Windows 7 has built-in network diagnostic
capabilities so that, in many cases, if there is a problem with your
network connection, Windows knows about it before you do, displays a
message, and often solves the problem.
To discover and
resolve problems, Windows uses the Network
Diagnostics Framework (NDF). When a network-dependent activity (for example, browsing
to a website) fails, NDF automatically springs into action. NDF is
designed to address the most common network-related issues, such as
problems with file-sharing, website access, newly installed network
hardware, connecting to a wireless network, and using a third-party
firewall.
Note:
For more information about
NDF, see "New Network Diagnostic Framework and Network Tracing Features
in Windows 7" at w7io.com/1901.
If you encounter
network problems that don't trigger an automatic response from Windows,
you should first try to detect and resolve the problem with one of the
built-in troubleshooters. In Network And Sharing Center, click Troubleshoot Problems to display the choices
shown in Figure
1. (Alternatively, in the Troubleshooting control panel, click
Network And Internet.)
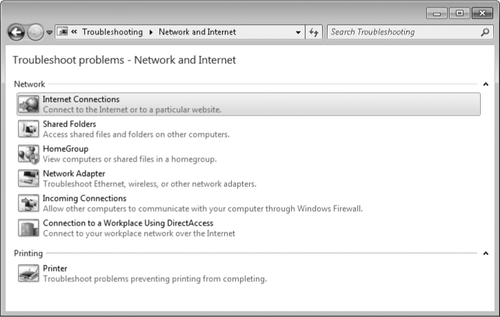
Each of the troubleshooting wizards performs several
diagnostic tests, corrects some conditions, suggests actions you can
take, and ultimately displays a report that explains the wizard's
findings.
1.
Troubleshooting HomeGroup Problems
The HomeGroup troubleshooting wizard provides a good
example of how these trouble-shooters work. If you're having problems
seeing shared resources in a homegroup and you didn't have the benefit
of the troubleshooter's assistance, you'd need to check the following
settings, among others:
The network
location profile must be set to Home Network.
In Windows Firewall With
Advanced Security, you'd need to ensure that the following groups of
rules are enabled on private networks:
Core Networking
Network Discovery
HomeGroup
File/Printer Sharing (not on domain-joined machines)
Windows Media Player (not on
domain-joined machines)
Windows Media Player Network Sharing Service (not on
domain-joined machines)
The following services must be configured so
that they can run:
HomeGroup Listener
HomeGroup Provider
Function
Discovery Provider Host
Function
Discovery Resource Publication
Peer Name
Resolution Protocol
Peer Networking
Grouping
Peer Networking Identity Manager
Running the HomeGroup
troubleshooter—which you can launch from HomeGroup or by right-clicking
HomeGroup in Windows Explorer as well as from the list of
troubleshooters shown in Figure
1—checks each of these items and more. When
you get to the wizard's last window, click View Detailed Information to
see a troubleshooting report that lists the potential problems that the
wizard attempted to identify and fix, as shown below:
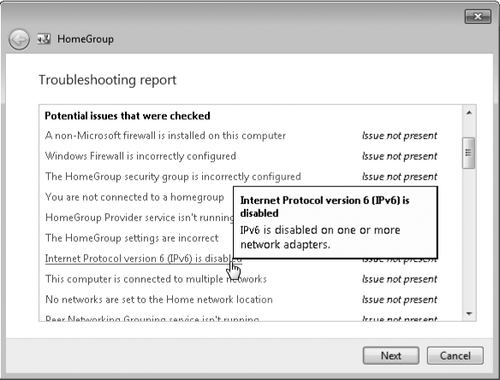
2. Network
Troubleshooting Tools
When the troubleshooters
don't solve the problem, it might be time to dig deeper into the Windows
toolbox. Windows 7 contains an assortment of utilities you can use to diagnose, monitor, and
repair network connections. Table 1 lists some of the more useful networking-related
command-line
utilities and summarizes how you can use them. To learn more about each
utility, including its proper syntax, in a Command Prompt window type
the executable name followed by /?.
Table 1. Windows Network Utilities
| Utility Name | What It's Used For |
|---|
| Get MAC Address
(Getmac.exe) | Discovers
the Media Access Control (MAC) address and lists associated network
protocols for all network cards in a computer, either locally or across a
network. |
| Hostname (Hostname.exe) | Displays the host name of the
current computer. |
| IP Configuration Utility (Ipconfig.exe) | Displays all
current Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) network
configuration values, and refreshes Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
(DHCP) and DNS settings. |
| Name Server Lookup (Nslookup.exe) | Displays information
about Domain Name System records for specific IP addresses and/or host
names so that you can troubleshoot DNS problems. |
| Net services commands
(Net.exe) | Performs a
broad range of network tasks. Type net with no parameters to see a full list of available
command-line options. |
| Netstat (Netstat.exe) | Displays active TCP connections, ports on which the
computer is listening, Ethernet statistics, the IP routing table, and
IPv4/IPv6 statistics. |
| Network Command Shell (Netsh.exe) | Displays or modifies the
network configuration of a local or remote computer that is currently
running. This command-line scripting utility has a huge number of
options, which are fully detailed in Help. |
| PathPing
(Pathping.exe) | Combines the functions of Traceroute and Ping
to identify problems at a router or network link. |
| TCP/IP NetBIOS
Information (Nbtstat.exe) | Displays statistics for
the NetBIOS over TCP/IP (NetBT) protocol, NetBIOS name tables for both
the local computer and remote computers, and the NetBIOS name cache. |
| TCP/IP Ping (Ping.exe) | Verifies IP-level connectivity to another
internet address by sending Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP)
packets and measuring response time in milliseconds. |
| TCP/IP Route (Route.exe) | Displays and modifies
entries in the local IP routing table. |
| TCP/IP Traceroute
(Tracert.exe) | Determines
the path to an internet address, and lists the time required to reach
each hop. It's useful for troubleshooting connectivity problems on
specific network segments. |
A more powerful tool is
available as a free download from Microsoft. Network Monitor is a protocol analyzer
that lets you capture network traffic, view it, and analyze it. Download
it at w7io.com/1906,
and learn more about it on the Network
Monitor blog at w7io.com/1907.