
learn how you can enable and configure each of these options later in
this lesson. To enforce these settings, the Parental Controls feature is
integrated with several other operating system features. For example,
filtering Web sites requires interactions with Internet Explorer. Similarly, games-related restrictions
are based on ratings provided as a part of certified Games for Windows
entertainment titles. This integration enables Parental Controls
settings to manage which types of content children can access.
Configuring User Accounts
Parental Controls
restrictions are based on the creation and management of user accounts.
Users who have Administrator accounts are able to create new user
accounts and enable controls on them. Standard user accounts may have
restrictions placed on them. The primary method of managing user
accounts is by accessing Control Panel and selecting User Accounts And
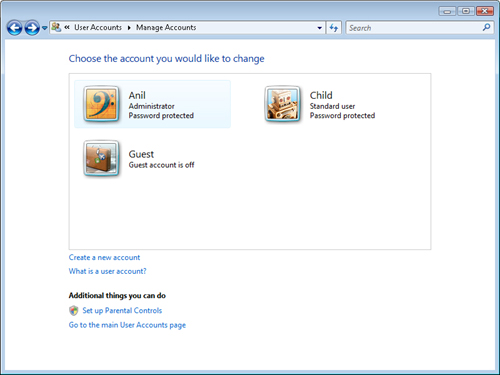
Family Safety. The Add Or Remove User Accounts link launches the Manage
Accounts window (see Figure 1).
Note: A note about user names
Although it might seem a
little strange, the screen shots in this lesson use a standard user
account simply named Child. This helps identify the account for which
Parental Controls are enabled. Customers usually use their children’s
first names for the user account names.
Typically,
parents create and use an Administrator account for themselves. They
then create a separate user account for each of the children for whom
they want to restrict access. Although it is possible to allow multiple
children to share the same user account, it is generally preferable to
create individual accounts for each user. You can also access the
Parental Controls feature by clicking the Set Up Parental Controls link
at the bottom of the Manage Accounts page.
Enabling Parental Controls
By default, Parental
Controls are not enabled in Windows Vista. You can start the process of
creating and managing these settings by accessing Control Panel. The
User Accounts And Family Safety section includes a Set Up Parental
Controls For Any User link. Figure 2 shows the default view of the Parental Controls window.
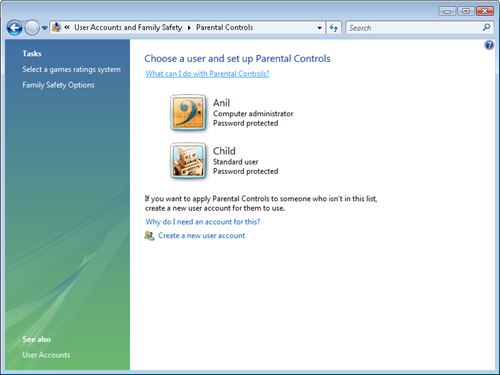
The main Parental
Controls window provides access to several different functions. As
mentioned in the previous section, the first step in configuring a
computer to enable Parental Controls is to create at least one standard
user account for a child. (If you have not done so already, you can
create the child’s account by clicking the Create A New User Account
link in the Parental Controls window.) To enable restrictions, start by
clicking the name of the account that the child uses to log on to the
computer. This provides a list of all of the major types of controls
that you can manage (see Figure 3).
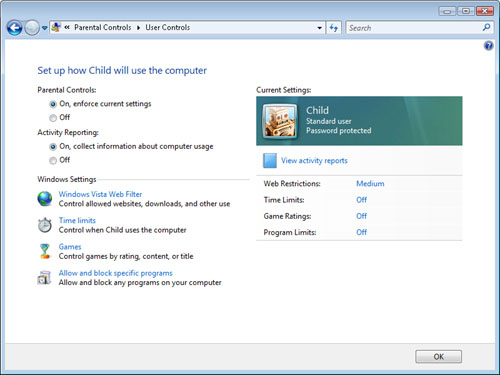
The
first two options determine whether Parental Controls are enabled for
this user account. When you select On, Enforce Current Settings, all of
the other restrictions are enforced when the user logs on to the
computer. This option is also useful for testing purposes because it
does not automatically change any of the other settings on the system.
For example, if you suspect that Parental Controls are preventing access
to a particular program, you can temporarily select the Off option to
see whether that resolves the problem. Because all of the other settings
remain at their original values, you can then easily reenable Parental
Controls without reconfiguring all of the options. When you click OK to
save the settings, the Parental Controls window shows the message
“Parental Controls On” for the child’s user account.
Anil Desai
Windows Vista
includes numerous features that enhance security and oversight
significantly over which types of content children can access. These
improvements can help filter out unwanted materials. They are not,
however, perfect. Determining which types of content are appropriate is
often a matter of significant subjectivity. Some types of filtering
(such as Web site access) are based on voluntary ratings. The majority
of online businesses use valid settings, but some might ignore or
circumvent the guidelines.
So how can parents
help ensure that their children are accessing acceptable content only?
One of the most important security measures is not directly related to
technology. Parents should educate their children about the potential
security risks and other problems associated with accessing unapproved
content. The children should also feel confident in reporting those
issues to their parents. Additionally, parents should review the content
regularly that their children access. In some cases, natural curiosity
might lead children to access unexpected content. Children can also be
extremely clever in their attempts to circumvent security-related
configuration options.
Overall, the
task of maintaining parental control and oversight must be a team effort
to be successful. By informing and educating children about potential
risks, you can decrease their ability to access undesirable content.