Synchronous Foreground Refresh
Group Policy processing
occurs at computer startup, shutdown, and periodically during the
background refresh interval for computers. Processing for users occurs
at user logon and logoff and periodically during the background refresh
interval. Certain functions of Group Policy, including software
installation, user folder redirection, computer startup and shutdown
scripts, and user logon and logoff scripts, require the network to be
available during processing. Windows XP, Windows Vista, and Windows 7
systems do not wait for the network during computer startup and user
logon by default and by design. This feature provides faster computer
reboots and faster user logon processes but can also cause some Group
Policy processing issues. When software installations, folder
redirection, computer startup, and/or user logon scripts are defined
within domain group policies, it might be required to also enable the
Always Wait for the Network at Computer Startup and Logon setting within
group policies. The setting is stored in the Computer Configuration
node and must be applied as follows:
GPOs
that define computer startup scripts or computer-assigned software
installations should have this setting enabled within the policy.
Software installations that are assigned should be set to this
configuration but published software installation GPOs can be left with
the default processing configuration. If
GPOs exist that define user logon scripts, assigned software
installations, or folder redirection settings that require processing
before Windows Explorer is opened, the computers that the users will log
on to must have a GPO that applies this setting. Configuring this
setting within the policy that contains the user settings will not have
the desired effect unless the user’s computer is also in the container
that is linked to the GPO or unless a different policy that applies to
the user enables this setting.
To configure Synchronous Foreground Processing of group policies, perform the following steps:
1. | Log on to a designated Windows Server 2008 R2 administrative server.
| 2. | Open the Group Policy Management Console from the Administrative Tools menu.
| 3. | Expand the domain to expose the Group Policy Objects container and select it.
| 4. | Right-click the Group Policy Objects container and select New or select an existing policy to update.
| 5. | If a new GPO is being created, type in a name for the new GPO, and click OK to create the new GPO.
| 6. | After the GPO is created or if an existing GPO will be updated, right-click on the desired GPO and select Edit.
| 7. | When
the Group Policy Management Editor opens, expand Computer
Configuration, expand Policies, and select the Administrative Templates
node.
| 8. | Beneath the Administrative Templates node, expand System, and select Logon in the tree pane.
| 9. | In the Settings pane, double-click on the Always Wait for the Network at Computer Startup and Logon setting.
| 10. | On the setting tab, select the Enabled option button, and click OK, as shown in Figure 11.
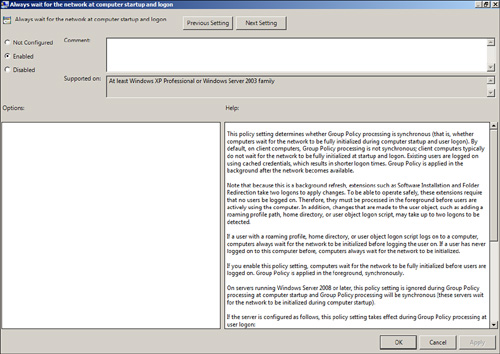
| 11. | Close the Group Policy Management Editor, and return to the GPMC.
| 12. | In the GPMC, if necessary, adjust the links to the updated GPO and close the GPMC when finished.
|
GPO Modeling and GPO Results in the GPMC
When an organization decides
to perform administrative and management tasks using group policies, it
is essential that the system administrators understand how to check to
see if Group Policy processing is working correctly. In the case when
Active Directory hierarchies are being restructured, or if new policies
are being deployed, performing a simulated application of group policies
to review the results can help avoid unexpected issues. To perform
Group Policy simulations, an administrator can use Group Policy
Modeling, available in the GPMC. Group Policy Modeling is the equivalent
of Resultant Set of Policies (Planning), which is the name of the
administrative right that must be delegated in Active Directory to run this tool. To perform Group Policy Modeling, perform the following tasks:
1. | Log on to a designated Windows Server 2008 R2 administrative server.
| 2. | Open the Group Policy Management Console from the Administrative Tools menu.
| 3. | In the tree pane, select the Group Policy Modeling node, right-click the node, and select Group Policy Modeling Wizard.
| 4. | On the Welcome page, click Next to continue.
| 5. | On
the Domain Controller Selection page, specify a domain controller or
accept the default of using any domain controller, and click Next.
| 6. | On
the User and Computer Selection page, the Group Policy Modeling Wizard
can be used to run a simulation based on a specific user and computer in
their current locations, or containers can be specified for either the
user or computer to simulate GPO processing of a specific user, logging
on to a Computer in a specific container. For this example, select the
Users container and the Computers container of the domain to determine
which policies and settings will be applied by default, as shown in Figure 12. Click Next to continue.
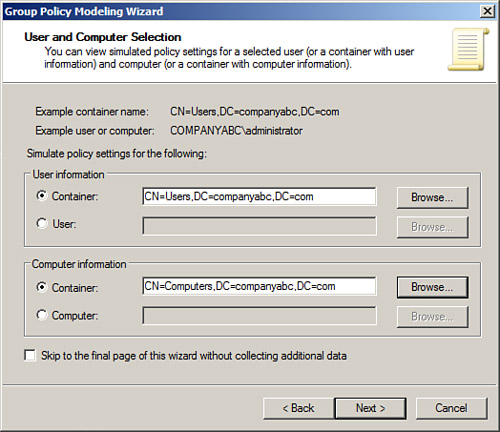
| 7. | On
the Advanced Simulations page, loopback processing, slow network
connections, and site-specific testing can be specified. Accept the
defaults and click Next to continue.
| 8. | On
the User Security Groups page, specific security groups can be
specified to run policy modeling against. Accept the defaults and click
Next to continue.
| 9. | On
the Computer Security Groups page, specific security groups can be
specified to run policy modeling against. Accept the defaults and click
Next to continue.
| 10. | On the WMI Filters for Users page, select the All Linked Filters option button, and click Next to continue.
| 11. | On the WMI Filters for Computers page, select the All Linked Filters option button, and click Next to continue.
| 12. | On the Summary of Selections page, review the choices and if everything looks correct, click Next to run the GPO modeling tool.
| 13. | When the process completes, click Finish to return to the GPMC and review the modeling results.
| 14. | In
the Settings pane, the summary of the computer and user policy
processing will be available for view. Review the information on this
page and then click on the Settings tab to review the final GPO settings
that would be applied, as shown in Figure 13.
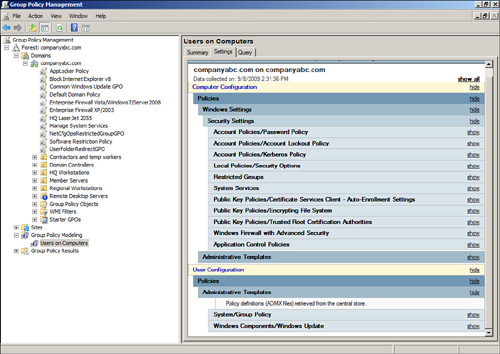
| 15. | Close the GPMC and log off.
|
In situations when Group
Policy is not delivering the desired results, GPO Results can be run to
read and display the Group Policy processing history. GPO Results are
run against a specific computer, but can also be used to collect user
policy processing. To run GPO Results to review the GPO processing
history, perform the following steps:
1. | Log on to a designated Windows Server 2008 R2 administrative server.
| 2. | Open the Group Policy Management Console from the Administrative Tools menu.
| 3. | In the tree pane, select the Group Policy Results node, right-click the node, and select Group Policy Results Wizard.
| 4. | On the Welcome page, click Next to continue.
| 5. | On
the Computer Selection page, choose to run the policy against another
computer and locate a Windows 7 system that a user has already logged on
to. Also be sure to uncheck the Do Not Display Policy Settings for the
Selected Computer in the Results check box, and click Next.
| 6. | On
the User Selection page, select the Display Policy Settings For option
button, and then select the Select a Specific User option button. Select
a user from the list, and click Next to continue. Only users who have
previously logged on to the selected computer will be listed and they
will only be listed if the user running the tool is a domain admin or
has been granted the right to run Resultant Set of Policies (Logging)
for the particular users.
| 7. | On the Summary of Selections page, review the choices and click Next to start the GPO Results collection process.
| 8. | When the process completes, click Finish to return to the GPMC.
| 9. | When
the process completes, the results will be displayed in the Settings
pane on the Summary, Settings, and Policy Events tabs. Review the
results and close the GPMC when finished.
|
Managing Group Policy from Administrative or Remote Workstations
It is very common for
Windows system administrators to manage group policies from their own
administrative workstations. To manage a Windows Server 2008 R2
environment properly, domain group policy administration should be
performed using a Windows Server 2008 R2 or Windows 7 system with the
Group Policy Management tools and the Print Services tools installed.
The main reason for this is that by using the latest version of the
tools possible, the administrator ensures that all possible features are
available and that the most stable version of the tools are being used.
Group Policy management,
aside from creating and managing policies, provides administrators with
the ability to simulate policy processing for users and computers in
specific containers in Active Directory using the Group Policy Modeling
node in the GPMC. Furthermore, the previous application of Group Policy
for users and computers can be collected and reviewed in the Group
Policy Management Console using the Group Policy Results node in the
GPMC. For an administrator, even a member of the Domain Admins group, to
perform remote Group Policy Modeling using the GPMC from a machine
other than a domain controller, the following requirements must be met:
The administrator must be a member of the domain Distributed COM Users security group. The administrator must be delegated the Generate Resultant Set of Policy (Planning) right in Active Directory, as shown in Figure 14.
This right must be applied to the domain, OU, container, or site that
contains all of the computers and users the administrator will run
simulated GPO processing against.
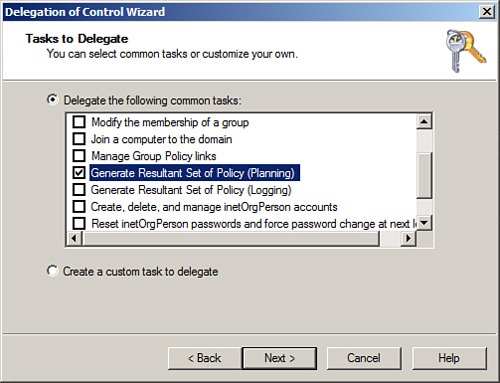
The administrator must have the right to read all the necessary group policies, and this should be allowed by default.
To
perform remote Group Policy Results tasks using the GPMC from a machine
other than a domain controller, the following requirements must be met:
The administrator must be a member of the remote computer’s local Distributed COM Users security group. The
administrator must be a member of the remote computer’s local
Administrators security group for legacy desktop platforms and the
remote system must be accessible on the network. The
Windows Firewall must be configured to allow the inbound Remote
Administration exception and the remote workstation must be on a network
that is defined within this exception. The
administrator must be delegated the Generate Resultant Set of Policy
(Logging) right in Active Directory. This right must be applied to the
domain, OU, container, or site that contains all of the computers and
users the administrator will run simulated GPO processing against. The administrator must have the right to read all the necessary group policies, and this should be allowed by default.
|